
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Shot put is a track and field event in which a heavy spherical ball (the "shot") is thrown (or "put",
using the sport's terminology) as far as possible. A "shot" with mass of 6.6 kg is "put" into the air. Its
initial speed is 9.6 m/s, directed at an angle 54 degrees above the horizontal. After 0.16 seconds,
what is the horizontal component of the ball's velocity (in m/s)?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
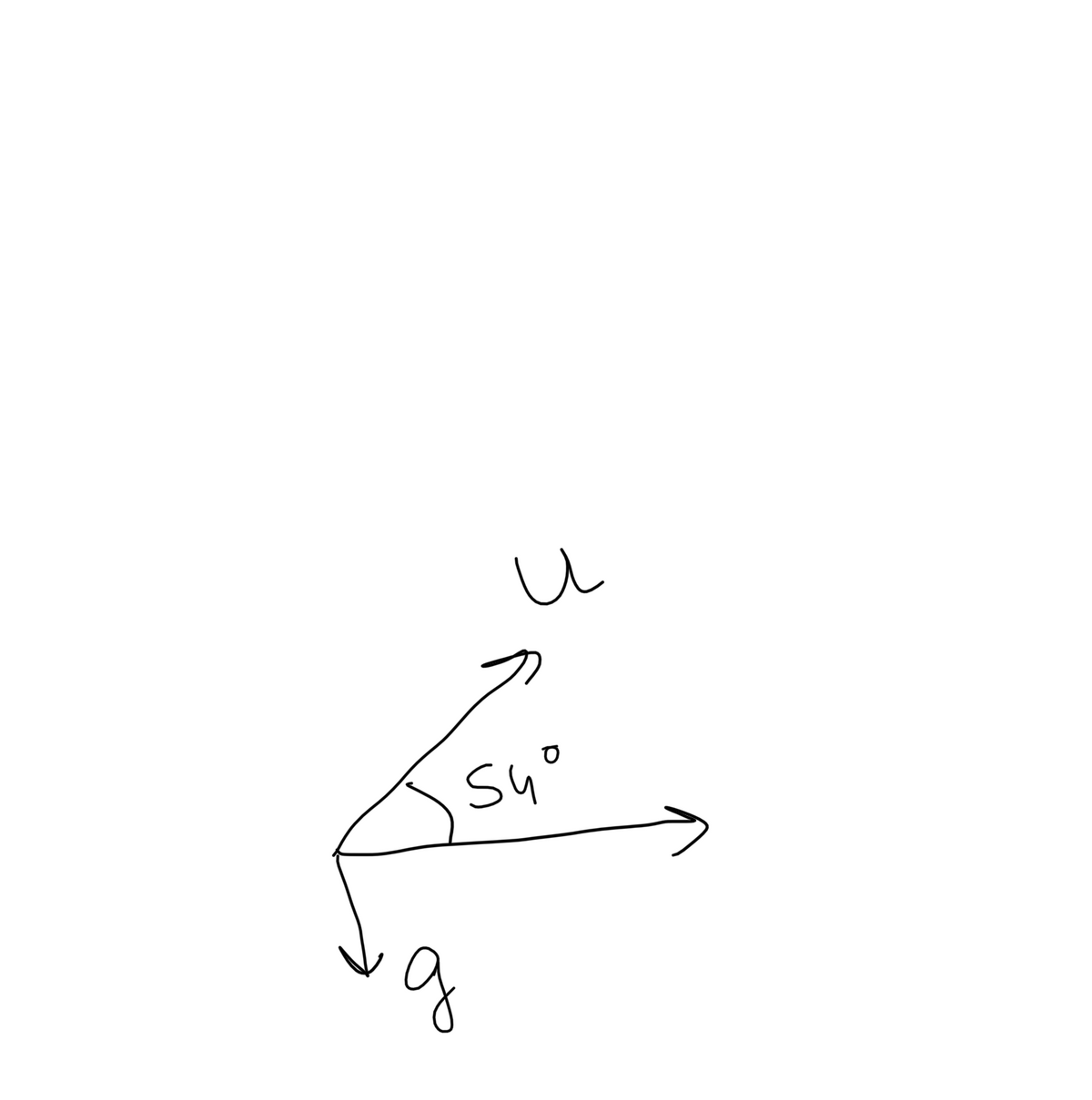
The component of initial velocity in x direction is u cos54o.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A rocket, which is in deep space and initially at rest relative to an inertial reference frame, has a mass of 86.2 × 105 kg, of which 14.7 × 105 kg is fuel. The rocket engine is then fired for 180 s, during which fuel is consumed at the rate of 480 kg/s. The speed of the exhaust products relative to the rocket is 2.98 km/s. (a) What is the rocket's thrust? After the 180 s firing, what are (b) the mass and (c) the speed of the rocket?arrow_forwardA rocket, which is in deep space and initially at rest relative to an inertial reference frame, has a mass of 75.8 x 105 kg, of which 15.3 × 105 kg is fuel. The rocket engine is then fired for 410 s, during which fuel is consumed at the rate of 390 kg/s. The speed of the exhaust products relative to the rocket is 2.81 km/s. (a) What is the rocket's thrust? After the 410 s firing, what are (b) the mass and (c) the speed of the rocket? (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA baseball of mass m1 = 0.27 kg is thrown at another ball hanging from the ceiling by a length of string L = 1.05 m. The second ball m2 = 0.77 kg is initially at rest while the baseball has an initial horizontal velocity of V1 = 3.5 m/s. After the collision the first baseball falls straight down (no horizontal velocity). (a) Select an expression for the magnitude of the closest distance from the ceiling the second ball will reach d. (b) What is the angle that the string makes with the vertical at the highest point of travel in degrees?arrow_forward
- A projectile (mass = 0.151 kg) is fired at and embeds itself in a target (mass = 2.58 kg). (The target is initially stationary). The target (with the projectile in it) flies off after being struck. What percentage of the projectile's incident kinetic energy does the target (with the projectile in it) carry off after being struck?arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a fisherman in a boat on a lake. The fisherman's mass is 77 kg, and the boat's is 132 kg. The fisherman and boat are initially at rest when the fisherman throws a package of mass m = 15 kg horizontally to the right with a speed of v; = 4.6 m/s. What is the velocity of the boat after the package is thrown? Neglect any resistance force from the water. (Give the magnitude in m/s, and select the correct direction from the options given.) magnitude direction ---Select--- m/s m V;arrow_forwardIdentical twins, each with mass 52.5 kg, are on ice skates and at rest on a frozen lake, which may be taken as frictionless. Twin A is carrying a backpack of mass 12.0 kg. She throws it horizontally at 2.55 m/s to Twin B. Neglecting any gravity effects, what are the subsequent speeds of Twin A and Twin B?arrow_forward
- A rocket ship is travelling through space. The fuselage section has a mass of 505 kg. The Nose Cone (front end) section has a mass of 100 kg. The rocket is travelling at 52.0 m/s when the rocket engine stops and the two sections are separated by an explosion in such a way that they stay in a straight line. If the Nose Cone section (front end) continues forward at 98.0 m/s, determine the speed of the Fuselage section after the separation.arrow_forwardA 2.06-kg particle has a velocity (1.92 î − 2.98 ĵ) m/s, and a 2.90-kg particle has a velocity (1.06 î + 5.93 ĵ) m/s. (a) Find the velocity of the center of mass. (b) Find the total momentum of the system.arrow_forwardA wagon is rolling forward on level ground. Friction is negligible. The person sitting in the wagon is holding a rock. The total mass of the wagon, rider, and rock is 99.5 kg. The mass of the rock is 0.277 kg. Initially the wagon is rolling forward at a speed of 0.488 m/s. Then the person throws the rock with a speed of 16.6 m/s. Both speeds are relative to the ground. Find the speed of the wagon after the rock is thrown (a) directly forward in one case and (b) directly backward in another. (a) vi (b) v-arrow_forward
- A rocket, which is in deep space and initially at rest relative to an inertial reference frame, has a mass of 72.9 x 105 kg, of which 14.7 x 10° kg is fuel. The rocket engine is then fired for 300 s, during which fuel is consumed at the rate of 360 kg/s. The speed of the exhaust products relative to the rocket is 3.82 km/s. (a) What is the rocket's thrust? After the 300 s firing, what are (b) the mass and (c) the speed of the rocket? (a) Number i Units (b) Number Units (c) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA rocket, which is in deep space and initially at rest relative to an inertial reference frame, has a mass of 78.4 × 105 kg, of which 8.68 × 105 kg is fuel. The rocket engine is then fired for 340 s, during which fuel is consumed at the rate of 340 kg/s. The speed of the exhaust products relative to the rocket is 3.78 km/s. (a) What is the rocket's thrust? After the 340 s firing, what are (b) the mass and (c) the speed of the rocket? (a) Number 1290000 Units N (b) Number 7720000 Units kg (c) Number 3830 Units m/sarrow_forwardThe mass of a particular skateboard plus its rider is m, = 76.6 kg, and the skateboarder is holding a book with mass mo = 3.27 kg. Initially atrest, the skateboarder tosses the textbook with a velocity of vb = 4.44 m/s at an angle 0 = 23.3° above the horizontal, and the book is caught by a friend.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON