
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Standing waves are a useful phenomenon to use to study waves. When a standing wave forms, it is easy to measure the wavelength because the wave appears motionless.
Now let's think about the experiment you will do. Today, you are going to look for a relationship between the frequency of a wave and the wavelength.
What variables do you need to keep constant during this experiment? (This question has more than one choice)
Select all that apply:
-
The cord
-
The hanging weight
-
Frequency
-
Wavelength
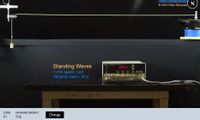
Transcribed Image Text:Direct Measurement
义
© 2015 Peter Bohacek
Standing Waves
1 mm elastic cord
hanging mass = 50 g
%3D
SIBLEY 4
CORD
HANGING WEIGHT
Change
# 1
50g
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 1 Which question would be the BEST to ask to determine if a wave is an EM wave or a mechanical wave? A Does the wave contain energy? B Does it require a medium to travel? C Is it a longitudinal or transverse wave? D Does the wave have a crest and trough?arrow_forwardConstants I Periodic Consider a sine wave traveling down the stretched two- part cord of the figure.(Figure 1) Determine a formula for the ratio of the wavelengths in the two sections. (The frequency is the same in both sections.) Express your answer in terms of the variables µH and uL. ? Ан Submit Request Answer Figure 1 of 1 Part C Light section Heavy section Is the wavelength larger in the heavier cord or the lighter? (a) in the heavier cord Transmitted in the lighter cord pulse Submit Request Answer Reflected pulse (b) Provide Feedback IIarrow_forwardplease answer the questions based on the wave equation: v=fλ a) What is the independent parameter? b) What is the dependent parameter? c) What parameter will you plot on your y-axis? d) If you perform a line of best fit, what will be your slope? e) How will get g from your line of best fit? What's the equation for g? f) What is the equation for the uncertainty in g? g) write a procedure for experimenting to measure garrow_forward
- The figure below shows two waves that occupy the same point in space. Copy the sketch into a sheet of paper using the dimensions indicated. Draw the wave that results from the interference of these two waves.arrow_forwardHow to solve this questionarrow_forwardHandwrite and as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- Please download the following worksheets, which show 4 separate grids. Each grid has two different waves (e.g., Wave and Wave B). Your goal is to draw the resulting wave (i.e., Wave C) if the two waves would have been superposed on top of each other. To do this, you'll need to add the two amplitudes (height of the Wave A and Wave B on the y-axis) at a given point on the x-axis to get the resulting one. For example, using number 3 as an example: a. At point 0 on the x axis, Wave A has an amplitude of 0, and Wave B has an amplitude of 0, so Wave C at point 0 would be 0. b. At point 4 on the x axis, Wave A has an amplitude of 6, and Wave B has an amplitude of 4, so Wave C at point 3 would have an amplitude of 10. c. At point 8 on the x axis. Wave A has an amplitdue of 0, and Wave B has an amplitude of -4, so Wave C at point 8 would be -4. You do not have to find the points for every single point along the x-axis, but just enough to get the general shape of the resulting wave. Once you…arrow_forwardWhat steps would I take to better understand how D(x,t) = f(x - v t) + g(x + v t) could be a solution to the general wave equation?arrow_forwardThe amplitude of two beating waves is described by the equation ψ = Amod(t)cos (ωavt). What is the main difference between this equation and the equation of a simple harmonic oscillator? A. The frequency changes in time. B. The amplitude changes in time. C. The phase changes in time.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON