
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
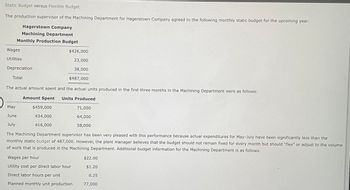
Transcribed Image Text:Static Budget versus Flexible Budget
The production supervisor of the Machining Department for Hagerstown Company agreed to the following monthly static budget for the upcoming year:
Hagerstown Company
Machining Department
Monthly Production Budget
Wages
Utilities
$426,000
23,000
38,000
$487,000
The actual amount spent and the actual units produced in the first three months in the Machining Department were as follows:
Amount Spent Units Produced
May
71,000
June
64,000
July
58,000
The Machining Department supervisor has been very pleased with this performance because actual expenditures for May-July have been significantly less than the
monthly static budget of 487,000. However, the plant manager believes that the budget should not remain fixed for every month but should "flex" or adjust to the volume
of work that is produced in the Machining Department. Additional budget information for the Machining Department is as follows:
Wages per hour
Utility cost per direct labor hour
Direct labor hours per unit
Planned monthly unit production
Depreciation
Total
$459,000
434,000
416,000
$22.00
$1.20
0.25
77,000

Transcribed Image Text:b. Compare the flexible budget with the actual expenditures for the first three months.
Total flexible budget
Actual cost
May
June
Excess of actual cost over budget
What does this comparison suggest?
The Machining Department has performed better than originally thought.
The department is spending more than would be expected.
July
100
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Print Item Static Budget versus Flexible Budget The production supervisor of the Machining Department for Hagerstown Company agreed to the following monthly static budget for the upcoming year: Hagerstown CompanyMachining DepartmentMonthly Production Budget Wages $2,250,000 Utilities 72,000 Depreciation 36,000 Total $2,358,000 The actual amount spent and the actual units produced in the first three months in the Machining Department were as follows: Amount Spent Units Produced May $1,600,000 40,000 June 1,950,000 48,000 July 2,200,000 52,000 The Machining Department supervisor has been very pleased with this performance because actual expenditures for May–July have been significantly less than the monthly static budget of $2,358,000. However, the plant manager believes that the budget should not remain fixed for every month but should “flex” or adjust to the volume of work that is produced in the Machining Department. Additional budget…arrow_forwardHesterman Corporation makes one product and has provided the following information to help prepare the master budget for the next four months of operations: Budgeted selling price per unit Budgeted unit sales (all on credit): $ 118 April 7,800 May 9,400 June 14,000 July 12,100 Raw materials requirement per unit of output 3 pounds $ 3.00 per pound Raw materials cost Direct labor requirement per unit of output Direct labor wage rate 2.8 direct labor-hours $ 25.00 per direct labor-hour Credit sales are collected: 40% in the month of the sale 60% in the following month The ending finished goods inventory should equal 40% of the following month's sales. The ending raw materials inventory should equal 20% of the following month's raw materials production needs. The budgeted required production for May is closest to:arrow_forwardStatic Budget versus Flexible Budget The production supervisor of the Machining Department for Niland Company agreed to the following monthly static budget for the upcoming year: Niland CompanyMachining DepartmentMonthly Production Budget Wages $663,000 Utilities 38,000 Depreciation 64,000 Total $765,000 The actual amount spent and the actual units produced in the first three months in the Machining Department were as follows: Amount Spent Units Produced January $721,000 128,000 February 691,000 117,000 March 657,000 105,000 The Machining Department supervisor has been very pleased with this performance because actual expenditures for January–March have been significantly less than the monthly static budget of 765,000. However, the plant manager believes that the budget should not remain fixed for every month but should “flex” or adjust to the volume of work that is produced in the Machining Department. Additional budget information for the…arrow_forward
- Alpesharrow_forwardPreparing an Overhead Budget Patrick Inc. makes industrial solvents. Budgeted direct labor hours for the first 3 months of the coming year are: January 13,140 February 12,300 March 15,075 The variable overhead rate is $0.60 per direct labor hour. Fixed overhead is budgeted at $2,580 per month. Required: Prepare an overhead budget for the months of January, February, and March, as well as the total for the first quarter. Do not include a multiplication symbol as part of your answer. Round total variable overhead and total overhead to the nearest dollar. Patrick Inc. Overhead Budget For the Coming First Quarter Overhead: January February March Total Total direct labor hrs Variable overhead rate Total variable overhead $4 Add: Fixed overhead Total overheadarrow_forwardMonthly budgeted fixed overhead cost?arrow_forward
- Static budget versus flexible budget: The I'm just started digging a production supervisor of the machine department for hanger town company agree to the following monthly static budget for the upcoming year. Hanger town machine Department monthly production budget, Wages- $570,000, utilities- 39,000, depreciation- 65,000 total 674,000 2196 the actual amount spent and the actual units produce in the first three months in the machines Department were as follow. May- amount spent $636,000 unit produced 55,000 June- 607,000 unit produced 50,000 July- 579,000 unit produced 45,000 The machine Department supervisor has been very pleased with his this performance because actual extra Dentures for May through July have been significantly Imagine lyrics less than the monthly static budget of 674,000. However the plant manager believes that the budget should not remain fixed for every month but should flex or adjust to the volume of the work that it is produced in the machine Department.…arrow_forwardPart #6: H Company’s Direct Labor Budget indicates the number of direct labor hours to be used in July, August, and September are 21,000 and 18,900 and 23,000 respectively. Variable overhead is expected to be $0.90 per direct labor hour. Fixed overhead per month is expected to be $8,200. Prepare an Overhead Budget with columns for July, August, September, and Total 3rd Quarter.arrow_forwardDirect Labor Cost Budget Hours required for assembly: Pasadena Candle Inc. budgeted production of 45,000 candles for January. Each candle requires molding. Assume that 15 minutes are required to mold each candle. If molding labor costs $12 per hour, determine the direct labor cost budget for January. Round total direct labor cost to the nearest dollar, if required. Pasadena Candle Inc. Direct Labor Cost Budget For the Month Ending January 31 Candles Convert minutes to hours Molding hours Hourly rate Total direct labor cost -1. ÷ X $ r=&inprogress=false $ min. min. ✩✩ = ☆ hrs. Previous Next Updaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education