
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
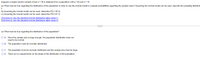
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a simple random sample of size n = 38 is obtained from a population with u = 65 and o = 18.
(a) What must be true regarding the distribution of the population in order to use the normal model to compute probabilities regarding the sample mean? Assuming the normal model can be used, describe the sampling distributi
(b) Assuming the normal model can be used, determine P(x < 69.4).
(c) Assuming the normal model can be used, determine P(x2 67.3).
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1).
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2).
(a) What must be true regarding the distribution of the population?
O A. Since the sample size is large enough, the population distribution does not
need to be normal,
O B. The population must be normally distributed.
OC. The population must be normally distributed and the sample size must be large.
O D. There are no requirements on the shape of the distribution of the population.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose a simple random sample of size n= 39 is obtained from a population with µ = 62 and o = 19. (a) What must be true regarding the distribution of the population in order to use the normal model to compute probabilities regarding the sample mean? Assuming the normal model can be used, describe the sampling distribution x. (b) Assuming the normal model can be used, determine P(x<65.2). (c) Assuming the normal model can be used, determine P(x2 63.2). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1) Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2). (a) What must be true regarding the distribution of the population? O A. The population must be normally distributed. O B. The population must be normally distributed and the sample size must be large. O C. Since the sample size is large enough, the population distribution does not need to be normal. O D. There are no requirements on the shape of the distribution of the population. Assuming the normal…arrow_forwardI got that it is approximately normal with mean 67 and sd is 15/square root of 48 but do not know how to get part b or part c. thank youarrow_forwardSuppose a simple random sample of size n = 47 is obtained from a population with µ = 68 and o= 16. (a) What must be true regarding the distribution of the population in order to use the normal model to compute probabilities regarding the sample mean? Assuming the normal model can be used, describe the sampling distribution X. (b) Assuming the normal model can be used, determine P(x<71.5). (c) Assuming the normal model can be used, determine P(x ≥ 70.2). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2). Assuming the normal model can be used, describe the sampling distribution X. O A. Approximately normal, with μ = 68 and o= Approximately normal, with = 68 and o- = μx ox 16 √47 (b) P(x < 71.5)= (c) P(x ≥ 70.2) = 47 √16 O B. O c. Approximately normal, with μ = 68 and o- = 16 x (Round to four decimal places as needed.) (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- Solve by showing steps properlyarrow_forwardThe central limit theorem states that the sampling distribution of sample means has a mean equal to the population -- mean mean mean divided by the population standard deviation mean divided by the population standard deviation standard deviation standard deviation standard deviation divided by the square root of N.arrow_forwardwhen a population is uniformly distributed (flat), is the sampling distribution of xbar for random samples of 2 observations roughly normal, strongly skewed, or triangular?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman