Question
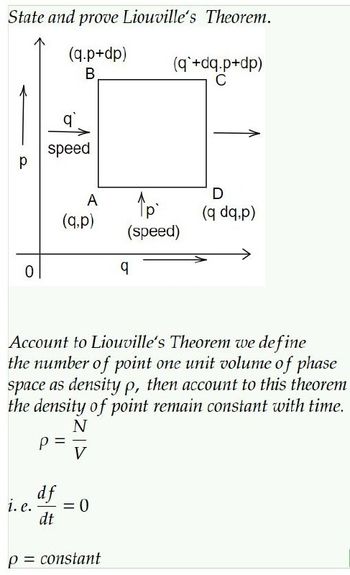
Transcribed Image Text:State and prove Liouville's Theorem.
(q.p+dp)
B
р
0
q
speed
i. e.
df
dt
A
(q.p)
N
-
Account to Liouville's Theorem we define
the number of point one unit volume of phase
space as density p, then account to this theorem
the density of point remain constant with time.
V
= :0
p = constant
(q +dq.p+dp)
C
↑p
(speed)
q
D
(q dq,p)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Given vectors a=(5,3) and b=(-1,-2) Find the x-component of the resultant vector: T` = 2 a + 36arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide gas, CO2, travels at about 340 m/s at room temperature. What is the travel rate (velocity) of helium, He, at the same temperature?arrow_forward(0, 1, 0) is Consider a two-dimensional incompressible flow in the xz plane: u = - ey x Vo, where e the unit vector perpendicular to the xz plane. Denote the two velocity components in the xz plane as u and w in the x, z directions, respectively. Write down the expressions for them in terms of o. If the function of o assumes = x2² calculate the values of u and w at the coordinate x = = 2, z = 1. Ou= Ou= 86 əz > Ou=- - 86 əx W= ap dz 7 W= W= 8p Əz ap əz " ap " əI u = 4, w = -1 u = -1, w = 4 u = −4, w = 1 86 0₂7 86 Ou=- W=- u= -1, w = -4 5 dr =arrow_forward
- The gas law for a fixed mass mm of an ideal gas at absolute temperature T, pressure P, and volume V is PV=mRT, where R is the gas constant. Find the partial derivative (∂P/∂V) (∂V/∂T) (∂T/∂P) = ?arrow_forward4.2.1 The velocity components of u and v of a two-dimensional flow are given by u = ax + bx x²y² by and v=ay+ .2.2 where a and b are constants. Calculate the acceleration.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios