
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Calculating equilibrium composition from an equilibrium constant.
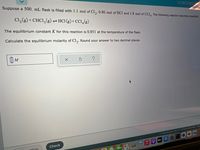
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 1.1 mol of Cl,, 0.80 mol of HCl and 1.8 mol of CCI. The following reaction becomes possible:
Cl,(g) + CHCI,(g)– HCI (g)+ CCI,(g)
The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.851 at the temperature of the flask.
Calculate the equilibrium molarity of Cl,. Round your answer to two decimal places.
72022 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved Tern
Check
dtv
tion
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Label the following statements as true or false.True False When Q < Kc, the reaction shifts to the left to reduce stress on the system. True False When a system is at equilibrium, the reactants and the products of the reaction will be equal in concentration. True False When a system is at equilibrium, the reaction rate of the forward reaction is less than to the reaction rate of the reverse reaction. True False When Q > Kc, the reaction shifts to the right to reduce stress on the system. True False For a reversible reaction, the ΔH of the forward reaction is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the ΔH of the reverse reaction. True False If Kc=5 for the reaction A + B <--> AB, then AB <--> A + B has a Kc=0.2arrow_forwardIf the equilibrium constant of a given reaction is 4.10, what is the equilibrium constant of its reverse reaction?arrow_forwardUse the data table provided to answer the questionarrow_forward
- At equilibrium, the concentration of N2 is 5.32x10-3 M, O2 is 3.28 x10-3 M and that of NO is 6.19 x10-6 M. Evaluate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forwardIf concentration of a substance is increased, does the equilibrium shift toward or away from that side of the reaction? If concentration of a substance is decreased, does the equilibrium shift toward or away from that side of the reaction? If temperature is increased, does the equilibrium shift toward the side that contains heat or away from the side that contains heat? If temperature is decreased, does the equilibrium shift toward the side that contains heat or away from the side that contains heat? When a reaction shifts due to stress, what is the reaction trying to reach?arrow_forward1. The shape of boron trihydride, BH3, is 2. In an exothermic reaction, the potential energy of the products is than the potential energy of the reactants. 3. A system at equilibrium always has forward and reverse reaction rates which are 4. A solution at 25°C with a pOH of 3.45 has a pH of 5. When nitric acid is titrated to an end point by lithium hydroxide, two products are and O 6. The standard reduction potential table lists the Evalues of half-cell reactions measured in combination with the standard half-cell.arrow_forward
- When heat is added to exothermic reactions the equilibrium shifts towards the products. True Falsearrow_forwardWhat is the percentage of HCl in the solution if the molarity is 0.268398000? Assume the density of the solution is 1.00 g/mL.arrow_forward"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 25 L tank with 11. mol of carbon monoxide gas and 12. mol of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 6.9 mol of carbon monoxide gas, 7.9 mol of water vapor and 4.1 mol of hydrogen gas. The engineer then adds another 3.0 mol of water, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of carbon dioxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. molarrow_forward
- Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of H2arrow_forwardIf the equilibrium constant of a given reaction is 2.10, what is the equilibrium constant of its reverse reaction?arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is a true statement concerning a reaction that has reached a state of equilibrium? A system has reached equilibrium when the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. A system has reached equilibrium when the reaction has stopped and no more products are formed. A system has reached equilibrium when the rate constant for the forward reaction equals the rate constant of the reverse reaction. A system has reached equilibrium when the concentrations of reactants and products correspond to the stoichiometric ratios determined by the balanced equation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY