
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Suppose that a firm produces 300,000 units a year and sells them all for $3 each. The explicit costs of production are $500,000 and the implicit costs of production are $200,000. The firm earns an accounting profit of:
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
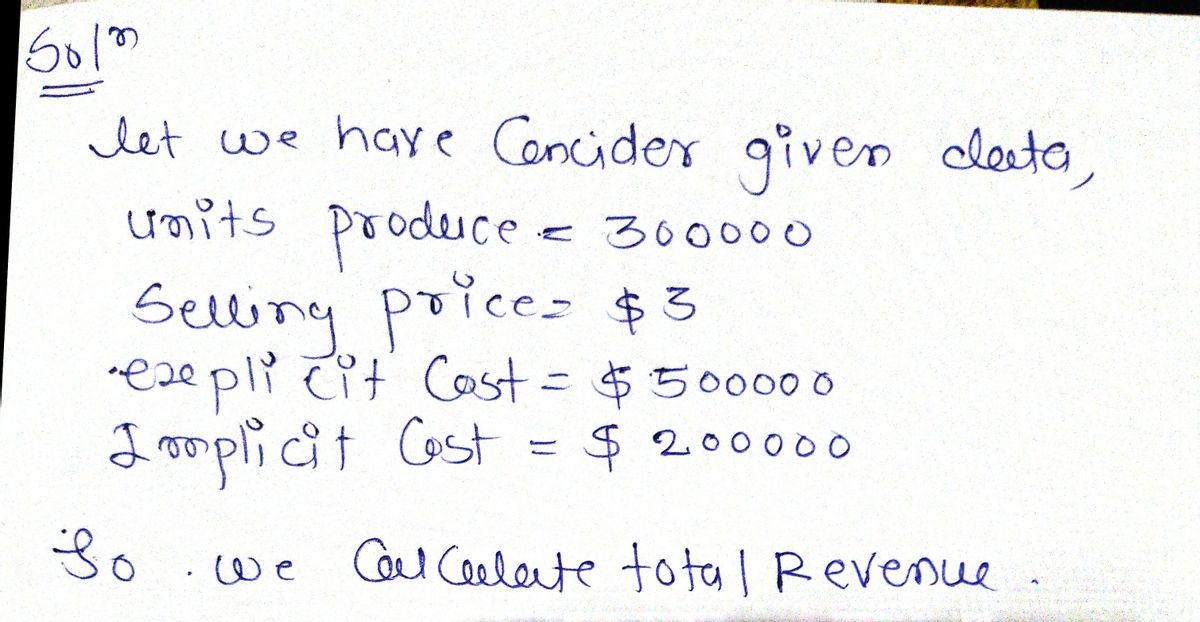
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7) What is the relationship between AFC, AVC & ATC? How are these calculated? 8) A firms produces an output of 10 units, when their total cost is $50 and their fixed costs are $10. Find: VC, AFC, AVC & ATC. 9) What are two examples of fixed costs?arrow_forwardI need help with this problem for business calculus. The revenue given is R(x)=275(0.974)^2x+1 I have to find the marginal revenue when 150 computers are sold and interpret the answer in a sentence. I know that I have to find the Marginal revenue function and I think it's -14.48918*0.974^2x+1 but I'm not 100% sure. I also need some clarification if I need to plug 150 into x to get the marginal revenue for 150 computers sold. Please help, thank you!arrow_forward2. A competitive firm uses two variable factors to produce its output, with a production function q min{x₁, x₂}. The price of factor 1 is $8 and the price of factor 2 is $5. Due to a lack of warehouse space, the company cannot use more than 10 units of x₁. The firm must pay a fixed cost of $80 if it produces any positive amount but doesn't have to pay this cost if it produces no butput. What is the smallest integer price that would make a firm willing to produce a positive amount? b. d. $44 $41 $29 $13 $21arrow_forward
- An economist estimated that the cost function of a single-product firm is:C(Q) = 60 + 30Q + 25Q2 + 5Q3.Based on this information, determine the following:a. The fixed cost of producing 10 units of output.$ b. The variable cost of producing 10 units of output.$ c. The total cost of producing 10 units of output.$ d. The average fixed cost of producing 10 units of output.$ e. The average variable cost of producing 10 units of output.$ f. The average total cost of producing 10 units of output.$ g. The marginal cost when Q = 10.$arrow_forwardThe table below shows ABC firm short-run production function. The company hires workers at a wage rate of $400 a day and his total fixed cost is $1000. Labor (workers) Total product (output) 0 0 1 12 2 25 3 30 4 44 5 50 Calculate the average total cost of producing 25 Calculate total cost of producing 47 units. Calculate average variable cost if 30 units are produced. Calculate the marginal product of producing 44 units. Calculate average product of the 4th workerarrow_forwardWhat do economists call the sum of a firm's fixed costs and its variable costs? sunk cost marginal cost implicit cost total costarrow_forward
- 22-23. Use this information to answer questions 22 and 23. A typical firm has a total cost function given by: TC = A.Q² + B.Q+ (C+D), where A, B, C & D are all positive constants and the term D represents the firm's fixed costs. 22. Suppose that the term C in the total cost function changes to a new figure that is twice as large. Thinking about the cost curves drawn on a graph, we would expect the following to happen (choose the best answer): A) B) H) I) J) ABOADAGAS 23. Use the information about the total cost function supplied above. The marginal cost curve will shift or rotate whenever (choose the best answer): A) B) C) D) H) I) Both the average variable cost curve AND the average cost curve shift (or rotate) down. Both the average variable cost curve AND the average cost curve shift (or rotate) up. The average cost curve shifts (or rotates) down. The average cost curve shifts (or rotates) up. J) The level of quantity where average cost is minimized falls. The level of quantity…arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm produces 475,000 units a year and sells them all for $20 each. The explicit costs of production are $1,300,000 and the implicit costs of production are $200,000. The firm earns an accounting profit ofarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education