
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
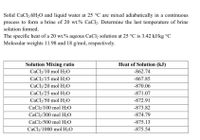
Transcribed Image Text:Solid CaCl2.6H2O and liquid water at 25 °C are mixed adiabatically in a continuous
process to form a brine of 20 wt.% CaCl2. Determine the last temperature of brine
solution formed.
The specific heat of a 20 wt.% aqeous CaCl2 solution at 25 °C is 3.42 kJ/kg °C
Molecular weights 11.98 and 18 g/mol, respectively.
Solution Mixing ratio
Heat of Solution (kJ)
CaCl2/10 mol H2O
-862.74
CaCl2/15 mol H2O
-867.85
CaCl2/20 mol H2O
-870.06
CaCl2/25 mol H2O
-871.07
CaCl2/50 mol H2O
-872.91
CaCl2/100 mol H2O
-873.82
CaCl2/300 mol H2O
-874.79
CaCl2/500 mol H2O
-875.13
CaCl2/1000 mol H2O
-875.54
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Example. 6.3.How much heat has to be added to a solution of 1g mol of HCl in H2O to concentrate the solution to 1 g mol of HCl in 4 g mol of H,0? g mol ofarrow_forwardLiquid gas undergoes combustion in air, releasing 100kf of heat and producing two gaseous products. Include energy in the reaction. When HCL reacts with NaOH to produce NaCl and H2O, 60kj of heat is released in the surroundings. a. State whether the surrounding gets warmer or colder. b. Sketch a PE graph for this reaction.arrow_forward8.29 Show complete solution and diagramarrow_forward
- Isopropanol, with 13 wt% water, can be dehydrated to obtain almost pure isopropanol at a 90% recovery by azeotropic distillation with benzene. When condensed, the overhead vapor from the col- umn forms two immiscible liquid phases. Use Table 2.4 with data in Perry's Handbook and the data below to compute the heat-transfer rate in Btu/h and kJ/h for the condenser. Water-Rich Organic-Rich Overhead Phase Phase Phase Vapor Liquid Liquid Temperature, °C 76 40 40 Pressure, bar 1.4 1.4 1.4 Flow rate, kg/h: Isopropanol 6,800 5,870 930 Water 2,350 1,790 560 Benzene 24,600 30 24,570arrow_forward9.12 A 50 wt% Ni-50 wt% Cu alloy is slowly cooled from 1400°C (2550 F) to 1200°C (2190 F). (a) At what temperature does the first solid phase form? (b) What is the composition of this solid phase? (c) At what temperature does the liquid solidify? (d) What is the composition of this last remaining liquid phase?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The