
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
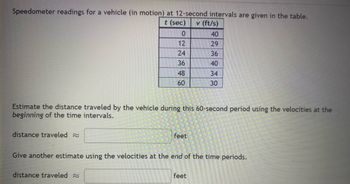
Transcribed Image Text:Speedometer readings for a vehicle (in motion) at 12-second intervals are given in the table.
t (sec)
v (ft/s)
distance traveled ~
0
12
24
36
48
60
Estimate the distance traveled by the vehicle during this 60-second period using the velocities at the
beginning of the time intervals.
distance traveled
feet
40
29
36
40
34
30
Give another estimate using the velocities at the end of the time periods.
feet
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 0 Assume that friction is so small that it can be ignored. If you think that none is correct, answer choice J. A force is applied to the car. Choose the one force graph (A through H) for the statement below which could allow the described motion of the car to continue. The car is at rest. B C F 0 I C e FOL C e O с e + + 0 0 1 + Time Time Time +arrow_forwardFigure below shows the position of a cart moves along the x-axis. What is the object's velocity at 2.0 s, in m/s? Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement. x (m) 2 1 A K 0 T -1 -2 B 2 4 6 8 10 C D 12 14 X6 E 18 -t (s)arrow_forwardShown below is a graph of velocity versus time for a moving object. The object starts at position x = 0. What is the final position in meters, from t = 0 seconds to t= 3 seconds? Represent your answer with 3 significant figures. (No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.)arrow_forward
- The equation for the motion of an object with constant acceleration is d= do + vt + at, where d is distance from a given point in meters, do is the initial distance from the starting point in meters, v is the starting velocity in meters per second, a is acceleration in meters per second squared, and t is time in seconds. A car is stopped at a traffic light. When the light turns green, the driver begins to drive, accelerating at a constant rate of 4 meters squared. A bus is traveling at a speed of 15 meters per second in another lane. The bus is 7 meters behind the car as it begins to accelerate. per second Find when the bus passes the car, when the car passes the bus, and how far each has traveled each time they pass one another. it lad wodarrow_forwardThe velocity - time graph of the journey of a person is shown in the attached graph. How much distance, in meters, did the person cover during the whole journey, from time = 0 to time = 50 seconds? Round your answer to the nearest integer. Speed (m/s) 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 10 20 Time (s) 30 40 50arrow_forwardWe first need to convert the period from days to seconds. (Pdays)(Ns/day) Ps Ps S = = Sarrow_forward
- A boulder starting from rest rolls down a hill in a straight line, which we shall call the xx axis. A graph of its position xx as a function of time tt is shown in the figure. (Figure attached) 1) Find the distance the boulder rolled between the end of the first second and the end of the third second. Express your answer in meters to one significant figure. 2) Find the boulder’s average speed during the first second. Express your answer in meters per second to one significant figure. 3) Find the boulder’s average speed during the second second. Express your answer in meters per second to one significant figure. 4) Find the boulder’s average speed during the third second. Express your answer in meters per second to one significant figure. 5) Find the boulder’s average speed during the fourth second. Express your answer in meters per second to one significant figure. 6) Find the boulder’s average speed during the first 4 seconds. Express your answer in meters per…arrow_forwardCurrent Attempt in Progress × Incorrect. Given the quantities a = 6.9 m, b = 7.1 s, c = 43 m/s, what is the value of the quantity d = Number i 43 eTextbook and Media Save for Later Units m/s 93 ? cb2 Attempts: 3 of 5 used Submit Answearrow_forwardAverage sum of the data number of trials Refer to the data table to find the mean for the time it took a toy car to travel certain distances. Distance (cm) 10 20 30 Time (s) Trial 1 2.02 4.11 Toy Car Time Trials Time (s) Trial 2 6.07 2.10 4.03 5.99 Time (s) Trial 3 1.95 4.06 6.03 What is the mean (average) of the trials for the 30 cm distance? 6.03 Average time (s) ?arrow_forward
- In heavy traffic, a car travels 39.2 km in 35.5 min. Determine the average velocity of the car over the 35.5 min span, and report your answer in km/hr.arrow_forwardProblem 6: Part (a) Determine the amount of time in s it would take to travel 1.25 mm. t1 = ______ Part (b) Determine the amount of time in s it would take to travel 1.1 cm. t2 = ______arrow_forwardA car is traveling at a constant speed of 32.7km/h. It begins to accelerate at a rate of 6.2m/s2 for 9.2 seconds. How far (in meters) does it travel during this time? Do NOT include units in your answer. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Do NOT change to scientific notation. Ignore significant figures.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON