
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
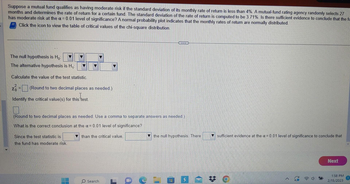
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a mutual fund qualifies as having moderate risk if the standard deviation of its monthly rate of return is less than 4%. A mutual-fund rating agency randomly selects 27
months and determines the rate of return for a certain fund. The standard deviation of the rate of return is computed to be 3.71%. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the fu
has moderate risk at the a= 0.01 level of significance? A normal probability plot indicates that the monthly rates of return are normally distributed.
Click the icon to view the table of critical values of the chi-square distribution.
The null hypothesis is Ho
The alternative hypothesis is H₁:
Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Identify the critical value(s) for this test.
(Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
What is the correct conclusion at the α = 0.01 level of significance?
than the critical value.
Since the test statistic is
the fund has moderate risk.
T
www
Search
the null hypothesis. There
LOOLON
sufficient evidence at the x = 0.01 level of significance to conclude that
Next
1:58 PM
2/15/2023
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose a mutual fund qualifies as having moderate risk if the standard deviation of its monthly rate of return is less than 4%. A mutual-fund rating agency randomly selects 24 months and determines the rate of return for a certain fund. The standard deviation of the rate of return is computed to be 3.62%. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the fund has moderate risk at the a= 0.05 level of significance? A normal probability plot indicates that the monthly rates of return are normally USPRILAAOIogy w uetermne ume r-varue iur uie est stausut. The P-value is. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Vi (00) More Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer. (? 1 part remaining Clear All Check Answer PPearson OVI 10:29 hp esc DII %23 96 & 4. 6. backspa r y a j k V alt alt ctrl USE YOUR SMAR Reviews Vld Specsarrow_forwardSuppose a mutual fund qualifies as having moderate risk if the standard deviation of its monthly rate of return is less than 6%. A mutual-fund rating agency randomly selects 23 months and determines the rate of return for a certain fund. The standard deviation of the rate of return is computed to be 5.37%. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the fund has moderate risk at the a= 0.10 level of significance? A normal probability plot indicates that the monthly rates of return are normally distributed. What are the correct hypotheses for this test? The null hypothesis is H.: = 0.06. The alternative hypothesis is H₁: O Calculate the value of the test statistic. = 17.62 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Use technology to determine the P-value for the test statistic. The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed) n example Get more help - < 0.06. 16 (DELL) Marrow_forwardThe stock price for International Business Machines (IBM) historically has followed an approximately normal distribution (when adjusting for inflation) with a mean of $166.305 and standard deviation of $4.2216. What is the probability that on a selected day the stock price is below $162.5?arrow_forward
- Jack invests in a mutual fund with annual returns that follow a Normal model with mean 14% and standard deviation 9%. What is the probability Jack obtains an annual return greater than 25%?arrow_forwardThe monthly utility bills in a city are normally distributed, with a mean of $100 and a standard deviation of $13. Find the probability that a randomly selected utility bill is (a) less than $69, (b) between $85 and $120, and (c) more than $130.arrow_forwardThe average return for large-cap domestic stock funds over certain three years was 7.2%. Assume the three-year returns were normally distributed across funds with a standard deviation of 2.2%. What is the probability an individual large-cap domestic stock fund had a three-year return of 5% or less? Group of answer choices 0.10 0.28 0.21arrow_forward
- Suppose a mutual fund qualifies as having moderate risk if the standard deviation of its monthly rate of return is less than 5%. A mutual-fund rating agency randomly selects 21 months and determines the rate of return for a certain fund. The standard deviation of the rate of return is computed to be 3.37%. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the fund has moderate risk at the a = 0.01 level of significance? A normal probability plot indicates that the monthly rates of return are normally distributed. What are the correct hypotheses for this test? The null hypothesis is Ho: 0.0337. > The alternative hypothesis is H4: 0.0337. Calculate the value of the test statistic. 0.05. x² = (Round to three decimal places as n 0.0337. Use technology to determine the P-value for tie iosi diaidiu. The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the correct conclusion at the a = 0.01 level of significance? Since the P-value is than the level of significance, the null…arrow_forwardSuppose a mutual fund qualifies as having moderate risk if the standard deviation of its monthly rate of return is less than 6%. A mutual-fund rating agency randomly selects 23 months and determines the rate of return for a certain fund. The standard deviation of the rate of return is computed to be 5.26%. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the fund has moderate risk at the α=0.05 level of significance? A normal probability plot indicates that the monthly rates of return are normally distributed. What are the correct hypotheses for this test? The null hypothesis is? The alternative hypothesis is? Calculate the value of the test statistic The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the correct conclusion at the α=0.05 level of significance?arrow_forwardSuppose a mutual fund qualifies as having moderate risk if the standard deviation of its monthly rate of retum is less than 5%. A mutual-fund rating agency randomly selects 29 months and determines the rate of return for a certain fund. The standard deviation of the rate of return is computed to be 4.63%. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the fund has moderate risk at the a=0.01 level of significance? A normal probability plot indicates that the monthly rates of return are normally distributed. What are the correct hypotheses for this test? The null hypothesis is Ho: The alternative hypothesis is H₁: Calculate the value of the test statistic. ²=(Round to three decimal places as needed.) Use technology to determine the P-value for the test statistic. The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the correct conclusion at the a = 0.01 level of significance? than the level of significance. the null sufficient evidence to conclude that the fund has moderate…arrow_forward
- The monthly utility bills in a city are normally distributed, with a mean of $100 and a standard deviation of $13. Find the probability that a randomly selected utility bill is (a) less than $69, (b) between $87 and $100,and (c) more than $130.arrow_forwardSuppose a mutual fund qualifies as having moderate risk if the standard deviation of its monthly rate of return is less than 3%. A mutual-fund rating agency randomly selects 26 months and determines the rate of return for a certain fund. The standard deviation of the rate of return is computed to be 2.58%. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the fund has moderate risk at the α=0.10 level of significance? A normal probability plot indicates that the monthly rates of return are normally distribute identify the null and alternate hypotnese,test statistic,pvalue and conclusionarrow_forwardSuppose a mutual fund qualifies as having moderate risk if the standard deviation of its monthly rate of return is less than 4%. A mutual-fund rating agency randomly selects 21 months and determines the rate of return for a certain fund. The standard deviation of the rate of return is computed to be 2.71%. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the fund has moderate risk at the α=0.05 level of significance? A normal probability plot indicates that the monthly rates of return are normally distributed. What are the correct hypotheses for this test? The null hypothesis is H0: σ or μ or p and less than or not equal or greater than or equals 2.7. The alternative hypothesis is H1: μ or p or σ , greater than or less than or not equals or equals 2.7. Calculate the value of the test statistic. X2 = _____ (Round to three decimal places as? needed.) Use technology to determine the? P-value for the test statistic. The? P-value is _______ (Round to three decimal places as?…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman