
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
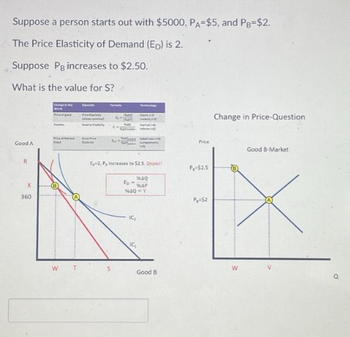
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a person starts out with $5000, PA-$5, and PB-$2.
The Price Elasticity of Demand (ED) is 2.
Suppose Pg increases to $2.50.
What is the value for S?
Good A
R
X
360
Changel
Pri
Good
E-2, P, increases to 52.5. Depict
S
%64Q
Ep
MAP
5640-Y
IC₂
Good B
Price
P-$2.5
P=52
Change in Price-Question
W
Good B-Market
Q
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a demand curve: P = 20 - 2Q. The the new price is $10 dollars. The old quantity is 3 units. %3D What is the elasticity of demand and how do you characterize it? -1, unit elastic -0.67, inelastic 1.4, elastic -1.5, elasticarrow_forwardA small elasticity of a good rises from $8 to $12 and the quantity demanded fall from 110to90 unitsarrow_forwardSuppose the own price elasticity of demand for good X is -2, its income elasticity is -1, its advertising elasticity is 2, and the cross- price elasticity of demand between it and good Yis-3. Determine how much the consumption of this good will change it Instructions: Enter your responses as percentages. If you are entering a negative number, be sure to use a (-) sign. a. The price of good X decreases by 4 percent. percent b. The price of good Y increases by 10 percent. percent c. Advertising decreases by 3 percent. percent d. Income increases by 2 percent. percentarrow_forward
- can u solve point d to i d. What is the notation used for this limit value? e. Calculate the limit value. f. Find the point elasticity of demand for p = 1 and determine whether demand is (perfectly) inelastic, is (perfectly) elastic or has unit elasticity. g. Use your answer to question f. to approximate the change in demand when the price of 1 is increased by 0.25%. h. What can you derive from your answer to question f. about the change in revenue when the price is slightly increased starting from p=1? i. Find the price level at which the demand has unit elasticity.arrow_forwardIf Judy's income elasticity of demand for burgers is negative, then we know that burgers are a(n) [ Select ] good for Judy. a. normal b. inferior c. superiorarrow_forwardA The table describes the weekly prices and quantity demanded for two goods, A and B, over a three-week period. In the space following the E record what type of elasticity you are calculating. Assume the price and income changes indicated in the table are large. Round numerical answers to two decimal places, if necessary. Don't forget to include the negative sign if appropriate. Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Qp of Good A 2 3 4 QD of Good B 3 3 2 Goods A and B are Price of Good A $9 $6 $6 with an E Price of Good B $8 $8 $8 Part a) Calculate the numerical value of the appropriate elasticity to determine whether Goods A and B are complements, substitutes, or unrelated. Use 1-2 sentences to explain how you've arrived at this conclusion. Income (Y) $42 $42 $40arrow_forward
- a. Explain what “cross-elasticity of demand” is. b. What is a “substitute good”? Give an example. Does it have a positive or negative cross-elasticity of demand?arrow_forwardThe equation for a demand curve has been estimated to be Q = 100 - 10P + 0.5Y, whereQ is quantity, P is price, and Y is income. Assume P = 7 and Y = 50.a. Interpret the equation.b. At a price of 7, what is price elasticity?c. At an income level of 50, what is income elasticity?d. Now assume income is 70. What is the price elasticity at P = 8?arrow_forward1. Calculate the Price elasticity of demand, & for the following examples: a) Demand is given by Q = 50 – P at the price of $10. b) Demand is given by Q= 100 - P, at the price of $50. %3D c) Demand is given by Q= 25 - .25P, at the price of $40. d) Demand is given by Q = 20 - .1P, at the price of $80. e) Demand is given by Q = 60 – 1/3P, at the price of $60.arrow_forward
- If the cross-price elasticity of demand between Good A and Good B is -1.2, the price of Good B increases, and the price elasticity of demand for Good B is elastic, we can expect to see a quantity demanded for Good A. change in the Answer Choices: A. negative, infinite B. negative, one-for-one C. positive, zero D. negative, large E.positive, smallarrow_forward11 BIUA + Arlal I| II1 I I 2 The following questions are about income elasticity of demand. 9) Mr. Leon's income increased by 10%. (His "mommy" gave him a raise in his allowance because he was a "good little boy.") His consumption of Lego's then increased by 25%. Calculate his income elasticity. Does this imply that Lego's are a regular or an inferior product for Mr. Leon? 10) Mr. Mendivil's income increased by 20%. His consumption of pictures of Mr. Leon then decreased by 100%. Calculate the income elasticity of demand for the product. Does this imply that pictures of Mr. Leon are regular or inferior products? 11) Larry the Wild & Crazy Monkey saw a decrease in his income by 25%. With this, his consumption of berries increased by 50%. Calculate his income elasticity of demand. What can we conclude about berries as a consumer good for Larry the Wild & Crazy Monkey? Explain. ip lili 司arrow_forwardAnswer this for me mate. Much appreciated.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education