
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![**Calculating ΔS° for the Reaction at 25°C**
Given the following information, calculate ΔS° for the reaction:
\[ \text{SO}_3(g) + \text{H}_2\text{O}(l) \rightarrow \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4(l) \]
**Hint:** Because ΔS° is a state function (like ΔH°), you can use a table to calculate it in the same way. This means you should add up all the entropy for the products (times the number of each) and subtract all the entropy for the reactants.
**Entropy Values:**
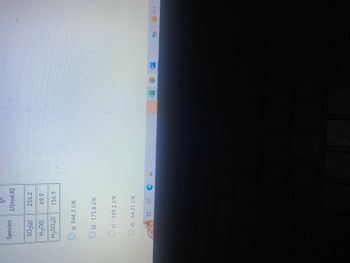
| Species | S° (J/mol·K) |
|-------------|--------------|
| SO₃(g) | 256.2 |
| H₂O(l) | 69.9 |
| H₂SO₄(l) | 156.9 |
**Solution Choices:**
- a) 544.3 J/K
**Explanation:**
To calculate the standard entropy change (ΔS°) for the reaction, use the following equation:
\[ ΔS° = ΣS°_{\text{products}} - ΣS°_{\text{reactants}} \]
1. Calculate the sum of the entropies of the products:
- H₂SO₄(l): 156.9 J/mol·K
2. Calculate the sum of the entropies of the reactants:
- SO₃(g): 256.2 J/mol·K
- H₂O(l): 69.9 J/mol·K
3. Subtract the total entropy of the reactants from the total entropy of the products to find ΔS°.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/065e3530-493f-4c36-b85d-4fbc9e0fed20/7d6cb2e7-122e-419a-9a87-43218657582b/7iupqam_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Calculating ΔS° for the Reaction at 25°C**
Given the following information, calculate ΔS° for the reaction:
\[ \text{SO}_3(g) + \text{H}_2\text{O}(l) \rightarrow \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4(l) \]
**Hint:** Because ΔS° is a state function (like ΔH°), you can use a table to calculate it in the same way. This means you should add up all the entropy for the products (times the number of each) and subtract all the entropy for the reactants.
**Entropy Values:**
| Species | S° (J/mol·K) |
|-------------|--------------|
| SO₃(g) | 256.2 |
| H₂O(l) | 69.9 |
| H₂SO₄(l) | 156.9 |
**Solution Choices:**
- a) 544.3 J/K
**Explanation:**
To calculate the standard entropy change (ΔS°) for the reaction, use the following equation:
\[ ΔS° = ΣS°_{\text{products}} - ΣS°_{\text{reactants}} \]
1. Calculate the sum of the entropies of the products:
- H₂SO₄(l): 156.9 J/mol·K
2. Calculate the sum of the entropies of the reactants:
- SO₃(g): 256.2 J/mol·K
- H₂O(l): 69.9 J/mol·K
3. Subtract the total entropy of the reactants from the total entropy of the products to find ΔS°.
Transcribed Image Text:Below is the transcription of the image content, designed for an educational website:
---
**Species Entropy Values**
| Species | \( S^\circ \) (J/mol·K) |
|-----------|-----------------------|
| SO₃(g) | 256.2 |
| H₂O(l) | 69.9 |
| H₂SO₄(l) | 156.9 |
**Question:**
Calculate the change in entropy (\( \Delta S \)) for a given process using the above species.
**Options:**
a) 544.3 J/K
b) -175.8 J/K
c) -169.2 J/K
d) -64.21 J/K
---
This table provides standard molar entropy values for specific chemical species, and you are required to calculate the entropy change for a reaction involving these species. Select the correct entropy change from the options provided.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For each system listed in the first column of the table below, decide (if possible) whether the change described in the second column will increase the entropy S of the system, decrease S, or leave S unchanged. If you don't have enough information to decide, check the "not enough information" button in the last column. System Change AS O AS 0 not enough information AS 0 not enough information AS 0 8.0 L. not enough informationarrow_forwardThe decomposition of nitrogen pentoxide in the reaction 2N₂O5 (s)→ 4NO2(g) + O2(g) is endothermic with AH = +110 kJ/mol. Even so, this reaction is spontaneous for temperatures above 230 K because the change of a solid into a gas is a large increase of entropy.arrow_forwardQ7. For each reaction, predict the sign of entropy of system and find the value of ASuniv. a. 3NO (g) N₂O (g) + NO2 (g) b. P4 (g) +5 Oz (g) → P4010 (S) c. Combustion of ethane (C2H6) gas to form carbon dioxide and gaseous water.arrow_forward
- 5. Note: Please don't write on a paper. I can't understand handwrittens.arrow_forwardThe heat of vaporization AH, of heptane (C-H₁6) is 31.2 kJ/mol. Calculate the change in entropy AS when 736. g of heptane condenses at 98.4 °C. Be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. x10 ロ・ロ X H ■arrow_forward1. Please consider 0.15 gm of Constantan (a Cu/Ni alloy widely used in thermocouples, c = 390 J/•K-kg) that cooled through exposure to the laboratory atmosphere (T 22 •C) from 620 C to 20 C. a. Please determine the change in entropy of the Constantan (in J/ K- kg). b. Please determine the change in entropy of the laboratory atmosphere (in J/ K-kg). c. Please determine the change in entropy of the universe (in J/ K-kg). %3Darrow_forward
- Given the following reaction, calculate the standard entropy at 25oC. 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) (Sof NO2 = 240.1 J mol-1K-1; Sof NO = 210.8 J mol-1K-1; Sof O2 = 205.1 J mol-1K-1)arrow_forwardConsider the reaction HCI(g) + NH3(g)- →NH4Cl(s) Using standard thermodynamic data at 298K, calculate the entropy change for the surroundings when 2.34 moles of HCI(g) react at standard conditions. ASO surroundings = J/Karrow_forwardWhich of the following substances has the largest molar entropy? Why?arrow_forward
- given rgetable of standard molar entropy values of each substance in the reaction below, what is the standard change in entropy, delta s, for the following reaction? 2CH3OH(g)+3OH2- 2CO2(g)+4H2O(g) Substance= CH3OH(g) S(J/mol•K) 240 Substance=O2(g) S(J/mol•K) 205 Substance=CO2(g) S(J/mol•K) 214 Substance=H2O(g) S(J/mol•k) 189 a. -352 J/K b. -1302 J/K c. 315 J/K d. 89 J/K E. 1830 J/Karrow_forwardouming Calculate the standard molar entropy of vaporization of water at 43.0 °C, given that its standard molar entropy of vaporization at 100.0 °C is 109.0 J-K mol and the molar heat capacities at constant pressure for liquid water and water vapor are 75.3 J-K1.mol-1 and 33.6 J-K.mol, respectively, in this temperature range. J.K-1. mol-1 ASvap TOOLS x10 Question Source: Atkins 7e - Chemical Principles | Publisher: W.H. Fm We Thearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY