
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
What is the reduction (from equilibrium) in
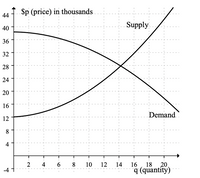
Transcribed Image Text:$p (price) in thousands
44
Supply
40
36
32
28
24
20
16
Demand
12
8.
4
16
18
20
q (quantity)
2
4
6
8.
10
12
14
-4 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the market for bicycles in the fictional province of Westvale. The market demand function for bicycles is given by P=300-2Q. The marginal cost curve for firms in this market is given by P=40+Q. Prices are measured in dollars. a) Under a competitive market equilibrium, what is the price of a bicycle? b) How many bicycles are produced under a competitive market equilibrium? c) Calculate consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total surplus under the competitive market equilibrium Suppose that the firms that were once competing in this market merge into one single firm, forming a monopoly. This monopoly has a marginal revenue function of P=300-4Q. d) What price does this monopolist charge? e) How many bicycles does the monopolist produce? f) Calculate consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total surplus under the monopolistic market outcome g) How much deadweight loss resulted from the creation of the monopolist?arrow_forwardSuppose the market for pizzas in the U.S. is perfectly competitive and is characterized by the following demand and supply equations (Q = quantity and P = Price): Demand for pizza: Qd = 100 – P Supply of pizza: Qs = 2P − 50 A) Find the market clearing equilibrium price P* and quantity Q*. B) Find the the consumer surplus and producer surplus at the equilibrium. C) Suppose that the U.S. imposes a price ceiling at $40. What is the quantity demanded by consumer (Qd’)? What is the quantity supplied by suppliers (Qs’)? D) Suppose that the U.S. imposes a price ceiling of $40. Is there a shortage or surplus for pizzas? E) Suppose that the U.S. imposes a price ceiling of $40. What is the new CS’ and PS’? Assuming that the government purchases/provides the surplus/shortage. Under the same assumption, what is the deadweight loss caused by the price floor?arrow_forwardGiven a demand of q = 100 – 5p and a cost of c(q) = 4q. What is the equilibrium retail price p, wholesale price w, and profits from the manufacture and sale of the product?arrow_forward
- Hi! I'm fairly confident that the answer here is none of these, but I want to be as thorough as possible in reviewing for my exam.arrow_forwardIn a competitive market, if price is higher than the equilibrium price then the quantity demanded will be lower than the quantity supplied. True or Falsearrow_forwardd) What will be the deadweight loss? e) What will be the firm’s maximum profits? f) How much would the firm would save in additional costs, if it had decided to supply all of that output at the point of equilibrium?arrow_forward
- Demand for apartments in town is D (x) =860 – 3x, and the supply is S (x) =500+9x, %3D where x is the number of apartments, in hundreds, and D (x) and S(x) are the rent in dollars per month, per apartment. The equilibrium point is (30, 770). Suppose a maximum rent of $644 per month is imposed by the town council. Find the deadweight loss. $ 1176 $ 1152 $ 16 $ 3072arrow_forwardA vertical demand curve or supply curve would be called:arrow_forwardSuppose that at equilibrium, the price elasticity of demand for wheat is -1.5 and the price elasticity of supply is 0.5. If the government imposes a price ceiling that is 12% below the equilibrium price, this price constraint will lead to: A) A shortage equal to 24% of the equilibrium quantity B) A surplus equal to 24% of the equilibrium quantity C) A shortage equal to 2.4% of the equilibrium quantity D) A surplus equal to 2.4% of the equilibrium quantityarrow_forward
- Show that any linear inverse supply that passes through the origin (i.e., an inverse supply with the functional form p = c Q with c > 0) has a price elasticity of supply equal to one. Show that any linear inverse supply curve with a positive intercept (i.e., having the functional form p = k + c Q with c, k > 0) must be elastic.arrow_forwardThe widget market is competitive and includes no transaction costs. Five suppliers are willing to sell one widget at the following prices: $26, $14, $10, $5, and $3 (one seller at each price). Five buyers are willing to buy one widget at the following prices: $10, $14, $26, $34, and $42 (one buyer at each price). For each price shown in the following table, use the given information to enter the quantity demanded and quantity supplied. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied ($ per widget) (widgets) (widgets) $3 $5 $10 $14 $26 $34 $42 In this market, the equilibrium price will be per widget, and the equilibrium quantity will be widgets.arrow_forwardThe demand curve for rooms at a hotel in Oakland is given by PD = 250 - 1.5*QD. The supply curve of rooms for the same hotel in Oakland is given by Ps = 45 + Qs. The equilibrium quantity is rooms and the equilibrium price is $.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education