
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
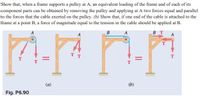
Transcribed Image Text:Show that, when a frame supports a pulley at A, an equivalent loading of the frame and of each of its
component parts can be obtained by removing the pulley and applying at A two forces equal and parallel
to the forces that the cable exerted on the pulley. (b) Show that, if one end of the cable is attached to the
frame at a point B, a force of magnitude equal to the tension in the cable should be applied at B.
A
B
A
в т
A
A
T
T T
T
T
т
(a)
(b)
Flg. P6.90
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 1 The 80 lb boy stands on the beam and pulls on the rope with a force of 40 lb. ()D=0.4 and ()D = 0.35 between his shoes and the beam. The beam has a weight of 0.641 lb/in all along it's length. Neglect the thickness of the beam. Also neglect the size of the pulleys (i.e. assume the rope acts at points F & G). a) Is the boy stationary or slipping? b) Determine the beam support reactions at 4 and B. E₂ T 13 12 5 ft E D 1 ft 3 ft -4 ft Barrow_forwardKnowing that the rod ABC and the cable BD are both made of steel, determine (a) the deflection at B, (b) the reaction at A. Use E=200 GParrow_forwardThe length of the bar AP is 650 mm. The radius of the pulley is 120 mm. Equal forces T=50 N are applied to the ends of the cable. What is the sum of the moments of the forces? About A About Parrow_forward
- Determine the Reactions of the beam. Show the Distributed Load Resultant magnitude and location on the loading diagram.arrow_forwardUsing the method of joints only, determine the force in each member of the truss shown, and state whether the members are in tension or compression. Note: cable tension at D applies a load on the joint D, and support at E is a pin. You need to find support reactions first by drawing the FBD of the entire truss, and then finding support reactions at the pin at E, and cable tension along the cable at D, using equations of rigid body equilibrium. 20 kN 5 m D B 5 m 5 m 5 m 5 m А 5 m C 5 m E 20 kN 20 kNarrow_forward4.95 A 250 x 400-mm plate of mass 12 kg and a 300-mm-diameter pulley are welded to axle AC that is supported by bearings at A and B. For B = 30°, determine (a) the tension in the cable, (b) the reactions at A and B. Assume that the bearing at B does not exert any axial thrust.arrow_forward
- For the given girders of the frame shown which carries a uniform load of 14.6 kN/m along span GH and HI and a unifoem load of 33.8 kN/m along soan DE and EF Dimensions are given as follows: A=3.7m B=5.9m C=7.5m Using the approximation frames under vertical loads. Compute the value of the absolute moment at reaction B. (kN-m) Answer: 46.7 Need solutionarrow_forwardA horizontal rigid bar ABC is pinned at end A and supported by two cables at points B and C. A vertical load P = 10 kN acts at the end of the bar. The two cables are made of steel with a modulus elasticity E = 200 GPa and have the same cross-sectional area. Calculate the minimum cross sectional area of each cable if the yield stress of the cable is 400 MPa and the factor of safety is 2.0. Consider load P only; ignore the weight of bar ABC and the cables.arrow_forwardIf the tension in the gantry-crane hoisting cable is T= 24 kN, determine the unit vector n in the direction of T and use n to determine the scalar components of T. Point B is located at the center of the container top. Assume a = 18 m, b = 9 m, c = 4 m, d = 10 m, e = 12 m, f = 7 m, and h = 25 m. B d Answers: The unit vector n: n = i+ i j+ i karrow_forward
- Find the internal forces in all the cables. The applied loads are P1 = 6 kN and P2= 7 kN. E A 2 m D 3 m В 8 kN P1 4 m 5 m 4 m 1.5 marrow_forwardThe cargo box as shown weighs W = 1200 lb. The force P = 800 lb is just sufficient to lift the box off the floor. The 2-D concurrent force system of the joint O is shown as well. Using the equilibrium equations: ∑ ???= 0 ; ∑ ???= 0, 1) Determine the tension force in the cable T;2) Determine the corresponding value of βarrow_forward2/93 SS If the tension in the gantry-crane hoisting cable is T = 14 kN, determine the unit vector n in the direction of T and use n to determine the scalar components of T. Point B is located at the center of the container top. z A 3 m 0 20 m 5m T B 16 m PROBLEM 2/93 12 m m 13 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning