
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Uncertain if what I have so far is correct and unsure how to solve the rest properly
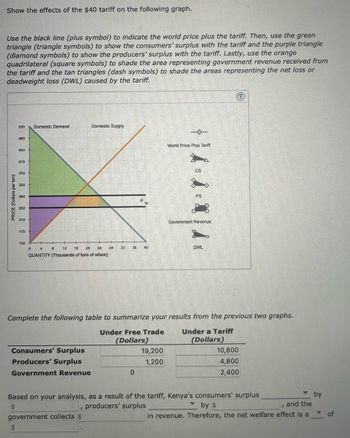
Transcribed Image Text:Show the effects of the $40 tariff on the following graph.
Use the black line (plus symbol) to indicate the world price plus the tariff. Then, use the green
triangle (triangle symbols) to show the consumers' surplus with the tariff and the purple triangle
(diamond symbols) to show the producers' surplus with the tariff. Lastly, use the orange
quadrilateral (square symbols) to shade the area representing government revenue received from
the tariff and the tan triangles (dash symbols) to shade the areas representing the net loss or
deadweight loss (DWL) caused by the tariff.
PRICE (Dollars per ton)
530
490
450
410
$
370
330
290
250
210
170
130
Domestic Demand
0
4
8 12 16 20 24
QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of wheat)
Consumers' Surplus
Producers' Surplus
Government Revenue
Domestic Supply
I
government collects $
28
32
36
P
0
W
40
+-
19,200
1,200
World Price Plus Tariff
CS
Complete the following table to summarize your results from the previous two graphs.
Under Free Trade
(Dollars)
PS
Goverment Revenue
DWL
?
Under a Tariff
(Dollars)
Based on your analysis, as a result of the tariff, Kenya's consumers' surplus
$
producers' surplus
by $
and the
t
in revenue. Therefore, the net welfare effect is a
10,800
4,800
2,400
by
of
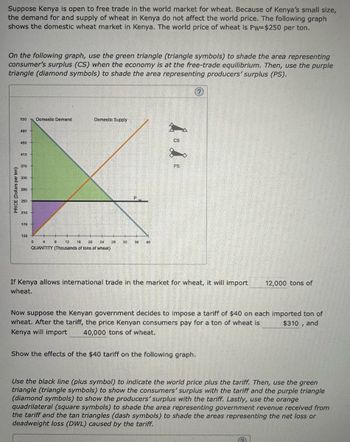
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose Kenya is open to free trade in the world market for wheat. Because of Kenya's small size,
the demand for and supply of wheat in Kenya do not affect the world price. The following graph
shows the domestic wheat market in Kenya. The world price of wheat is Pw=$250 per ton.
On the following graph, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing
consumer's surplus (CS) when the economy is at the free-trade equilibrium. Then, use the purple
triangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing producers' surplus (PS).
PRICE (Dollars per ton)
530 Domestic Demand
490
450
410
370
330
290
250
210
170
130
0
Domestic Supply
4
8 12 16 20 24
QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of wheat)
P
28 32 36 40
CS
PS
Ⓡ
If Kenya allows international trade in the market for wheat, it will import
wheat.
Now suppose the Kenyan government decides to impose a tariff of $40 on each imported ton of
wheat. After the tariff, the price Kenyan consumers pay for a ton of wheat is
Kenya will import 40,000 tons of wheat.
$310, and
Show the effects of the $40 tariff on the following graph.
12,000 tons of
Use the black line (plus symbol) to indicate the world price plus the tariff. Then, use the green
triangle (triangle symbols) to show the consumers' surplus with the tariff and the purple triangle
(diamond symbols) to show the producers' surplus with the tariff. Lastly, use the orange
quadrilateral (square symbols) to shade the area representing government revenue received from
the tariff and the tan triangles (dash symbols) to shade the areas representing the net loss or
deadweight loss (DWL) caused by the tariff.
(2)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education