
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%

Transcribed Image Text:Simulation of Vapour Pressure
1. Record the temperature and then the vapour pressure for each substance. Temperature =
°C
2. Indicate the type(s) of intermolecular force acting between the molecules for each substance.
methanol CH3OH
ethanol CH3CH2OH
propan-1-ol CHзCH:CH2ОH
Vapour pressure:
Vapour pressure:
Vapour pressure:
O Dispersion
Dispersion
O Dispersion
Dipole/dipole
Dipole/dipole
Dipole/dipole
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding
Substance with highest normal boiling point:
Briefly discuss the trend in vapour pressure for these substances in terms of intermolecular forces:
CI
OH
2-chloropropanc H,C-C- CH3
| propan-2-ol H,c-с-сн,
H;C-C- CH3
propanone
H.
H
Vapour pressure:
Vapour pressure:
Vapour pressure:
Dispersion
Dipole/dipole
Dispersion
Dispersion
Dipole/dipole
Dipole/dipole
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding
Substance with highest normal boiling point:
Briefly discuss the trend in vapour pressure for these substances in terms of intermolecular forces:
pentane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
hexane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 heptane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
Vapour pressure:
Vapour pressure:
Vapour pressure:
Dispersion
Dispersion
Dispersion
Dipole/dipole
Dipole/dipole
O Dipole/dipole
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding
Substance with highest normal boiling point:
Briefly discuss the trend in vapour pressure for these substances in terms of intermolecular forces:
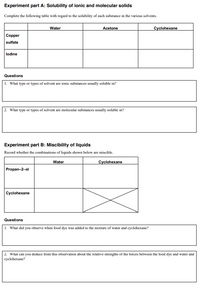
Transcribed Image Text:Experiment part A: Solubility of ionic and molecular solids
Complete the following table with regard to the solubility of cach substance in the various solvents.
Water
Acetone
Cyclohexane
Copper
sulfate
lodine
Questions
1. What type or types of solvent are ionic substances usually soluble in?
2. What type or types of solvent are molecular substances usually soluble in?
Experiment part B: Miscibility of liquids
Record whether the combinations of liquids shown below are miscible.
Water
Cyclohexane
Propan-2-ol
Cyclohexane
Questions
1. What did you observe when food dye was added to the mixture of water and cyclohexane?
2. What can you deduce from this obscrvation about the relative strengths of the forces between the food dye and water and
cyclohexane?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The change in enthalpy, AH, for dissolving toluene (C,H,) in water is approximately zero. Do you predict toluene will dissolve in water? Why or why not? O Toluene will dissolve in water because LDFs and dipole-induced dipole interactions will form between them. O Toluene will dissolve in water because there are more arrangements for the toluene molecules when mixed with water. O Toluene will not dissolve in water because toluene is non-polar and water is polar. Toluene will not dissolve in water because there would be fewer arrangements for the water molecules if it were to dissolve. O O Toluene will not dissolve in water because there are no attractive forces that exist between toluene and water.arrow_forwardThe vapour pressure of a pure substance at various temperatures is presented below. T (°C) Pvap (mmHg) 0.0 10.5 15.0 18.6 25.0 26.4 40.0 42.8 60.0 76.2 80.0 127.0 a) Calculate H°vap for this substance. b)What is the substance's normal boiling point?arrow_forwardAt high altitudes, the ambient air pressure can be significantly less than 1 bar, so water boils at a lower temperature than 100 C. What is the boiling point of water at an altitude where the ambient air pressure is 0.4 bar? The enthalpy of vaporization of water near its boiling point is 40.7 kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- kJ and its normal boiling point is 41. °C. Calculate the vapor pressure of X at -22. °C. The enthalpy of vaporization of Substance X is 20.0 mol Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atm Submit Assignr O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessi solubility chem h...pdf 24 CH.9 PP ASSES MacBook Air D00 F7 F8 F9 F10arrow_forwardNeed solution urgentlyarrow_forward24 Feb 2021 2odium chloride (NaCI) is completely saluble in water. What is responsible for its solubility in water? A. Na+ and Clions are favorable sites for H-bonding to torm. В. The presence of charged ends in NaCl enables dipole-dipole interaction with water. e lons in Načl participate in on-induced dipole attractions with water. C. D. London dispersion forces in NaCl predominate leading to strong dipole interactions with water. 5. Kenon (Xe) has a greater atomic weight than Neon (Ne). Xe has 131.3 amu while Ne has 20.2 amu, The melting points are 166.1K and 27.3K, respectively. How do intermolecular forces account for the difference? A. Dipole- dipole interaction is greater in Xe than Ne so more energy is needed to break the bonds. B. H-bonding is greater for substances with higher atomic weight so greater energy is needed to change Xe to vapor. C. Atomic weight increases the chance of lesser dispersion forces so greater energy is needed to separate Xe atoms to change to vapor. D.…arrow_forward
- Glaciers are not stationary bodies of ice, but instead slowly move over time (mean speed of 1 meter/day). One reason for this is because these very large glaciers melt from the bottom, and the liquid water beneath the glacier acts as a lubricant for the glacier to move. Using the phase diagram for water (below) and concepts discussed in class, what is one potential reason that glaciers melt from the bottom at temperatures below 0°C?arrow_forwardIntermolecular Forces and Physical Properties of Pure Substances Which has the greatest vapour pressure at 25°C? SO2 H2O CO2 O3 Which has the greatest viscosity? CH3CH2OH CH3(CH2)4CH3 HOCH2CH2OH HOCH2CHOHCH2OH Which has the least heat of vaporization? H2Te Xe H2Se H2S Which has the highest enthalpy of fusion? Li2O HCl H2O MgO Which has the smallest heat of vaporization? PH3 CH4 H2O H2Sarrow_forwardAt high altitudes, the ambient air pressure can be significantly less than 1 bar, so water boils at a lower temperature than 100 C. What is the boiling point of water at an altitude where the ambient air pressure is 0.72 bar? The enthalpy of vaporization of water near its boiling point is 40.7 kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- At a given temperature, which of the following has the highest vapour pressure? Select one: CH2O CH3COOH CH3CN CH3Cl C2H6arrow_forward29.Which of the liquids in the following pair has the lower vapour pressure? Propanol (CH3CH2CH2OH) / Methanol (CH3OH)arrow_forwardThe figure shows the phase diagram corresponding to the element sulfur. Sulfur exists as liquid, gas, and two solids, rhombic and monoclinic. 1- Describe the phase changes that occur when S is decompressed (lower P) from 10 atm to 106atm at constant temperature of 100 °C. 2- Indicate the temperature and the pressure for the triple point B, and which phases coexist В 10.0 Solid(rhombic) Liquid 1.0 Solid (monoclinic) 5х 104 Gas A 1 x 104 95.4 114 119 445 Temperature (in degree C) Pressure (in atm)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY