
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780134746241
Author: Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
SUBJECT : DISASTER READINESS AND RISK REDUCTION
TOPIC : SENDAI FRAMEWORK FOR DISASTER RISK REDUCTION
DIRECTIONS : ANALYZE THE CHART AND MAKE AN ASSESSMENT ON IT
FOR EXAMPLE : WHERE IT LACKS, WHAT NEEDS TO BE ADD

Transcribed Image Text:Chart of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
2015-2030
Scope and purpose
The present framework will apply to the risk of small-scale and large-scale, frequent and
infrequent, sudden and slow-onset disasters, caused by natural or manmade hazards as well
as related environmental, technological and biological hazards and risks.
It aims to guide the multi-hazard management of disaster risk in
development at all levels as well as within and across all sectors
Substantially reduce
global disaster
mortality by 2030,
aiming to lower
average per 100,000
global mortality
between 2020-2030
compared to 2005-
2015
Expected outcome
The substantial reduction of disaster risk and losses in lives, livelihoods and health and in
the economic, physical, social, cultural and environmental assets of persons, businesses,
communities and countries
Goal
Prevent new and reduce existing disaster risk through the implementation of integrated and
inclusive economic, structural, legal, social, health, cultural, educational, environmental,
technological, political and institutional measures that prevent and reduce hazard exposure
and vulnerability to disaster, increase preparedness for response and recovery, and thus
strengthen resilience
Substantially reduce
the number of affected
people globally by
2030, aiming to lower
the average global
figure per 100,000
between 2020-2030
compared to 2005-
2015
Reduce direct disaster
economic loss in
relation to global
gross domestic
product (GDP) by
2030
Targets
Substantially reduce
disaster damage to
critical infrastructure
and disruption of basic
services, among them
health and educational
facilities, including
through developing
their resilience by 2030
Substantially increase
the number of
countries with national
and local disaster risk
reduction strategies by
2020
Substantially
enhance international
cooperation.
to developing countries
through adequate and
sustainable support
to complement their
national actions for
implementation of this
framework by 2030
Substantially increase
the availability of
and access to multi-
hazard early warning
systems and disaster
risk information and
assessments to people
by 2030
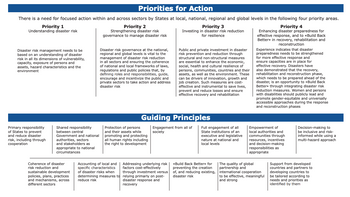
Transcribed Image Text:Priorities for Action
There is a need for focused action within and across sectors by States at local, national, regional and global levels in the following four priority areas.
Priority 4
Enhancing disaster preparedness for
effective response, and to «Build Back
Better»> in recovery, rehabilitation and
reconstruction
Priority 1
Understanding disaster risk
Disaster risk management needs to be
based on an understanding of disaster
risk in all its dimensions of vulnerability,
capacity, exposure of persons and
assets, hazard characteristics and the
environment
Primary responsibility
of States to prevent
and reduce disaster
risk, including through
cooperation
Shared responsibility
between central
Government and national
authorities, sectors
and stakeholders as
appropriate to national
circumstances
Coherence of disaster
risk reduction and
sustainable development
policies, plans, practices
and mechanisms, across
different sectors
Priority 2
Strengthening disaster risk
governance to manage disaster risk
Disaster risk governance at the national,
regional and global levels is vital to the
management of disaster risk reduction
in all sectors and ensuring the coherence
of national and local frameworks of laws,
regulations and public policies that, by
defining roles and responsibilities, guide,
encourage and incentivize the public and
private sectors to take action and address
disaster risk
Protection of persons
and their assets while
promoting and protecting
all human rights including
the right to development
Accounting of local and
specific characteristics
of disaster risks when
determining measures
reduce risk
Priority 3
Investing in disaster risk reduction
for resilience
Guiding Principles
Engagement from all of
society
Addressing underlying risk
factors cost-effectively
through investment versus
to relying primarly on post-
disaster response and
recovery
Public and private investment in disaster
risk prevention and reduction through
structural and non-structural measures
are essential to enhance the economic,
social, health and cultural resilience of
persons, communities, countries and their
assets, as well as the environment. These
can be drivers of innovation, growth and
job creation. Such measures are cost-
effective and instrumental to save lives,
prevent and reduce losses and ensure
effective recovery and rehabilitation
Full engagement of all
State institutions of an
executive and legislative
nature at national and
local levels
«Build Back Better» for
preventing the creation.
of, and reducing existing,
disaster risk
Experience indicates that disaster
preparedness needs to be strengthened
for more effective response and
ensure capacities are in place for
effective recovery. Disasters have
also demonstrated that the recovery,
rehabilitation and reconstruction phase,
which needs to be prepared ahead of the
disaster, is an opportunity to Build Back
Better»> through integrating disaster risk
reduction measures. Women and persons
with disabilities should publicly lead and
promote gender-equitable and universally
accessible approaches during the response
and reconstruction phases
Empowerment of
local authorities and
communities through
resources, incentives
and decision-making
responsibilities as
appropriate
The quality of global
partnership and
international cooperation
to be effective, meaningful
and strong
Decision-making to
be inclusive and risk-
informed while using a
multi-hazard approach
Support from developed
countries and partners to
developing countries to
be tailored according to
needs and priorities as
identified by them
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Recommended textbooks for you
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134041360
Author:Greg Carbone
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:9781260153125
Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134543536
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:9781337569613
Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:9781259916823
Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,