
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
QN.3
Transcribed Image Text:po Tutorial3_212.pdf
Not syncing
O File | C:/Users/alvin/Downloads/Tutorial3_212.pdf
A Read aloud
V Draw
F Highlight
Erase
(D Page view
1
of 2
Q
Q1. “A Gaussian surface has zero net flux," a tutor at a review session says. "Therefore, there are no
charges inside the surface." Do you agree? Disagree? Explain.
Q2. A pyramid-shaped Gaussian surface is drawn over the top half of a uniformly charged sphere (of
charge Q) What's the net flux g through the pyramid?
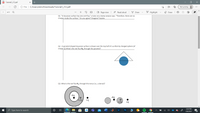
Q3. What is the net flux Og through this torus (i.e., a donut)?
-49
-49
+2q,
+9
+2g
+q
2:26 PM
Lr
Ps
2/8/2021
19
e Type here to search
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which scientist discovered that a compass can be deflected by a current-carrying wire? a. Hans Oersted b. Albert Einstein c. Galileo Galilei d. Sir Isaac Newton e. Michael Faradayarrow_forwardneed the correct and unique solves with explanation.choose the correct answers onlyarrow_forwardUse the equation E=Fq E= Gravitational constant q= mass of the protonarrow_forward
- Consider a long, horizontal Large Wire with current of 10 A running through it. We want to levitate a horizontal, thin, 0.50 m length of wire above it. If the thin wire has a mass of 10 grams, and a current of 300 mA, how far above the Large Wire will it hover (net force of zero) due to magnetic and gravitational forces? A. If the thin wire hovers above the Large Wire due to their magnetic fields, are their currents going the same direction, or opposite directions. Explain. B. Draw a diagram and label the directions of currents, and all other relevant quantities and vectors. C. Find the distance above the Large Wire the small thin wire will hover (net force of zero). D. Would your answers to parts A and C change if we wanted to find a distance below (rather than above) the Large Wire that the smaller thin wire could hover, due to their magnetic fields. Explain. Don't calculate any values but draw a new diagram and explain how this situation compares to the problem above.arrow_forwardme: 3. a. Draw Electric and Magnetic Field lines: Please differentiate between them. b. What would the separation between these objects, one carrying 1 C of positive charge and the other 1 C of negative charge, have to be if the electrical force on each was precisely 1 N? used in Hydrogen. ar the absorbed I I oton? Bus vrs. (6 rints) WLLS? I What is the esiste une light bulbs in ohms? D. What is ne pow consumed by the light bulb i c. If tw identic slide projectors are connected in par Vit Jurce nat is the total current draw c + project draw current 5/04/2023 peres when operating on uss th state Souce? same 1arrow_forwardThe velocity selector in the problem prior to this one is used in a mass spectrometer. Protons(with zero neutrons) are the most common hydrogen nuclei. Some hydrogen isotopes, however, haveeither one or two neutrons in addition to the proton. If a beam of hydrogen nuclei is shot into amagnetic field of strength 2.0T and the nuclei do a u-turn after which they strike a detector, how farapart will the three isotopes be on the detector surface? Assume both protons and neutrons have amass of 1.67 × 10−27kg and e = 1.60 × 10−19C.arrow_forward
- Figure 22.57 56. Find the direction and magnitude of the force that each wire experiences in Figure 22.58(a) by, using vector addition.arrow_forwardFour point charges with charge +q=6.7µC are arranged in a square of side length L = 5.0 cm in the x/y plane. A fifth point charge -q=-6.7µC is placed in the center of the square but displaced a distance d=3.6 cm in the z direction. What is the net force on the negative point charge?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON