
SQL code for:
Create a stored procedure “setRelocationFee” to set the relocation fee for a given
employee. If the employee’s office is in San Francisco, the relocation fee is $10000; if
the employee’s office is in Boston, the relocation fee is $8000; if the employee’s office
is in London, the relocation fee is $20000; if the employee works in other offices, the
relocation fee is $15000.
Below is a sample statement to test your stored procedure.
set @employeeID = 1501;
call setRelocationFee(@employeeID, @relocationfee);
select @employeeID, @relocationfee;
Having this
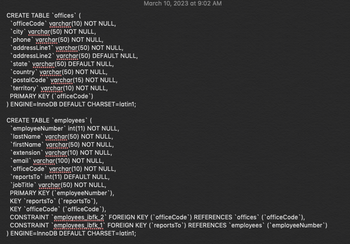
CREATE TABLE `offices` (
`officeCode` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`city` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`phone` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`addressLine1` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`addressLine2` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`state` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`country` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`postalCode` varchar(15) NOT NULL,
`territory` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`officeCode`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
CREATE TABLE `employees` (
`employeeNumber` int(11) NOT NULL,
`lastName` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`firstName` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`extension` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`officeCode` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`reportsTo` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`jobTitle` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`employeeNumber`),
KEY `reportsTo` (`reportsTo`),
KEY `officeCode` (`officeCode`),
CONSTRAINT `employees_ibfk_2` FOREIGN KEY (`officeCode`) REFERENCES `offices` (`officeCode`),
CONSTRAINT `employees_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`reportsTo`) REFERENCES `employees` (`employeeNumber`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- SQL CODE FOR For the players who show up in Batting, Bowling, and Fielding tables, create a list that shows their names, runs they have scored, wickets they have taken, and catches they have taken? table is in picture (bowling table is same as batting and fielding )arrow_forwardWrite a stored procedure called sp_apply_discount() that will apply percent discount to books in a subject. The stored procedure takes in 2 parameters, percentDiscount (DECIMAL(8,2)) and subject (VARCHAR(120)). Using these parameters, the stored procedure computes the discount for the book cost and stores it in the FINAL_PRICE field. For example, the following stored procedure call: call sp_apply_discount(0.15, 'Database');would compute 15% percent discount from the book cost in the Database subject category and store it in the FINAL_PRICE column as depicted in this image:arrow_forwardCreate a stored procedure that will return the number of customers in a given state. The parameter for your stored procedure should accept the state abbreviation ('UT') and return the results of a query that returns the number of customers in that state.arrow_forward
- ISBN Title Author 12345678 The Hobbit J.R.R. Tolkien 45678912 DaVinci Code Dan Brown Your student ID DBS311 Your Name use the following statement to Write the PL/SQL code to create a procedure that accepts a product price and increases it by 10%arrow_forwardWrite SQL code for the following: Create a stored procedure “setRelocationFee” to set the relocation fee for a givenemployee. If the employee’s office is in San Francisco, the relocation fee is $10000; ifthe employee’s office is in Boston, the relocation fee is $8000; if the employee’s officeis in London, the relocation fee is $20000; if the employee works in other offices, therelocation fee is $15000. (see image for table structure) I am stuck for the part that I have to select employeeNumber and officeCode and set the relocationFee to be able to obtain the result but I do not know how. Bellow is what I have gotten. Delimiter| CREATE PROCEDURE setRealocationFee(IN EmployeeID INT(11), OUT realocationFee INT(5))arrow_forwardSQL code for: (1) Hint: A NULL in the hours column should be considered as zero hours. Find the ssn, lname, and the total number of hours worked on projects for every employee whose total is less than 40 hours. Sort the result by lname */ /* (2) For every project that has more than 2 employees working on it: Find the project number, project name, number of employees working on it, and the total number of hours worked by all employees on that project. Sort the results by project number. /* (3) For every employee who has the highest salary in their department: Find the dno, ssn, lname, and salary. Sort the results by department number. */ /* (4) For every employee who does not work on any project that is located in Houston: Find the ssn and lname. Sort the results by lname /* (5) Hint: This is a DIVISION query For every employee who works on every project that is located in Stafford: Find the ssn and lname. Sort the results by lname */arrow_forward
- Write a PL/SQL stored procedure to print number of employees who are working in a job with Title "Tester". Include procedure call also. If the total count of Employees is more than 5 then print "Sufficient number of Employees" If the total count of Employees is less than 5 then print "Insufficient number of Employees" Else print "there are 5 employees". Use Oracle's NO DATA_FOUND build in exception to display the last message. DEPARTMENTS LOCATIONS P DEPARTMENT_ID * DEPARTMENT_NAME MANAGER_ID LOCATION_ID P LOCATION_ID STREET ADDRESS POSTAL_CODE * CITY STATE PROVINCE COUNTRY_ID JOB_HISTORY PF* EMPLOYEE_ID P * START DATE * END DATE F JOB ID F DEPARTMENT_ID EMPLOYEES P EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST NAME * LAST_NAME EMAIL COUNTRIES COUNTRY_ID COUNTRY_NAME F REGION ID PHONE_NUMBER * HIRE DATE F JOB_ID JOBS P JOB_ID * JOB_TITLE MIN_SALARY MAX_SALARY SALARY COMMISSION_PCT MANAGER_ID F REGIONS DEPARTMENT_ID P* REGION_ID REGION_NAME I--arrow_forwardCreate a function to insert a new product into an existing order, include the product id, unit price, quantity. The output of the function is the message to notify the calling program whether the update succeeded or not. note : Note: Sql code need not java don't waste my time by giving java codearrow_forwardhttps://www.w3schools.com/sql/trysql.asp?filename=trysql_select_allarrow_forward
- Database: https://www.w3schools.com/sql/trysql.asp?filename=trysql_select_allarrow_forwardQuery 3: Write a parameter query to display the names of all prospects each member tried to recruit based on the member’s first name and the member’s last name you input. List the member’s First Name, member’s Last Name, prospect’s First Name, and prospect’s Last Name (in this order in the query grid). Display the member’s First Name Heading as Member First Name, member’s Last Name Heading as Member Last Name, prospect’s first name heading as Prospect First Name, and prospect’s last name heading as Prospect Last Name. Sort the list by Member Last Name, Member First Name, Prospect Last Name, and Prospect First Name, all ascending order. (WE ARE USING ACCESS SO I AM JUST TRYING TO UNDERSTAND WHAT TO PUT AND PLUG IN ETC. USE MY PICTURES AS REFERRENCE!)arrow_forwardAdjust the following information so that1) all users on the system are able to run the SQL Executable and 2) multiple users (such as a team of software engineers) have the power to modify the SQL Executable Introduce any new groups that are needed and assign them group IDs USERS SQL Manager UID: 3 GROUPS SQL Users GID: 5 FILESDatabase File Owner 3 Group NA owner: rw group: - world: - setUID: 0 setGID: 0 sticky: 0 SQL Executable Owner 3 Group 5 owner: rwx group: r-x world: - setUID: 1 setGID: 0 sticky: 0arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





