
Concept explainers
Single crystal silicon consists of three-dimensional arrays of the basic unit cell as shown. (a) How many atoms are in each unit cell? (b) What is the volume of the unit cell in cm3? (c) Show that the atomic density of silicon is 5 × 1022 atoms/cm3. (d) The density of silicon is 2.33g/cm3.What is the mass of one unit cell? (e) Based on your calculations here, what is the mass of a proton? Assume that protons and neutrons have the same mass and that electrons are much much lighter. Is your answer reasonable? Explain.
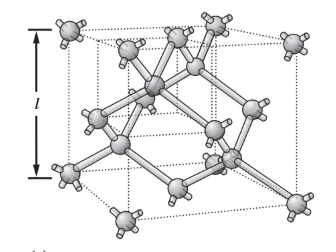
- Total number of atoms in unit cell = 8 atoms at corners at 1/8 each cell
+6 atoms in faces at ½ each in cell
+4 atoms within cell.
= (1+3+4)
= 8
So the total number of Si atoms per unit cell is 8.
The dimension of unit cell is (l) = 5.43 Å = 5.43 × 10-8 cm
- The volume of unit cell = l3
= (5.43 × 10-8 cm) 3 cm3
= 16.01 × 10-23 cm3
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- A silicon crystal having a cross-sectional area of 0.002 cm² and a length of 0.01 cm is connected across a 20-V battery. At T = 300 K, a current of 0.25 A in the semiconductor is required. Calculate the required conductivity and use that to determine the density of donor atoms to be added to achieve this conductivity. Nd= 2.31 X 1014 cm-3 Nd = 3.09 X 1014 cm -3 Nd= 2.89 X 1014 cm-3 Nd=4.63 X 10¹4 cm-3arrow_forwardThe difference between insulator and semiconductor is a. wider gap between valence and conduction band b. the number of free electrons c. the atomic structure d. all of the abovearrow_forwardQ1) a)Explain how doping a pure silicon crystal with donor impurity atoms makes more charge carriers available for conduction.b)Does the above doping result in a p-type or n-type semiconductor? Explain your answer. c) When the diode is forward biased:i) What happens to the barrier potential?ii) What happens to the depletion region?iii) Indicate on your diagram the directions in which the holes and electrons movearrow_forward
- A p-type bar of silicon below the left is subjected to electron injection from the left and hole injection from the right. Determine the total current flowing through the device if the cross- section area equals 1 μm x 1 μm.arrow_forwardHi, can you please help me with this whole question. Thank youarrow_forwardTrue/False- (TorF) 1. Silicon Crystals are formed by the bonding of impurity atoms. 2. A p-type semiconductor is formed when a Group III element is injected into a semiconductor material.arrow_forward
- Consider four of semiconductor samples: solid A is orange, solid B is black, solid C is white, and solid D is yellow. Given their colors, rank these semiconductors in order of increasing band gap. A. B < A < D < c B. B < D < A < C C. C < D < A < B D. C < A < D < Barrow_forwardFigure Q4 shows the silicon wafer. This silicon has been added with the two elements as listed in Table Q3. Identify the majority charge carrier in each extrinsic silicon wafer and justify your answer with illustrations.arrow_forwardİNGİLİZCE TÜRKÇE RUSÇA In a doped semiconductor, Please choose one: a. no free electrons b. free electrons are generated thermally C. there are only holes D. answers B. and D. to. there are as many electrons as holesarrow_forward
- question 7arrow_forwardA semiconductor is a crystalline material. Please choose one: a. have strong covalent bonds between neighboring atoms b. has many free electrons held by the attraction of positive ions c. with only one electron in its outer shell D. has a full valence shellarrow_forwardCalculate the equivalent resistances Rin of the following circuits. (The resistance value of the diodes in the conduction will be 0, the resistance value of the diodes in the insulation will be taken as infinity. R1=10ohmarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





