
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
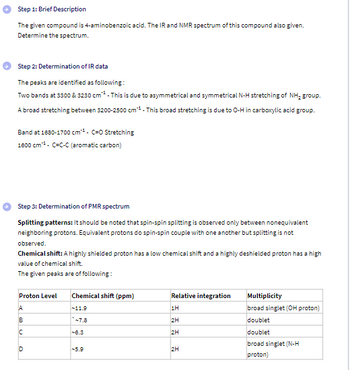
Transcribed Image Text:Step 1: Brief Description
The given compound is 4-aminobenzoic acid. The IR and NMR spectrum of this compound also given.
Determine the spectrum.
Step 2: Determination of IR data
The peaks are identified as following:
Two bands at 3300 & 3230 cm. This is due to asymmetrical and symmetrical N-H stretching of NH₂ group.
A broad stretching between $200-2500 cm** - This broad stretching is due to O-H in carboxylic acid group.
Band at 1680-1700 cm¹. C=O Stretching
1600 cm C-C-C (aromatic carbon)
Step 3: Determination of PMR spectrum
Splitting patterns: It should be noted that spin-spin splitting is observed only between nonequivalent
neighboring protons. Equivalent protons do spin-spin couple with one another but splitting is not
observed.
Chemical shift: A highly shielded proton has a low chemical shift and a highly deshielded proton has a high
value of chemical shift.
The given peaks are of following:
Proton Level
Chemical shift (ppm)
Relative integration
Multiplicity
ABC
-11.9
7.8
8.3
broad singlet (N-H
D
-5.9
2H
proton)
2H
%%%%
1H
broad singlet (OH proton)
2H
doublet
doublet
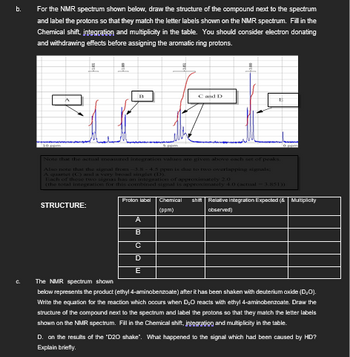
Transcribed Image Text:b.
For the NMR spectrum shown below, draw the structure of the compound next to the spectrum
and label the protons so that they match the letter labels shown on the NMR spectrum. Fill in the
Chemical shift, integration and multiplicity in the table. You should consider electron donating
and withdrawing effects before assigning the aromatic ring protons.
Ε
B
C and D
E
Note that the actual measured integration values are given above each set of peaks.
Also note that the signal from -3.8-4.5 ppm is due to two overlapping signals;
A quartet (C) and a very broad singlet (D).
Each of these two signas has an integration of approximately 2.0
(the total integration for this combined signal is approximately 4.0 (actual -3.851))
STRUCTURE:
Proton label
Chemical shift Relative Integration Expected (& Multiplicity
(ppm)
observed)
C.
The NMR spectrum shown
A
B
C
D
E
below represents the product (ethyl 4-aminobenzoate) after it has been shaken with deuterium oxide (D₂O).
Write the equation for the reaction which occurs when D₂O reacts with ethyl 4-aminobenzoate. Draw the
structure of the compound next to the spectrum and label the protons so that they match the letter labels
shown on the NMR spectrum. Fill in the Chemical shift, integration and multiplicity in the table.
D. on the results of the "D20 shake". What happened to the signal which had been caused by HD?
Explain briefly.
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The mass spectrum and 13C NMR spectrum of a hydrocarbon are shown. Propose a structure for this hydrocarbon, and explain the spectral data.arrow_forwardThe infrared spectrum of the compound with the mass spectrum shown below has a medium-intensity peak at about 1650 cm-1. There is also a C-H out-of-plane bending peak near 880 cm-1. Propose a structure consistent with the data.arrow_forwardPlease assist in identifying the all the major peaks of the NMR and what they corresponds with. Please explain.arrow_forward
- A STK2083_Molecular_Spectroscopy_Group Assignment.pdf - Adobe Acrobat Reader DC File Edit View Sign Window Help Home Tools STK2083_Molecular. x Sign In 1 /1 119% a. Which of the compounds below best matches the following 'H NMR spectrum? Integration values are indicated next to their corresponding signal. 2. Search 'Signature' Convert PDF но Edit PDF A B Comment OH HO Combine Files D E EI Organize Pages 24 16 2 Redact A Compress PDF 16 U Protect 8 D Fill & Sign Create, edit and sign PDF forms & agreements PPM b. Briefly explain your answer 2 (a) based on number of signals, position of signals and the integration of the signals. Start Free Trialarrow_forwarddetermine compound based on this spectrum data: MS Data- m/z = 112(45.45 %), 113 (3.961 %), and 114 (0.195%) IR Peaks-0.9 ppm (t, 6H), 1.5 ppm (dt, 4H), 2 ppm (td, 4H), 5.4 ppm (tt, 2H) C NMR Peaks- 15, 24, 36, and 127 ppmarrow_forwardAnalysis given IR, CNMR (written below), HNMR and mol weight: weight: 142g/mol C NMR: 4 uniques C's, small peak at 220ppm, medium peak at 50ppm, 2 strong peaks at 21 and 22ppmarrow_forward
- Only Typed solution. Please answer fastarrow_forwardCan u explain in detail what the percentages mean what the spectral data means and what the structure is and how to find it thank uarrow_forwardDraw the structure for a compound with the formula C8H10O3 that exihibits the 1H-NMR spectrum provided integral parts are also provided in a table above the 1H-NMR picture.arrow_forward
- Need help answer and simple explanationarrow_forwardAttached is the 13C-NMR Spectrum of Benzil (in CDCl3 and TMS) Can you provide (chemical shift (experimental), chemical shift (literature), assignment)arrow_forwardWhat compound is consistent with the NMR spectrum below? d6-DMSO solution F0.60 0.55 -0.50 -0.45 -0.40 -0.35 -0.30 -0.25 -0.20 -015 -0.10 -0.05 -0.00 0.05 6.5 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 6.0 f1 (ppm) 7.5 7.0 HOI HO. но но (A) (B) (C) (D) Forarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole