
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
show the leverage, studentized residual, and influence for each of the five observations in a small dataset.
Table Data.
| ID | X | Y | h | R | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 2 | 0.39 | -1.02 | 0.40 |
| B | 2 | 3 | 0.27 | -0.56 | 0.06 |
| C | 3 | 5 | 0.21 | 0.89 | 0.11 |
| D | 4 | 6 | 0.20 | 1.22 | 0.19 |
| E | 8 | 7 | 0.73 | -1.68 | 8.86 |
| h is the leverage, R is the studentized residual, and D is Cook's measure of influence. |
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
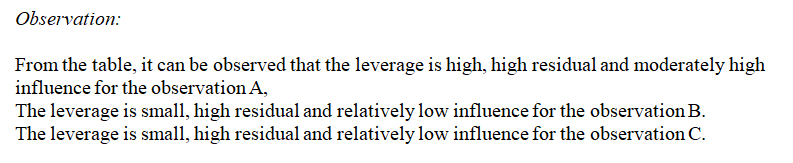
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Perform rank correlation analysis on the following data set: x y -5 1.9 -4 0.9 -3.25 0.7 -2.55 -0.5 -1.85 -1.2 -0.9 -1.7 5.5511151231258E-17 0.7 0.8 1.5 1.55 1.6 2.35 -0.1 3.3 0.8 4.1 -1.1 5.1 -0.9 5.8 -0.8 6.7 0.7 What is the rank correlation coefficient? (Round to three decimal places.) What is the critical rho value at a 0.01 significance? Do we have correlation? Yes, the rank correlation coefficient is smaller (in absolute value) than the critical rho value. No, the rank correlation coefficient is larger (in absolute value) than the critical rho value. No, the rank correlation coefficient is smaller (in absolute value) than the critical rho value. Yes, the rank correlation coefficient is larger (in absolute value) than the critical rho value.arrow_forwardUse the given data to find the equation of the regression line. Examine the scatterplot and identify a characteristic of the data that is ignored by the regression line. 11 8 11 13 6 13 6 y 7.24 6.87 12.78 6.87 7.75 8.85 6.28 5.61 8.28 6.72 5.52 Create a scatterplot of the data. Choose the correct graph below. VA. OB. OC. OD. 25- Ay 25- 25- 25- 20- 20 20- 20 15 155 155 155 10- 10- 10 10- 5- 5- 5 55 0- 05 10 15 20 25 0- O 5 10 15 20 25 04 05 10 15 20 25 0- 05 10 15 20 25 Find the equation of the regression line. (Round the constant two decimal places as needed. Round the coefficient to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardRun a regression analysis on the following bivariate set of data with y as the response variable. x y -9.7 -66.2 5.6 28.3 -4.5 11.9 35.6 94.9 15.7 21.1 30.8 86.3 48.7 127.9 13 57.3 35.3 109 23.6 32.4 58 166.3 28.1 64.4 19.1 51.5 25.6 53.3 46.1 186.4 43.5 128 Predict what value (on average) for the response variable will be obtained from a value of 14.8 as the explanatory variable. Use a significance level of α=0.05 to assess the strength of the linear correlation.What is the predicted response value? y =arrow_forward
- Run a regression analysis on the following bivariate set of data with y as the response variable. x y 61.1 78.9 58.6 84.5 70.2 58.1 62.3 65.4 64.2 68.9 58 84.1 63.7 70.2 64.6 71.9 68.3 71.5 61.7 77.5 59.3 77.4 64.6 71.2 Find the correlation coefficient and report it accurate to three decimal places.r = What proportion of the variation in y can be explained by the variation in the values of x? Report answer as a percentage accurate to one decimal place. (If the answer is 0.84471, then it would be 84.5%...you would enter 84.5 without the percent symbol.)r² = %Based on the data, calculate the regression line (each value to three decimal places)y = x + Predict what value (on average) for the response variable will be obtained from a value of 61.9 as the explanatory variable. Use a significance level of α=0.05α=0.05 to assess the strength of the linear correlation.What is the predicted response value? (Report answer accurate to one decimal place.)arrow_forwardRun a regression analysis on the following bivariate set of data with y as the response variable. x y 85.1 61.8 40.6 -11.4 36.9 -15.1 72.5 47.9 62 41.8 74.2 19.4 91.3 55.4 57.7 -2.1 84.5 52.1 94.2 55.2 87.8 83.3 51.3 7.1 58.4 -4.9 72.3 16.7 72.6 35.4 71.3 19.2 64.4 16.7 Verify that the correlation is significant at an α=0.05α=0.05. If the correlation is indeed significant, predict what value (on average) for the explanatory variable will give you a value of 72.4 on the response variable.What is the predicted explanatory value?x =arrow_forwardGraph the scatterplot and find the equation of the regression line GDP. CO2 emissions (in millions metric tons) 1.7. 552.6 1.2. 462.3 2.5. 475.4 2.8. 374.3 3.6. 748.5 2.2. 400.9 0.8. 253.0 1.5. 318.6 2.4. 496.8 5.9. 1180.6arrow_forward
- Run a regression analysis on the following data set with y as the response variable. y 114 67.1 40.3 87.2 89 91.4 26.5 92.3 9.8 94.9 22.2 88.3 -0.5 What is the predicted value of the response variable when x = 82.5? y= || Round to 1 decimal place. xinarrow_forwardHere is data with y as the response variable. a. Make a scatter plot of this data. Which point is an outlier? Enter as an ordered pair, e.g., (x,y). (x, y) b. Find the regression equation for the data set without the outlier. Enter the equation of the form mx + b rounded three decimal places. y wo X 48.4 77.3 88 67.1 108.3 75.9 64.8 -161.3 61.2 67.9 ŷw y 45.7 40.3 27.3 54.5 -63.2 36.3 73.2 96.5 82.2 119.8 = -- c. Find the regression equation for the data set with the outlier. Enter the equation of the form mx + b rounded to three decimal places.arrow_forwardRun a regression analysis on the following bivariate set of data with y as the response variable. y 56.3 -257.6 14.5 670.8 49.4 431 60.7 200.3 60.1 70.3 52.6 -162.4 46.2 -406.9 45.1 -3.6 39.6 292.4 51.2 274.8 53.1 -77.4 50 496.6 46.9 251.5 48.5 -188.7 79.8 233 33.5 -415.6 49.2 431.3 download link provided here: Download CSV Predict what value (on average) for the response variable will be obtained from a value of 32.1 as the explanatory variable. Use a significance level of a = 0.05 to assess the strength of the linear correlation. What is the predicted response value? y = 169.94127 (Report answer accurate to one decimal place.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman