
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Set up the n, t axes and write the equations of motion for the 10-kg block along each of these axes.
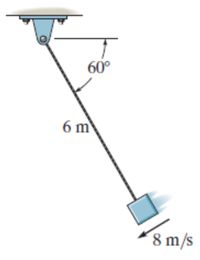
Transcribed Image Text:60°
6 m
8 m/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- THE WEIGHT OF THE UNBALANCED WHEEL IS 200 KG AND IT HS A RADIUS OF GYRATION ABOUT ITS MASS CENTER, G, OF 0.3 METERS. AT THE INSTANT SHOWN IT IS ROTATING AT 6 RAD/SIN A CLOCKWISE DIRECTION. FIND THE FORCES BETWEEN AT THE PIVOT POINT C. Please include a Free Body Diagramarrow_forwardWith the 360-lb cylindrical part P in its grip, the robotic arm pivots about O through the range -45° ≤ 0 ≤ 45° with the angle at A locked at 120°. Determine and plot (as a function of 0) the moment at O due to the combined effects of the 360-lb part P, the 100-lb weight of member OA (mass center at G₁), and the 60-lb weight of member AB (mass center at G₂). The end grip is included as a part of member AB. The lengths L₁ and L₂ are 2.8 ft and 2.0 ft, respectively. What is the maximum absolute value of Mo and at what value of 0 does this maximum occur? The moment is positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise. After you have the plot, answer the questions. lb-ft lb-ft lb-ft 52 120⁰ G₂ G₁ T! L₂ L₂ B Mi Questions: When 0 = -26°, Mo= When 0 = 6°, Mo When 0 = 20°, Mo= i The maximum absolute value Momax = 1834.87 lb-ft at 0= 21.60arrow_forwardThe rod AB is non-uniform with a radius of gyration of 4.00 ft with respect to a horizontal axis through the center of mass G. It weighs 161 lb. At the moment shown the rod has a counterclockwise angular velocity of 3.00 rad/sec, and the spring is compressed by 2.00 ft. Calculate the force constant of the spring that will reduce the angular velocity of the rod to 1.50 rad/sec when it reaches the horizontal position. Assume the blocks A and B are weightless.arrow_forward
- The 10 kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center O of ko = 300 mm. When the wheel is subjected to the couple moment, it slips as it rolls. Determine the angular acceleration of the wheel and the acceleration of the wheel's center O. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheel and the plane is = 0.2. (Figure 1) Figure M 100 N m < 1 of 1 0.4 m Part A Determine the angular acceleration of the wheel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. α = Submit ■ Part B ao = μÅ X Incorrect; Try Again Value Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Determine the acceleration of the wheel's center O. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. μA Units Value X Incorrect; Try Again Units ? Previous Answers Request Answer ? Units input for part Barrow_forwardA momentum wheel for dynamics class demonstration is show. It is basically a bicycle wheel modified with rim band-weighting, handles, and a pulley for cord startup. The heavy rim band causes the radius of gyration of the 3.1 kg wheel tobe 275 mm. If a steady 32 N pull F is applied to the cord, determien the angular acceleration of the wheel. Neglect bearing friciton.arrow_forwardThe car shown in the figure has a mass of 2500 kgs and a center of mass at G. Determine the acceleration if the rear "driving" wheels are always slipping, whereas the front wheels are free to rotate. Neglect the mass of the wheels. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheels and the road is uk = 0.3. Determine also the normal forces on A and B.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY