
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
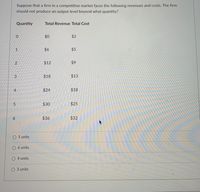
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following revenues and costs. The firm
should not produce an output level beyond what quantity?
Quantity
Total Revenue Total Cost
$0
$2
$6
$5
$12
$9
3.
$18
$13
$24
$18
$30
$25
$36
$32
5 units
6 units
4 units
3 units
4.
6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a perfectly competitive market for a product Y and assume that the market is at the long run equilibrium. (a) Examine the cost structure and demand faced by an individual Y producer. Relate that producer to the Y market at the perfectly competitive long run equilibrium. Support with market and individual producer diagrams. (b) Analyze the effects of the following news on price and quantity in the Y market as well as the profit and output of the individual Y producer “It is discovered that consuming Y is beneficial to health and can prolong your life”. Explain both the short run and the long run equilibria and support your answers with suitable diagrams. Hi, I have the answer sheet but may I request for a more detailed explanation for part b? Thank you.arrow_forwardQuestion 16 Refer to Figure 5-1 The firm will earn positive economic profits if the price is P4 only O P4 or P3 only P4, P3, or P2 only O any of P4, P3, P2, or P1arrow_forwardThe table below shows the price and cost information for a firm that operates in a perfectly competitive market. Based on this information, what is the profit-maximizing output quantity? Price Quantity Total Cost $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $6 $10 $15 $21 $28 $35 $45 1 2 3 4 5 6 Profit is maximized at a quantity of type your answer. units, where it is equal to $ type your answer. Is the long run price in this market likely to be higher or lower than the current price of $8? type your answer.arrow_forward
- Table 1 shows the total cost schedule for a competitive firm. Price per unit of output is £7. Quantity 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total Cost 15 25 30 34 38 45 55 70 100 Table 1 D) Assume that the firm's minimum average variable cost is £6.5. Should the firm continue operating in the market in the short run? In the long run? Explain. E) If the firm is typical of other firms in the market, what price will it charge in the long run? Explain.arrow_forwardThe cost curves below are for a firm competing in a perfectly competitive industry. If the market price is $7.50, a profit-maximizing firm would: Price and cost 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 2 MC y A A 1 B a 10 11 12 ATC AVC 13 Quantity Produce between 10 and 11, for a positive economic profit Produce about 9, for an economic profit of over $9 Produce between 10 and 11, for an economic profit of about $0 Produce about 9, for an economic profit of less than $9 Produce about 10, for an economic profit of about $20arrow_forwards 1, 12 & 13 Assignment Saved Help Save & Exit Assume a purely competitive increasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium. If a decline in demand occurs, firms will Multiple Choice leave the industry, price will fall, and quantity produced will rise. enter the industry and price and quantity will both rise. leave the industry and price and quantity will both rise. leave the industry, price will fall, and quantity produced will fall.arrow_forward
- $150 $145 $140 MC $135 $130 $125 $120 $115 ATC $110 $105 $100 $95 $90 $85 $80 AVC $75 $70 $65 $60 $55 $50 $45 $40 $35 $30 $25 0 1 2 3 5 6 Quantity Produced 7 8 9 10 11 The graph above shows the cost functions for a perfectly competitive profit maximizing firm. If the market price of the product is $70 per unit, the firm will produce units, will cover make an economic profit of dollars. dollars of its fixed cost, and willarrow_forward1) If a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price of $5, its marginal revenue: 2) A firm that is motivated by self interest should 3) If price is above the equilibrium level, competition among sellers to reduce the resulting 4) Camille's Creations and Julia's Jewels both sell beads in a competitive market. If at the market price of $5, both are running out of beads to sell (they can't keep up with the quantity demanded at that price), then we would expect both Camille's and Julia's to 5) Since their introduction, prices of DVD players have fallen and the quantity purchased has increased. This statement 6) In a market economy the distribution of output will be determined primarily by 7) In a competitive market economy firms will select the least-cost production technique because 8) Suppose that the price of peanuts falls from $3 to $2 per bushel and that, as a result, the total revenue received by peanut…arrow_forwardProblem #1: Assume that the following marginal costs exist in catfish production: 17 Quantity Produced (units per day) Marginal Cost (per unit) 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 $4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 (a) Graph the MC curve. (b) Use the data on market demand below and graph the demand and MR curves on the same graph. Quantity demanded (units per day) 10 Price (per unit) 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 $25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 (c) At what rate of output is MR = MC?arrow_forward
- Why does a firm in perfect competition produce the quantity at which marginal cost equals price? In a perfectly competitive market, the price of a handsaw is $25. When a firm maximizes its profit, it produces 6 handsaws a day. Draw the marginal revenue curve. Label it. Draw the marginal cost curve that illustrates the profit-maximizing output. Label it. Draw a point at the profit-maximizing output and price. A firm produces the quantity at which marginal cost equals price because when marginal cost is greater than price, the firm O A. can increase economic profit by producing 1 less handsaw O B. is maximizing economic profit OC. is at its shutdown point O D. can increase economic profit by producing 1 more handsaw 50- 45- 40- 35 30- 25- 20- 15- 10- 5 0- 0 Price (dollars per handsaw) 10 Quantity (handsaws per day) >>> Draw only the objects specified in the question.arrow_forwardA firm producing ice pop in a perfectly competitive market with an equilibrium price of $1.50 has the following Quantity of ice Total Cost pops 0 $3 10 $8.00 20 20 $10.50 30 $15.50 59 40 $30.50 50 $50.50 60 60 $75.50 70 70 $105.50 What is this firm's marginal revenue from the 50th unit? MR(50) = $ What is this firm's marginal revenue from the 60th unit? MR(60) = $arrow_forwardSuppose a competitive firm has the following cost: output(units): 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Total cost: $50 $52 $56 $62 $70 $80 $92 $106 $122 $140 3. If the market price dropped to $8, how much should this profit maximizing firm produce?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education