
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Help please. Draw the curved arrow notation and products for the each elementary step described by the sequence shown here.
Note that the products of each step should be used as the reactants in the next step, and you may need to draw in additional reagents as directed. Remember to click on each box to see step-specific instructions.
Draw H3CH2C–, and then add the curved arrow notation showing a nucleophilic addition.
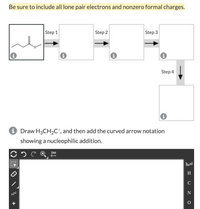
Transcribed Image Text:## Organic Chemistry Mechanism Exercise
**Instructions:** Be sure to include all lone pair electrons and nonzero formal charges in your diagram.
### Reaction Mechanism Steps
1. **Step 1:** Analyze the given structural formula (displayed as a starting point) and determine the initial interactions that will take place.
2. **Step 2:** Fill in the next box with the intermediate formed after the first chemical interaction, including all lone pair electrons and formal charges.
3. **Step 3:** Continue the reaction by identifying the next chemical transformation, filling the third box accordingly.
4. **Step 4:** Draw the final product in the last box, showcasing the complete reaction sequence.
### Structure and Notation Task
- **Objective:** Draw the structure H₃CCH₂C⁻.
- **Task:** Add the curved arrow notation to show a nucleophilic addition to the given substrate. Use the drawing tool provided to construct the molecule and depict the electron flow accurately.
### Drawing Tool
- A tool interface is provided for constructing and editing chemical structures. Use the tool palette to select appropriate elements and bonds to accurately depict the molecules and reactions.
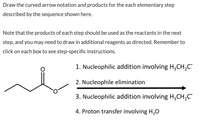
Transcribed Image Text:**Instructions for Curved Arrow Notation and Reaction Sequence**
1. **First Step: Nucleophilic Addition Involving \( \text{H}_3\text{CH}_2\text{C}^- \)**
- Begin by performing a nucleophilic addition where the nucleophile is the anion \( \text{H}_3\text{CH}_2\text{C}^- \).
2. **Second Step: Nucleophile Elimination**
- Follow the first step with a nucleophile elimination process. This step involves removing a nucleophile from the reactant.
3. **Third Step: Nucleophilic Addition Involving \( \text{H}_3\text{CH}_2\text{C}^- \)**
- Conduct another nucleophilic addition, using the same nucleophile \( \text{H}_3\text{CH}_2\text{C}^- \) as in the first step.
4. **Fourth Step: Proton Transfer Involving \( \text{H}_3\text{O} \)**
- End the sequence with a proton transfer, involving \( \text{H}_3\text{O} \).
**Notes:**
- Ensure that the products from each step are used as the reactants in the subsequent step.
- Additional reagents may need to be added where specified.
- Refer to individual instructions provided for each step in the boxes.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- The diagram illustrates an organic molecule featuring a 4-carbon chain connected to an ester functional group (\( \text{O=COC} \)).
- Curved arrow notations should reflect the movement of electrons during these transformations.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the following multistep synthesis of the target structure on right from the starting structure on the left choose the correct order of reagents. Ignore stereochemistry. To preview the image click here Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Step 1 Reagent(s) [Select] Step 2 Reagent(s)[Select] Step 3 Reagent(s)[Select] Step 4 Reagent(s) [Select] Step 5 Reagent(s) [Select] siearrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hend raitingarrow_forwardI don’t understand why the molecule circled is not more stable than the original product. Can someone explain why it’s wrong?arrow_forward
- Show a possible pathway and include all intermediate and reagents.arrow_forwardShow the mechanism for the given reaction conducted at -5 °C in CCI,. cyclohexene + bromine → dibromocyclohexane Draw structures, including charges and electrons, and add curved arrows. Details count. Draw each species (organic and inorganic) resulting from the previous step. Then, add curved arrows for the forward reaction. Include charges and nonbonding electrons. Add curved arrows to the first step. : Br - Br : Draw the major product. Include charges and nonbonding electrons.arrow_forwardPlease help with these and include the steps in the reaction so i can better understand how they work! just 1 or two of them is finearrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardUsing the curved arrow to guide your reasoning, draw the other product of this dissociation reaction.arrow_forwardThe substitution reaction studied here with Chlorobutane and KOH is known to have a second order rate equation meaning the transition state in the slow step involves both nucleophile and electrophile. Knowing that, which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply. A) Adding more Chlorobutane (the electrophile) will not change the rate of the reaction. B Adding more KOH (the nucleophile) will make the reaction go faster. Adding more Chlorobutane (the electrophile) will make the reaction go faster. D) Adding more KOH (the nucleophile) will not change the rate of the reaction. E Adding more KOH (the nucleophile) will make the reaction go slower.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY