
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
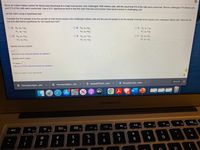
Transcribed Image Text:Since an instant replay system for tennis was introduced at a major tournament, men challenged 1426 referee calls, with the result that 415 of the calls were overturned. Women challenged 779 referee calls.
and 215 of the calls were overturned. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that men and women have equal success in challenging calls.
est the claim using a hypothesis test.
Consider the first sample to be the sample of male tennis players who challenged referee calls and the second sample to be the sample of female tennis players who challenged referee calls. What are the
null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test?
O B. Ho: P1 2 P2
O A. Ho: P1 = P2
Hy:Pq <P2
OC. Ho: P1 = P2
H4: P #P2
H: P #P2
O D. Ho: P1 SP2
H:Pq #P2
O E. Ho: P1 = P2
H: P > P2
OF. Ho: P1 # P2
H4: P1 = P2
Identify the test statistic.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Identify the P-value.
P-value =
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Click to select your answer(s).
Show All
A SamplePPTforP.pptx
a Persuasive Spe.docx
a Persuasive Spee.doc
PersuasiveSpch....doc
tv
MacBook Air
की
FIV
F10
F7
F3
esc
F2
&
2#
%
9
8
6
2
3
4
P
了
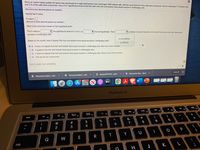
Transcribed Image Text:Since an instant replay system for tennis was introduced at a major tournament, men challenged 1426 referee calls, with the result that 415 of the calls were overturned. Women challenged 779 referee calls,
and 215 of the calls were overturned. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that men and women have equal success in challenging calls.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Identify the P-value.
P-value =
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test?
The P-value is
V the significance level of a = 0.01, so
V the null hypothesis. There
success in challenging calls.
V evidence
warrant rejection of the claim that women and men have equal
Based on the results, does it appear that men and women have equal success
challenging calls?
is not sufficient
is sufficient
O A. It does not appear that men and women have equal success in challenging calls. Men have more success.
O B. It appears that men and women have equal success in challenging calls.
O C. It does not appear that men and women have equal success in challenging calls. Women have more success.
O D. The results are inconclusive.
Click to select your answer(s).
Show All
A Persuasive Spee.doc
a PersuasiveSpch.doc
2 SamplePPTforP..pptx
a Persuasive Spe.docx
tv
MacBook Air
F9
80
888
F4
esc
F1
&
#
$
%
@
8
6
3
4
1
P
Y
Q
W
E
R
tab
K
G
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that in a random selection of 100 colored candies, 21% of them are blue. The candy company claims that the percentage of blue candies is equal to 25%. Use a 0.01 significance level to test that claim.The test statistic for this hypothesis test isarrow_forwardAs winter is here and I love planting my winter garden. I have planted my winter vegetables ( Broccoli, Artichoke, Cauliflower, ect.), on average 10 neighbors plant a garden during winter. I asked 20 neighbors of they were going to plant their winter gardens and 12 of them said yes. Test this hypothesis at .05 significance level. Assume a random sample.arrow_forwardSince an instant replay system for tennis was introduced at a major tournament, men challenged 1407 referee calls, with the result that 425 of the calls were overturned. Women challenged 771 referee calls, and 213 of the calls were overturned. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that men and women have equal success in challenging calls. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of male tennis players who challenged referee calls and the second sample to be the sample of female tennis players who challenged referee calls. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? A. Upper H 0 : p 1 equalsp 2 Upper H 1 : p 1 not equalsp 2 B. Upper H 0 : p 1 not equalsp 2 Upper H 1 : p 1 equalsp 2 C. Upper H 0 : p 1 greater than or equalsp 2 Upper H 1 : p 1 not equalsp 2 D. Upper H 0 : p 1…arrow_forward
- Since an instant replay system for tennis was introduced at a major tournament, men challenged 1413 referee calls, with the result that 414 of the calls were overturned. Women challenged 754 referee calls, and 211 of the calls were overturned. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that men and women have equal success in challenging calls. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. Consider the first sample to be the sample of male tennis players who challenged referee calls and the second sample to be the sample of female tennis players who challenged referee calls. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? А. Но: Р1 2 Р2 H4: P1 # P2 B. Ho: P1 = P2 C. Ho: P1 SP2 H1: P1> P2 H1: P1 # P2 O D. Ho: P1 = P2 H4: P1 #P2 E. Ho: P1 # P2 H1: P1 = P2 F. Ho: P1 = P2 H1: P1arrow_forwardDefine the related-repeated (pre/post) two-sample t-test and the related-matched two-sample t-test.arrow_forwardA political scientist claims that 38% of first-year college students characterize themselves as being “moderate” or “middle of the road” as far as their political affiliation is concerned. Believing this claimed value is too high, you survey a random sample of 400 first-year college students and find that 120 characterize themselves as being “moderate” or “middle of the road.” Based on this information, what will the test statistic be? Choose the answer below that is closest to what you calculate, and try not to do a lot of rounding until you get to the very end of your calculations. 1. -0.3 2. -1.2 3. -2.6 4. -3.3 5. None of the other answer options are correct because the test statistic should be positive, not negative.arrow_forwardSince an instant replay system for tennis was introduced at a major tournament, men challenged 1394 referee calls, with the result that 428 of the calls were overturned. Women challenged 755 referee calls, and 230 of the calls were overturned. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that men and women have equal success in challenging calls. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of male tennis players who challenged referee calls and the second sample to be the sample of female tennis players who challenged referee calls. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? A. Ho: P₁ P2 H₁: P₁ P2 D. Ho: P₁ = P2 H₁: P₁ P2 Identify the test statistic. Z= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) B. Ho: P₁ = P2 H₁: P₁ P2 E. Ho: P₁ P2 H₁: P₁ = P2 C. Ho: P₁ = P2 H₁: P₁ P2 OF. Ho: P₁ H₁: P₁ P2 P2arrow_forwardcurryarrow_forwardSince an instant replay system for tennis was introduced at a major tournament, men challenged 1432 referee calls, with the result that 421 of the calls were overturned. Women challenged 742 referee calls, and 214 of the calls were overturned. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that men and women have equal success in challenging calls. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of male tennis players who challenged referee calls and the second sample to be the sample of female tennis players who challenged referee calls. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? OA. Ho: P₁ P₂ H₁: P₁ P2 O D. Ho: P1 P2 H₁: P₁ P₂ Identify the test statistic. Z= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. P-value= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test? The P-value is b. Test the claim by constructing an…arrow_forwardSince an instant replay system for tennis was introduced at a major tournament, men challenged 1410 referee calls, with the result that 424 of the calls were overturned. Women challenged 764 referee calls, and 223 of the calls were overturned. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that men and women have equal success in challenging calls. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of male tennis players who challenged referee calls and the second sample to be the sample of female tennis players who challenged referee calls. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? Identify the test statistic? Identify the P-value? What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test? Is there enough evidence? b. Test the claim by constructing an appropriate confidence interval. The 99% confidence interval is ? <p1−p2< ?. What is the conclusion based on the…arrow_forwardSince an instant replay system for tennis was introduced at a major tournament, men challenged 1400 referee calls, with the result that 413 of the calls were overturned. Women challenged 772 referee calls, and 213 of the calls were overturned. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that men and women have equal success in challenging calls. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of male tennis players who challenged referee calls and the second sample to be the sample of female tennis players who challenged referee calls. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? OA. Ho: P₁ P2 H₁: P₁ P2 D. Ho: P₁ = P2 H₁: P₁ P2 B. Ho: P₁ P2 H₁: P₁ = P₂ O E. Ho: P1 H₁: P₁ ... P2 P2 OC. Ho: P₁ H₁: P₁ F. Ho: P₁ H₁: P₁ P2 P2 P2 P2arrow_forwardThe dataset "nurses" is a random sample of 1,000 cases from “Health Care Provider Credential Data” from Washington State Open Data Portal. In the sample, there are 418 CNA's and 278 of the CNA's have expired credentials. Use the statistics from the nurses dataset to answer the following question: "With 90% confidence, what percent of all CNA's on Washington State's healthcare provider list are expired?"arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman