
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Solve for the required value of the force P to raise the load if (a) the coefficient of static friction between the wedge and the ground is 0.20 in the absence of the rollers, and (b) the rollers exist as can be seen in the picture
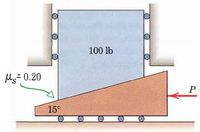
Transcribed Image Text:100 lb
My= 0.20
15°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Help Please.arrow_forwardHigh-strength bolts are used in the construction of many steel structures. For a 1-in.- nominal-diameter bolt, the required minimum bolt tension is 51 kips. Assuming the coefficient of friction to be 0.30, determine the required couple that should be applied to the bolt and nut. The mean diameter of the thread is 0.94 in., and the lead is 0.125 in. Neglect friction between the nut and washer, and assume the bolt to be square-threaded. You must show a free body diagram of your block and incline analysis of the bolt and nut, and clearly indicate your force triangle, if any.arrow_forwardIn the vise shown in the figure, the screw is single-threaded in the upper member: It passes through the lower member and is held by a frictionless washer. The pitch of the screw is 3 mm, its mean radius is 12 mm. and the coefficient of static friction is 0.15. Determine the magnitude P of the forces exerted by the jaws when M= 74-N.m couple is applied to the screw. Assuming that the screw is single-threaded at both A and B (right-handed thread at A and left-handed thread at B) The value of magnitude P is KN? Note: please consider everything. Refer to the image for more clarity. On occasions, I receive wrong answers!!. Kindly please show the magnitude of P which is the final answer in " KN" in the step by step working out please. Appreciate your time!. Side note, the answer in the image is wrong. This question is very annoying!. And a lot of experts have given me wrong answers!. So I beg to show concise working out!. Also I've attached another image something to help with…arrow_forward
- An arrangement of three boxes is shown in figure below. Box A weighs 25 N and rests on an inclined plane, while box B weighs 50 N and rests on a horizontal plane. The coefficient of friction between box A and the inclined plane is 0.3, and between box B and the horizontal plane is 0.4. The pulleys are all frictionless. Determine the range of weight of box C for which no motion will occur. Consider both sliding and tipping of boxes A and B. 0.6 m 0.75 m 25 N 5 A 4 C pome 0.8 m 0.6 m 50 N B 1.2 marrow_forwardA 150lb man stands on a 60lb bar to which a cable is fixed at B. The cable passes over two fixed pegs with coefficients of friction indicated. Assume that the arrangement of the pegs permits the cable to contact each peg over a total angle of 90-degrees (90-degrees per peg). Assume that the normal force exerted by the man on the bar acts downward through A. Find the largest force the man can exert on the cable and maintain the bar horizontal.arrow_forwardQuestion in photo. Thank youarrow_forward
- A wedge assembly, composed of wedges X and Y, is designed to lift crate W whose weight is 1CDE N, as shown in the figure below. What will be the maximum force P that can be applied before movement begins if the coefficient of friction for all surfaces of contact is 0.0875? Draw all necessary free-body diagrams and indicate the direction of impending motion. This is not your it in any way property so do not use were your own. 1CDE N W This is not your own property so do not use it in any way as if it were your own. 1C P property sol The not it in any way if your ow Parameters 1℃° 1D ° 1E ° 1CDE N 13° 14° 15° 1345 N 1Dº of use 1Eºarrow_forward1. The light bar is used to support the m kg block in its vertical guides. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.30 at the upper end of the bar and 0.4 at the lower end of the bar, m kg a. Find the friction force acting at each end for x = 75 mm. b. Find the maximum value of x for which the bar will not slip. 218 kg m = А l = 318 mm Figure 1.arrow_forwardFor the block system in figure below. Determine the smallest force P that impending motion. The block weights (A = 40 Kg, B = 50 Kg, C = 4O Kg and D = 3O Kg). The coefficients of static friction at all ground surfaces is us = 0.3 and between block C and D is us = 0.25 (neglect the friction on the pulleys)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY