
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
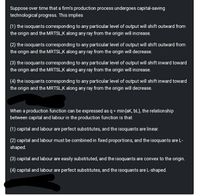
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose over time that a firm's production process undergoes capital-saving
technological progress. This implies
(1) the isoquants corresponding to any particular level of output will shift outward from
the origin and the MRTSL,K along any ray from the origin will increase.
(2) the isoquants corresponding to any particular level of output will shift outward from
the origin and the MRTSL,K along any ray from the origin will decrease.
(3) the isoquants corresponding to any particular level of output will shift inward toward
the origin and the MRTSL,K along any ray from the origin will increase.
(4) the isoquants corresponding to any particular level of output will shift inward toward
the origin and the MRTSL,K along any ray from the origin will decrease.
When a production function can be expressed as q = min{ak, bL}, the relationship
between capital and labour in the production function is that
(1) capital and labour are perfect substitutes, and the isoquants are linear.
(2) capital and labour must be combined in fixed proportions, and the isoquants are L-
shaped.
(3) capital and labour are easily substituted, and the isoquants are convex to the origin.
(4) capital and labour are perfect substitutes, and the isoquants are L-shaped.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What do economists mean by "deminishing returns" to an input? What causes diminishing returns? Where would one observe this principle at a job and the real world?arrow_forwardConstant returns to scale is the point on a production function where increasing inputs will no longer increase output. True False 00arrow_forwardSuppose there is a permanent increase in gL. What effect does this have on long-run output per person? Is there a change in the saving rates that could offset this effect? What other implications might such a change in savings have?arrow_forward
- The production function q = 9K0.8L0.1 exhibits: a. increasing retruns to scale b. constant returns to scale c. decreasing returns to scale d. none of the above The production function q = K1.2 + 3L1.2 exhibits a. increasing retruns to scale b. constant returns to scale c. decreasing returns to scale d. none of the abovearrow_forwarddon't use Al bot or chat GPT otherwise downvote.correct answer will get instant upvote show calculationarrow_forwardSuppose that the average yearly cost per item for producing x items of a business product is 81 If the current production is x - 9 and production is increasing at a rate of 4 items per year, find the rate of change of the average cost. The average cost is decreasing at the rate of S per year.arrow_forward
- Suppose that the production function is given by Y=AK0.4N0.6. What is the percentage change in output if both capital and labor rise by 42%? Write the answer in percent terms with up to two decimals (e.g., 10.22 for 10.22%, or 2.33 for 2.33%).arrow_forwardGiven the following aggregate production function: Y = K0.25 (AL) 0.75, where technology A grows at a fixed rate: = g> 0 (a) Obtain the marginal product of capital algebraically, also discussing the second derivative. (b) Transform the production function into efficiency-worker terms, showing how =ỹ depends AL on =k. K ALarrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- D A: F(LKHN) C A:F(L,KH N) 7- Suppose the U.S. economy is producing at point A on Production Function 1 (F). An increase in the labor force participation rate causes more labor to be used in production. The direct effect of this shift is to move the economy O A. Point A O B. Point B OC. Point C O D. Point D O E. Point Earrow_forwardIm so confused what I am doing wrong I need help.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education