
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
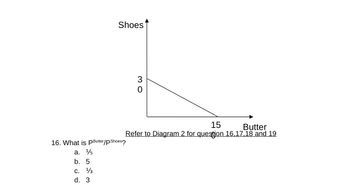
Transcribed Image Text:Shoes
16. What is PButter/pShoes?
a. ¹5
b. 5
C. ¹3
d. 3
30
15
Butter
Refer to Diagram 2 for question 16,17,18 and 19
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Table: Bongos and Frisbees Mkkey Frisbees Bll Bongos Frisbees Bongos 1 10 4 14 6. 12 3. 10 Reference: Ref 2-21 Table: Bongos and Frisbees (Table: Bongos and Frisbees) Use Table: Bongos and Frisbees. Bill and Mickey make bongos and Frisbees. Who should specialize in the production of bongos?arrow_forwardHelp!arrow_forward. TOTAL AND MARGINAL UTILITY E UTILITY CALCULATIONS Reset Total Utility Quantity Consumed Total Marginal Utility 70 Utility 60 50 22 40 1 22 30 18 20 2 40 10 14 3 4 6 8 3 54 Quantity Consumed Marginal Utility 10 20 4 64 6. 10 70 4 6. -10 72 -20 -2 Quantity Consumed 70 Quantity Consumed -6 8 64 2. 4 6 8arrow_forward
- 4: What are five fundamental questions (and answers) in economics? Five fundamental questions How do market system answer the question? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chapter 3 starts here. Define "demand" and State the law of demand. Demand is a (s (w_ specified period of (t d ) or a curve which shows the various amounts of a product buyers are ) to purchase at each price in a series of possible prices during a ) and (a ). Demand portrays relationship between ), they are (positively, negatively) related either in the table or in the ( graph ). The law of demand states that, other things being equal, as price increases, the corresponding quantity demanded (rises, falls). Restated, there is a (an) ( direct, inverse ) relationship between price and ) and ( q. quantity demanded with everything else held constant.arrow_forward7 Option (d) onlyarrow_forwardI cant seem to remeber the formula to use to fill out S2 and D2arrow_forward
- a. b. Quantity of good Y C. d. 0 Y e. 8 X1 X2 X3 The total effect is the movement from X3 to X₂. X4 to X₁. X3 to X₁. X4 to X₂. X₂ to X4. Answer A Answer D X4 Quantity of good X Answer B Answer E || O Answer C Xarrow_forward11 Refer to Figure 3. Assume Tom is on budget constraint AC. If the price of a hamburger is $5, Tom's monthly income is Select one: a. $20 b. $300 c. $60 d. $100arrow_forwardQuestion 25 The individual's budget constraint is a. the amount of money she has in the bank c. the maximum amount one good she can consume given her consumption of other goods O d. a line depicting all the possible budgets an individual could have at various occupationsarrow_forward
- 3. Refer to the information provided in Figure below to answer the following questions. Price of pizza +6 0 A B D₁ D₂ Number of pizzas per month D3 a. Under what situation consumer moves from A to B? When they move from C to A? Explain the reasons in both cases. b. Imagine your demand curve for pizza last year was D3. Now the demand is D1. Write down possible reasons for this. Explain this carefully c. Can you expect the demand to increase at the same price? Explain the reasons carefully. d. Can you expect the demand to decrease at the same price? Explain this carefully.arrow_forward10) Figure 1 shows some indifference curves and budget lines for consumer Yusuf. Milk A B Cheese Figure 1 If Yusuf's income increases, his optimal consumption changes from point A to point B. Which of the following statements is true for Yusuf? (a) Cheese and milk are substitutes. (b) Cheese is an inferior good. (c) Milk is an inferior good . (d) Milk is a normal good. (e) None of the above.arrow_forwardComplete this table on the picture.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education