
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
In the 1930’s the American great plains region was subjected to a period of severe dust storms, which became known as the Dust Bowl. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration report that severe dust storm clouds, such as the one shown here, can reach up to 3,000 meters in height.
Stokes’ Law
Use Stoke’s law or apply drag coefficient for a sphere in creeping flow to find terminal velocity; neglect any up or down draft air currents and take buoyance into account
a)Calculate how long the smallest of the dust cloud particles will take to settle to the ground from the maximum height of the plume
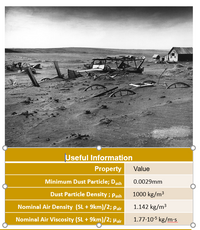
Transcribed Image Text:Useful Information
Property
Value
Minimum Dust Particle; Dash
0.0029mm
Dust Particle Density ; Pash
1000 kg/m3
Nominal Air Density (SL + 9km)/2; Pair
1.142 kg/m3
Nominal Air Viscosity (SL + 9km)/2; Hair
1.77.10-5 kg/m-s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pair 1.2041 kg/m³ = Calculate: Velocity profile and plotting the dynamic pressure vs. Velocity at main stream velocity 10 m/s and 20 m/s Location 1 2 3 4 5 Initial Velocity 10 m/s P static (Pa) P total (Pa) 123 143 176 256 274 109 132 142 200 136 Velocity (m/s)arrow_forwardAn air stream flows over a smooth plate with Reynolds number of 106. The boundary layer can be assumed to be turbulent over the entire plate. If the length of the plate is increased by 10%, taking all the factors same, what is percentage change in the total drag coefficient? [Take (1.1)0.2 = 1.019]arrow_forwardA 90° elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to direct water flow upward at a rate of 47 kg/s. Another identical elbow is attached to the existing elbow such that the water flow makes a U-turn as shown in the second figure. The diameter of the entire elbow is 10 cm. The elbow discharges water into the atmosphere, and thus the pressure at the exit is the local atmospheric pressure. The elevation difference between the centers of the exit and the inlet of the elbow is 50 cm. The weight of the elbow and the water in it is considered to be negligible. Take the momentum-flux correction factor to be 1.03 at both the inlet and the outlet. Take the density of water to be 1000 kg/m³. Water m kg/s Water 2 1 FRI 50 cm FRX 50 cm If another (identical) elbow is attached to the existing elbow so that the fluid makes a U-turn, determine the magnitude of anchoring force needed to hold the elbow in place. The magnitude of anchoring force needed to hold the elbow in place is 438 * N.arrow_forward
- A 90° elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to direct water flow upward at a rate of 43 kg/s. Another identical elbow is attached to the existing elbow such that the water flow makes a U-turn as shown in the second figure. The diameter of the entire elbow is 10 cm. The elbow discharges water into the atmosphere, and thus the pressure at the exit is the local atmospheric pressure. The elevation difference between the centers of the exit and the inlet of the elbow is 50 cm. The weight of the elbow and the water in it is considered to be negligible. Take the momentum-flux correction factor to be 1.03 at both the inlet and the outlet. Take the density of water to be 1000 kg/m3.arrow_forwardA body of length 3 m is moving normal to the direction of its motion moving through the water having viscosity of 0.0125 poise. If the total drag force acting on the body is 7,034 kN, then the projected area of the body will be Drag-coefficient and Reynold's Number to be 0.6 and 9 × 106 respectively. m². Assume Xarrow_forwardProblem 4: A film of oil exists between two horizontal plates spaced 3mm apart. The lower plate is fixed and the upper plate is pulled with a constant velocity. The velocity profile between the two plates is found to have a non- linear profile that is defined as u = (9y - 0.6y?) mm/s where y is in mm. Assuming the top plate has an area of 0.5 m? and the viscosity of the oil is u= 0.437 N.s/m?, determine (a) the shear stress 1mm above the fixed plate, and (b) the force required to pull the upper plate. 2. F 3 mmarrow_forward
- 2-liter soda bottles do not have flat bottoms. A bottle can be approximated as a cylinder filled from the bottom up to 0.26-m high with a hemispherical space of 10-cm-diameter underneath. If you treat the soda as having the density of water, what is the force in N of the soda on the curved bottom of the soda bottle?arrow_forwardThe following diagram shows a crate on an incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction (uk) between the crate and the incline is 0.1. The velocity of the box is zero, at which point in time it is subjected to a constant horizontal force F= 20 N. Determine the crate's velocity two seconds later. Weight of crate = 137 N %3D 20arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning