
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
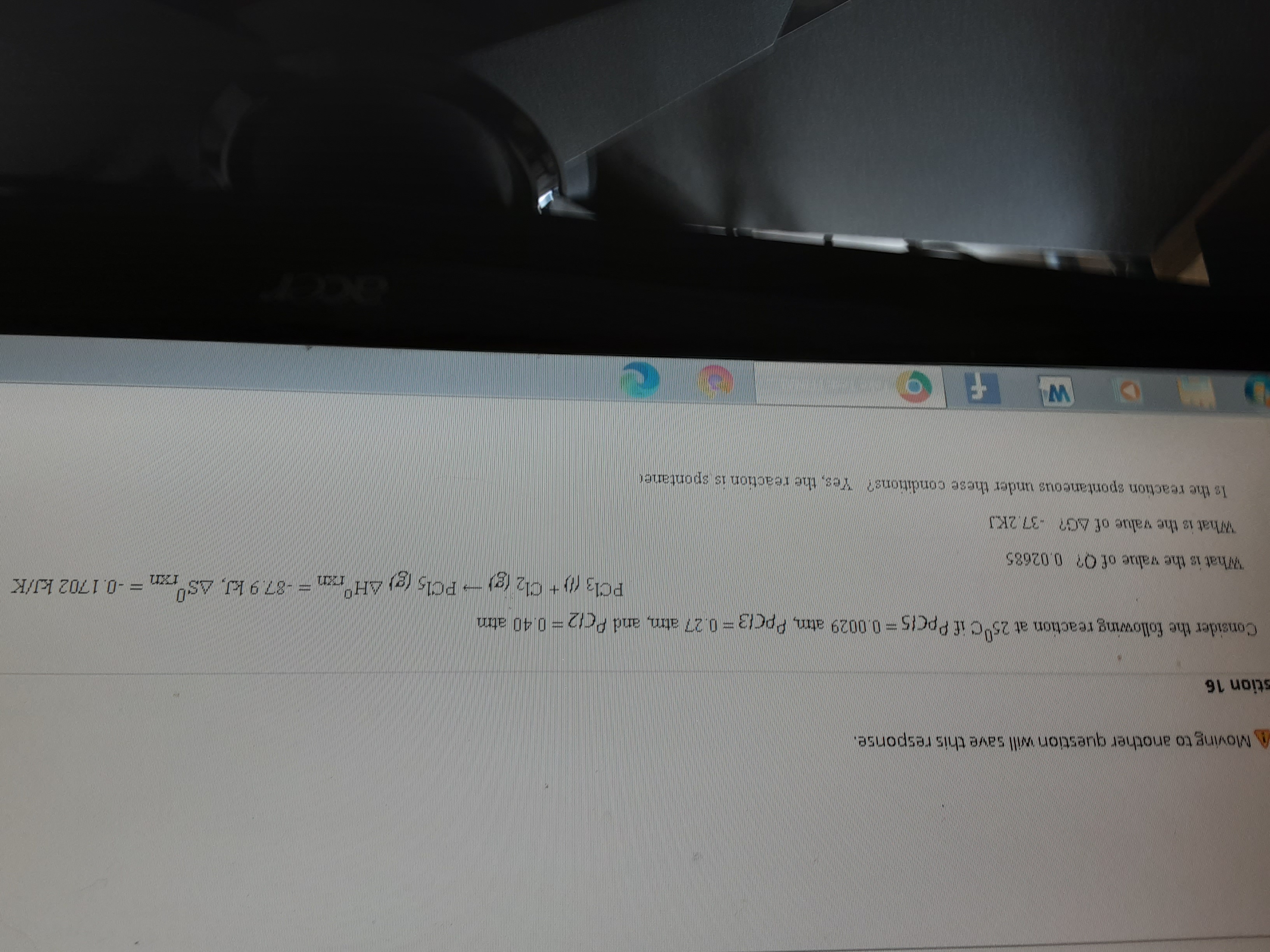
Transcribed Image Text:A Mo another question will save this response.
