
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
please complete parts a and b
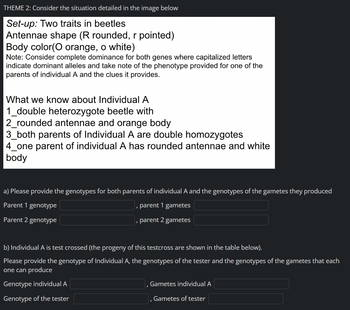
Transcribed Image Text:THEME 2: Consider the situation detailed in the image below
Set-up: Two traits in beetles
Antennae shape (R rounded, r pointed)
Body color(O orange, o white)
Note: Consider complete dominance for both genes where capitalized letters
indicate dominant alleles and take note of the phenotype provided for one of the
parents of individual A and the clues it provides.
What we know about Individual A
1_double heterozygote beetle with
2_rounded antennae and orange body
3_both parents of Individual A are double homozygotes
4_one parent of individual A has rounded antennae and white
body
a) Please provide the genotypes for both parents of individual A and the genotypes of the gametes they produced
Parent 1 genotype
parent 1 gametes
Parent 2 genotype
, parent 2 gametes
b) Individual A is test crossed (the progeny of this testcross are shown in the table below).
Please provide the genotype of Individual A, the genotypes of the tester and the genotypes of the gametes that each
one can produce
Genotype individual A
Genotype of the tester
Gametes individual A
I
Gametes of tester
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Another gene in Drosophila determines wing length. The dominant wild-type allele of this gene produces long wings; a recessive allele produces vestigial (short) wings. A female that is true- breeding for red eyes and long wings is mated with a male that has purple eyes and vestigial wings. F1 females are then crossed with purple-eyed, vestigial-winged males. From this second cross, a total of 600 offspring are obtained with the following combinations of traits: 252 with red eyes and long wings 276 with purple eyes and vestigial wings 42 with red eyes and vestigial wings 30 with purple eyes and long wings Are the genes linked, unlinked, or sex-linked? If they are linked, how many map units separate them on the chromosome?arrow_forwardINTERPRET DATA Using the graph in Figure 11-20, determine how many offspring were involved in the hypothetical cross studying skin color. What percentage had the lightest skin possible? the darkest skin possible? Figure 11-20 Polygenic inheritance in human s pigmentation This simplified example assumes that skin pigmentation in humans is governed by alleles of three unlinked loci. The alleles producing dark skin (A, B, and C) are represented by capital letters, but they are not dominant. Instead, their effects are additive. The number of dark dots, each signifying an allele producing dark skin, is counted to determine the phenotype. A wide range of phenotypes is possible when individuals of intermediate phenotype mate and have offspring (AaBbCc AaBbCc). The expected distribution of phenotypes is consistent with the superimposed normal distribution curve.arrow_forwardSolve for the genetic structure of a population with 12 homozygous recessive individuals (yy), 8 homozygous dominant individuals (YY), and 4 heterozygous individuals (Yy).arrow_forward
- Height in humans is controlled by the additive action of genes and the action of environmental factors. For the purposes of this problem, assume that height is controlled by four genesA, B, C, and Dand that there are no environmental effects. Assume further that additive alleles contribute two units of height and partially additive alleles contribute one unit of height. a. Given these assumptions, can two individuals of moderate height produce offspring that are much taller and shorter than either parent? If so, how can this happen? b. Can someone of minimum height and someone of intermediate height have children taller than the parent of intermediate height? Why or why not?arrow_forwardHow many different offspring genotypes are expected in a trihybrid cross between parents heterozygous for all three traits when the traits behave in a dominant and recessive pattern? How many phenotypes? 64 genotypes: 16 phenotypes 16 genotypes; 64 phenotypes 8 genotypes; 27 phenotypes 27 genotypes; 8 phenotypesarrow_forwardUsing the HardyWeinberg Law in Human Genetics Suppose you are monitoring the allelic and genotypic frequencies of the MN blood group locus (see Question 2 for a description of the MN blood group) in a small human population. You find that for 1-year-old children, the genotypic frequencies are MM = 0.25, MN = 0.5, and NN = 0.25, whereas the genotypic frequencies for adults are MM = 0.3, MN = 0.4, and NN = 0.3. a. Compute the M and N allele frequencies for 1-year-olds and adults. b. Are the allele frequencies in equilibrium in this population? c. Are the genotypic frequencies in equilibrium?arrow_forward
- More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of Independent Assortment Given the following matings, what are the predicted phenotypic ratios of the offspring? a. AABb Aabb b. AaBb aabb c. AaBb AaBbarrow_forwardWhich is one of the seven characteristics that Mendel observed in pea plants? flower size seed texture leaf shape stem colorarrow_forwardUsing the HardyWeinberg Law in Human Genetics In a given population, the frequencies of the four phenotypic classes of the ABO blood groups are found to be A = 0.33, B = 0.33, AB = 0.18, and i = 0.16. What is the frequency of the i allele?arrow_forward
- VISUALIZE Sketch a series of diagrams showing each of the following, making sure to end each series with haploid cells: (a)How a pair of alleles for a single locus segregate in meiosis (b)How the alleles of two unlinked loci assort independently in meiosis (c)How the alleles of two linked loci undergo genetic recombinationarrow_forwardSome recessive alleles have such a detrimental effect that they are lethal when present in both chromosomes of a pair. Homozygous recessives cannot survive and die at some point during embryonic development. Suppose that the allele r is lethal in the homozygous rr condition. What genotypic ratios would you expect among the living offspring of the following crosses? a. RRRr b. RrRrarrow_forwardList and briefly describe the three processes that lead to variation in offspring with the same parents.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning