
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
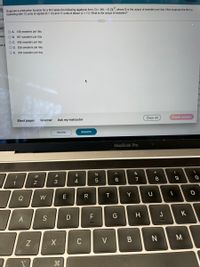
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a production function for a firm takes the following algebraic form: Q = 4KL - (0.2)L", where Q is the output of sweaters per day. Now suppose the firm is
operating with 12 units of capital (K = 12) and 11 units of labour (L = 11). What is the output of sweaters?
ign
O A. 108 sweaters per day
Hot
O B. 467 sweaters per day
OC. 459 sweaters per day
ke a
O D. 526 sweaters per day
O E. 504 sweaters per day
Clear all
Check answer
Etext pages
Grapher
Ask my instructor
Review
Resume
MacBook Pro
*
&
#
$
%
@
7
8
1
2
3
4
Y
Q
W
E
J
K
A
S
D
F
M
Z
C
V
この
つ
エ
くO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please give me the solution of Darrow_forward2. A firm has a production function given by the following table: Units of Labor 1 2 3 4 5 K=1 3 8 12 15 17 K=2 10 15 19 22 24 K=3 16 21 25 28 30 K=4 20 25 28 30 31 (1) Suppose that K is fixed at 2. Does this production function exhibit diminishing marginal returns? (ii) Does this production function exhibit constant returns to scale for all values of K and L?arrow_forwardI need answer typing clear urjent no chatgptarrow_forward
- A firm's production function takes the form: Q(L, K) = min{2L, 3K}, where Q represents output and L and K represent labour and capital, respectively and where w and r give the prices of labour and capital. Assuming no other costs, what would be the marginal cost if the firm increased output by 1 unit? O O MC = Q [ 12/2₁ = Q ( + 1/2 + 1/2 ) MC = W 3r 3w+2r 3w+2r + O MC=3w+2r O W r = 21/1/2+1/1/3/2 O MC =2w+3r MC=1/2arrow_forwardQ18arrow_forwardIn the short run production function O a. All inputs are variable O b. All inputs are fixed O C. There are fixed and variable inputs Od. Technology alone is variablearrow_forward
- 3. The Chipper Cookie Company's output is given by the Cobb-Douglas Production function P = 120L0.7 K0.3, where P is the number of units produced when Lis the amount spent on labor and K is the amount spent on capital. a. What is the production if L = 600 and K = 600? b. Find the marginal productivities. c. Evaluate the marginal productivities with L= 600 and K = 600. d. Interpret the meanings of the marginal productivities found in part c. e. If their budget is $1200 then there is a constraint L+ K = 1200. Use Lagrange multipliers (^) to find the values of L and K that will maximize production and find the maximum production f. Find and interpret 2 for this problem. only need part e and f!arrow_forward1. Assume a daily production function for a firm is Q= min(3L, 4K) a, If L = 100 and K = 100 what quantity is produced? Explain why. b. What would be the cost-minimizing labor and capital combination for this firm to produce Q = 1200? (show your work) Labor = Capital = At this level of production from part b (Q-1200), if the wage rate is: w- $30 and the rental rate of capital is: r= $100, what is the total cost of production? (show your calculations) C.arrow_forwardConsider the following production function: q = 2V1 + 3VK Assume K = 16, derive the marginal product schedule for L. What direction is it moving? a. b. What returns to scale does the production function exhibit? Explain Let w = $4, r = $2, and K = 16; for the given values of a determine average fixed costs, average variable costs, average total costs, and marginal costs: C. L AFC AVC ATC MC 9 12 13 14 15 16 K 16 16 16 16 16arrow_forward
- Suppose that the production function of a firm can be written as Q = 0.5K0.8L0.3. Which of the following is the equation for the average product of labor (APL)? O 0.3L-0.7 O K0.810.3 O 0.5K0.8L-0.7 O (0.7*0.5) K0.8L-0.7 O 0.5K0.810.3arrow_forward1arrow_forwardThe slope of an isocost line is equal to the Select one: O a. O b. and is negative of the ratio of input prices; constant decreases as we move down the line; the ratio of the marginal products O c. is constant; the ratio of the marginal products O d. increases as we move down the line; the ratio of input pricesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education