stion 16
Consider the following reaction at 25°C if PpcIs=0.0029 atm, PpCi3 =0.27 atm, and PC12= 0.40 atm
PC13 (0 + Cl2 (g)- PCl, (g) AH°,
= -0.1702 kJ/K
What is the value of O? 0.02685
What is the value of AG? -37.2KJ
Is the reaction spontaneous under these conditions? Yes, the reaction is spontaner
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. Given the thermodynamic data below, what is the equilibrium constant Kea of the following popular science fair reaction at 25°C: H'(aq) + HCO3(aq) + CO2(g) + H₂O(g) Species AG% (kJ/mol) H* (aq) 0 HCOs aq) -587.1 CO2(g) -394.4 H₂O(g) -228.6 A. 7.1 x 10¹0 B. 2.0 x 106 C. 89 D. 1.0 E. 4.3 x 10-8 Iarrow_forwardConsider the dissolution of nitrous acid: HNO₂(aq) For this reaction under standard conditions, AG° = 19.1 kJ/mol. Calculate A Gat 298 K, when [H*] = 5.0×10-² M, [NO₂¯] = 2.0×10−³ M and [HNO₂] = 0.10 M. (A) 2.0 kJ/mol (B) 12.5 kJ/mol (C) 16.6 kJ/mol (D) 19.1 kJ/mol (E) 36.2 kJ/mol - H+ (aq) + NO₂ (aq).arrow_forwardFor a particular reaction △H= -32 kJ and △S = -98J/K (A) At what temp will the reaction be at equilibrium ? (B) If the temperature is increased from the equilibrium temperature what will happen?arrow_forward
- 16arrow_forward(aq) assuming Which way will the equilibrium shift if you only had 22.67 grams of I" there is an excess of the other 2 reactant at 100°C. 31 (aq) + H3AS04(ag) + 2H*, 13 (aq) + H3ASO3(aq) + H2O) (aq) AH°{(kJ/mole) S° (J/mole*K) Substance or ion -55.19 180.7 I (aq) -345.69 212.34 H3ASO4(aq) -11.23 11.09 H* (aq) 69.77 -89.6 13 (aq) H3ASO3(aq) -301.27 199.78 H20 (1) -285.8 69.95 left then right Oat oguilibrium +hen loftarrow_forwardQuestion 15 of 16 Submit Consider the reaction below: 2 SO3(g) =2 SO2(g) + O2(g) The Kp is 1.81 × 10-5 at 350.0°C. Calculate Kc at the same temperature. (R = 0.08314 L·bar/ mol · K.) 1 2 3 4 C 7 8 9 +/- х 100 Tap here or pull up for additional resources LOarrow_forward
- Please answer this with work shown! Thanks!arrow_forwardCalculate AG° and AS°at 25 °C for the following fermentation reaction: 2. C,H1206(aq) → 2C2H;OH(aq) + 2C02(9) AG° (C,H1206, aq) = -910.4 kJ/mol AH°; (C,H1206,aq) = -1273.3 kJ/mol AG°; (C,H5OH,aq) = -181.64 kJ/mol AH°;(C2H50H,aq) = -288.3 kJ/mol AG°; (CO2,g) = -394.36 kJ/mol AH° (CO2,g) = -393.51 kJ/mol Note: Be mindful that we read all of your submissions individually. Corresponding deductions will be applied to students with the same output if plagiarism is detected.arrow_forward[References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Consider the following system at equilibrium where AH° = 16.1 kJ, and Kc = 6.50 x 10-3, at 298 K: 2NOBr(g) 2NO(g) + Br₂(g) If the VOLUME on the equilibrium system is suddenly increased at constant temperature: The value of Ke Oincreases O decreases O remains the same The value of Qc O is greater than Ke O is equal to Ke O is less than K The reaction must run in the forward direction to reestablish equilibrium. Orun in the reverse direction to reestablish equilibrium. Oremain the same. It is already at equilibrium. The number of moles of Br2 will O increase O decrease O remain the same Show Hint F5 6 H F6 & 7 KI F7 * 8 DII F8 ( 9 DD F9 ) O F10 P F11 Previous + Next Save and Exit F12 deletearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY