
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Sulfur hexafluoride SF6 is the most potent greenhouse gas to date. It is 22,800 times more effective at trapping heat than carbon dioxide (CO2), and lasts in the atmosphere for thousands of years. Please refer to the molecule diagrams below to answer the following questions:
|
|
|
a. Explain why SF6 has more asymmetrical vibrations than CO2
b. Explain why asymmetrical vibrations in SF6 bonds are stronger than asymmetrical vibrations in CO2 bonds
c. Explain the relationship between strength and quantity of asymmetrical vibrations and greenhouse gas potency
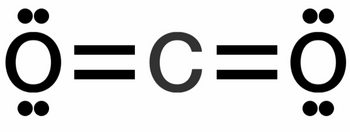
Transcribed Image Text:BO:
||
C
||
:O:
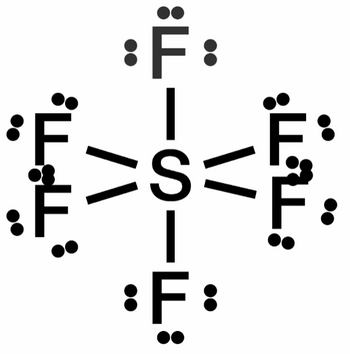
Transcribed Image Text::ד
ודיוד:
\/
מ-ד:
דד:
\/
יהד:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The amount of UVA radiation hitting a surface at sea level in a lightly clouded day isabout 70W/m2. About half of that can be absorbed by the skin. A typical carbon-carbon bond requires 348 kJ/mol to break. A person lies on the beach for about 1hour without sunscreen (i.e. fully exposed to UVA radiation). Estimate the numberof C-C bonds broken in this person’s back (about 0.18 m2) over that period. Assumethat the average wavelength of UVA is 335 nm.arrow_forward3. Select CO2 from the drop-down menu on the right of the simulation. Examine the model and real structures for CO2. a. Does each atom have the expected number of bonds? Explain your answer. b. Why is there agreement between the bond angle predicted by VSEPR theory and the actual bond angle?arrow_forwardAll I'm givenarrow_forward
- Methane, CH4, has the ideal tetrahedral angle (109.5°) and is a nonpolar molecule, while NH3 and H₂O show a deviation from the ideal bond angle. Explain the cause and why water has a greater deviation than ammonia.arrow_forwardExplain the trend that bond formation does to atomic order by selecting all those that apply. Larger molecules have higher entropies than smaller molecules. Larger molecules have larger entropies on a per atom basis. Larger molecules have lower entropies than smaller molecules. Larger molecules have smaller entropies on a per atom basis.arrow_forward11. What is the electron-domain geometry of water molecule (H2O)? a. bent b. tetrahedral c. trigonal planar d. linear 12. Write the correct Lewis dot structure for O2. Which statement correctly describes the structure of the whole molecule? a. There is a double bond and four lone pairs. b. There is a double bond and six lone pairs. c. There is a single bond and six lone pairs. d. There is a single bond, a double bond, and six lone pairs. 13. If there are four (4) electron pairs around the central atom of a molecule, these electron pairs are in a/n a. trigonal planar b. trigonal pyramidal arrangement. C. octahedral d. tetrahedral 14 The molecular geometry of the molecule NF3 is a. linear b. trigonal pyramidal c. tetrahedral d. trigonal planar 15 Which of the following species will exhibit tetrahedral molecular geometry? d. PCI5 a. CCI4 b. CO2 C. O3arrow_forward
- What information does the molecular representation provide? (more than one option)1. The number and type of atoms2. Two-dimensional structure of molecules3. The type of link4. How Atoms Bond5. The intermolecular force6. Three-dimensional structure of molecules7. Polarity8. More realistic representation of moleculesarrow_forward16. For the molecule BrF5, what is its molecular geometry? Group of answer choices A. Square pyramid B. Octahedral C. trigonal pyramid D. tetrahedralarrow_forward56. Use bond enthalpies to calculate AH° for the reaction of methane with rxn chlorine and fluorine to form CF₂Cl₂ (Freon–12). CH4(g) + 2 Cl₂(g) + 2 F₂(g) → CF₂Cl₂(g) + 2 HF(g) + 2 HCl(g)arrow_forward
- Compound ∆Hf (kJ/mole) ∆S (J/mole K) C2H4 52.4 219.3 C2H6 –84.68 229.2 SiO2 –910.7 41.5 HF –273.3 173.8 SiF4 –1615.0 282.8 NH3 –45.9 192.9 O2 1.88 2.43 NO 91.3 210.8 H2O(g) –241.8 188.8 For the following reactions, using the provided ∆H and ∆S data, determine whether each one would be spontaneous or nonspontaneous at 25°C. C2H4(g) + H2(g) --------à C2H6(g) SiO2 + 4 HF(g) -------------> SiF4 (g) + 2 H2O(g) 4 NH3(g) + 5 O (g) ---------> 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g)arrow_forwardConsider how bond strength affects the speed of particles. Describe what happens to the kinetic energy of particles after a single bond is broken compared to a stronger double bond. You can answer this question with words, pictures, or graphs.arrow_forwardWhat are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? H H H C H a a = C b = ⁰ C H Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal that might be caused by the fact that different electron groups may have slightly different sizes. H Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY