
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
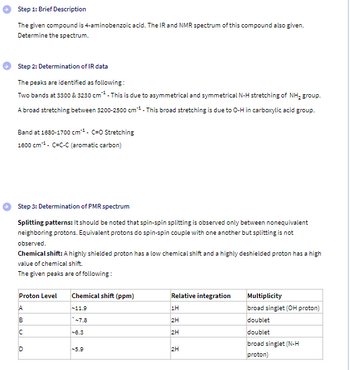
Transcribed Image Text:Step 1: Brief Description
The given compound is 4-aminobenzoic acid. The IR and NMR spectrum of this compound also given.
Determine the spectrum.
Step 2: Determination of IR data
The peaks are identified as following:
Two bands at 3300 & 3230 cm. This is due to asymmetrical and symmetrical N-H stretching of NH₂ group.
A broad stretching between $200-2500 cm** - This broad stretching is due to O-H in carboxylic acid group.
Band at 1680-1700 cm¹. C=O Stretching
1600 cm C-C-C (aromatic carbon)
Step 3: Determination of PMR spectrum
Splitting patterns: It should be noted that spin-spin splitting is observed only between nonequivalent
neighboring protons. Equivalent protons do spin-spin couple with one another but splitting is not
observed.
Chemical shift: A highly shielded proton has a low chemical shift and a highly deshielded proton has a high
value of chemical shift.
The given peaks are of following:
Proton Level
Chemical shift (ppm)
Relative integration
Multiplicity
ABC
-11.9
7.8
8.3
broad singlet (N-H
D
-5.9
2H
proton)
2H
%%%%
1H
broad singlet (OH proton)
2H
doublet
doublet

Transcribed Image Text:C.
The amine group is considered to be electron donating toward the ring by resonance, thus it
will place a partial negative charge on the (relative) ortho and para positions. Draw three
resonance structures for the product, showing the resulting charges at these positions.
H
H
d.
The carboxylic acid is considered to be electron withdrawing by resonance, thus it will place
a partial positive charge on the (relative) ortho and para positions. Draw three resonance
structures for the product, showing the resulting charges at these positions.
e.
Based on the resonance structures, which of the aromatic protons is more shielded and
which is less shielded? Which of these protons will appear at the larger chemical shift and
which will appear at the lower chemical shift? Decide which of the protons should be labelled
as HB and Hc. Explain briefly.
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Given the following NMR data, find the unknown compound. a. Identify the molecular formula; find IHDb. Identify the 1H and 13C NMR signalsarrow_forwardWhich compound is most consistent with this infrared spectrum and mass spectrum?arrow_forwardWhat functional groups are present in the IR spectra below. Functional Group cm-1 O-H 3600-3200 N-H 3500-3200 Csp-H 3300 Csp2-H 3150-3000 Csp3-H 2937 O=C-H 1740-1720 C=O 1693 C=C (aromatic) 1650arrow_forward
- THIS CAN NOT BE HAND DRAWN! MUST USE A COMPUTER or DIGITALLY ILLUSTRATEarrow_forwardA student performed a series of reactions and obtained the spectral data provided. The reaction sequence is shown below.. What are the structures for A, B, C, and D? Compound B NMR (relative integrated areas below peaks) CH;CH,O°N 1. BHTHF N-bromosuccnimide A CH;CH,OH B 2. H,O,/OH- D hv reflux Compound A NMR (relative integrated areas below peaks) PPM 5 Compound B IR INFRARED SPECTRUM PPM 5 1 6 0.8 Compound A IR INFRARED SPECTRUM 0.6 0.8 0.4 0.4 0.2- 3000 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 1000 The MS of compound B shows an M+ peak at 198 and an M+2 peak at 200 with a relative abundance of 1:0.97 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 3000 1000 Transmitance Relative Transmittancearrow_forwardlabel the IR peaks draw the structure of the compound and give reasoningarrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forwardMatch the four structures with the four IR spectra (by putting a proper letter in the box to the right of each spectrum). Use specific IR absorptions for various functional groups to identify the structures.arrow_forwardGiven the information about the unknown: Unknown: MP: 101-106 oC White solid IR: 2837, 1701, 1602, 1391, 1139 cm-1 ** Using the Reference sheet, The IR and the given H-NMR, and C-NMR. Deduce, what the unknown is. Please give the name of uknownarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY