Question
thumb_up100%
shows electrons 1 and 2 on an x axis and charged ions 3 and 4 of identical charge −q and at identical angles θ. Electron 2 is free to move; the other three particles are fixed in place at horizontal distances R form electron 2 and are intended to hold electrons 2 in place. For Physically possible values of q≤9e, what are the third smallest value of θ for which electron 2 is held in place?
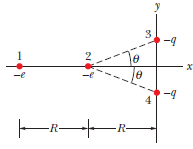
Transcribed Image Text:3
-4
1
2
le
-e
-4
4
b-
-R-
-R-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Problem 2: A certain lightning bolt moves Q = 35 C of charge. How many fundamental units of charge e is this? N = I sin() cos() cotan() asin() atan() acotan() cosh() tanh() O Degrees O Radians tan() π 7 acos() E ^^^ 4 sinh() 1 cotanh() * 8 9 5 6 2 3 + 0 VO BACKSPACE DEL HOME END CLEARarrow_forwardHow much work is required to set up the four-charge configuration of the figure if q = 3.59 pC, a = 74.0 cm, and the particles are initially infinitely far apart and at rest? +1 -9 +qarrow_forwardA circular plastic disk with radius R = 2.00 cm has a uniformly distributed charge Q = +(2.00 x 106)e on one face. A circular ring of width 30 µm is centered on that face, with the center of that width at radius r = 0.50 cm. In coulombs, what charge is contained within the width of the ring?arrow_forward
- A point charge, q = -5.0 nC, and m = 2.0 x 10-18 kg, is shot vertically upward with an initial speed of 3.0 x 105 m/s from a thin, infinite, planar sheet of uniform charge with surface charge density of σ = +4.0 nC/m^2 . To what vertical elevation will q rise above the sheet of charge? Neglect gravityarrow_forwardA long thin rod is bent into a perfect semicircle of radius 4.30 m. The linear change density of the rod is λ = 3.10 nC/m. How much charge is on a small piece of the rod that subtends an angle Δθ = 0.170 radians? 13.3 nC 0.527 nC 2.27 nC 4.24 nCarrow_forwardIn the figure particle 1 of charge +q and particle 2 of charge +9q are held at separation L = 10.1 cm on an x axis. If particle 3 of charge q3 is to be located such that the three particles remain in place when released, what must be the (a) x and (b) y coordinates of particle 3 and (c) the ratio q3/q? X (a) Number i 1.35 Units cm (b) Number 0 Units cm (c) Number i 1.00 Units No unitsarrow_forward
- A red blood cell typically carries an excess charge of about −2.5× 10-12 C distributed uniformly over its surface. The cells, modeled as spheres, are approximately 7.5 μm in diameter and have a mass of 9.0× 10-14 kg. (a) How many excess electrons does a typical red blood cell carry? (b) What is the surface charge density σ on the red blood cell? Express your answer in C/m2 and in electrons/m2. σ = C/m2 = electrons/m2arrow_forward+6q -29 E = -3q +3q -99 +2q -2q +2q ●+6q The figure above shows two square arrays of charged particles. The squares with edges of 2d and d are centered at point P and are misaligned. The particles are separated by either d or d/2 along the perimeters of the squares. -2q -3q +3q NOTE: Express your answer to part (a) in terms of the given variables and €0. (a) What is the magnitude of the net electric field at P? (Note: The symbol used in the subscript of eo is a zero, not an "O".) (b) What is the direction of the net electric field at P? leftwardarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios