
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
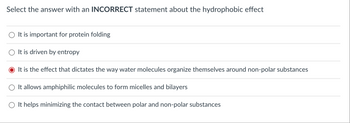
Transcribed Image Text:Select the answer with an INCORRECT statement about the hydrophobic effect
It is important for protein folding
It is driven by entropy
It is the effect that dictates the way water molecules organize themselves around non-polar substances
It allows amphiphilic molecules to form micelles and bilayers
It helps minimizing the contact between polar and non-polar substances
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What makes phospholipids good at forming cellular membranes? ○ Regions of aliphatic and hydrophilic atoms causing an internalization of phosphorous making a bilayer O The polar and non-polar regions create an amphipathic bilayer of phospholipids Covalent and ionic bonds between glycerols create a tight seal around the cell O The three saturated fatty tails in phospholipids create a semi solid like structure that maintains a cell's shape O The four ring structure of cholesterol serves as a scaffold for making hormonesarrow_forwardIn the space below draw a dipeptide composed of lysine and glutamic acid bound together by peptide bondarrow_forwardThe figure below shows that Adenosine P ATP Triphosphate P O A ADP can perform cellular work when it binds to an additional phosphate group O B. ATP can perform cellular work when it releases a phosphate group O C.ATP can be converted to ADP by adding a phosphate group ⒸD. energy is released from ATP during the process of cellular respiration Energy Adenosine ADP Diphosphate P P + P Phosphate (transferred to another molecule)arrow_forward
- Triheptanoin is a manufactured lipid. Glucose is a carbohydrate. The atoms in covalent bonds in Triheptanoin share electrons_____. The atoms in covalent bonds in glucose share electrons ______. ______ can get through the cell membrane without a transport protein. a) With unequal strength. With equal strength. Glucose. b) With unequal strength. With equal strength. Triheptanoin. c) With equal strength. With unequal strength. Glucose. d) With equal strength. With unequal strength. Triheptanoin.arrow_forwardStructure B is a Extracellular fluid B Nh Cytoplasm transport protein solute phospholipis water molecule low solvent [arrow_forwardHow would increasing the amount of saturated phospholipid tails in the cell membrane affect the membranes flexibility? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- What does phosphorylation do to a pl of amino acid? 1. The pl value is not changed. 2. pl is increased. 3. pl is decreased. 4. The answer depends on the pH and molar concentration of amino acid solution. O 1 O 2 O 3 O 4arrow_forwardSelect the hydrophobic part of this molecule. Η Η 56, 45 H-O. -C- -C-H C=O C=0 C=0 CH2 CH, ČH2 CH2 CH, CH2 CH2 CH2 ČH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH, CH, CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH, CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 CH3 CH3 Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Selected Coordinates Clear HICarrow_forwardLipid bilayers form spontaneously in a process driven by the hydrophobic effect. Explain how the hydrophobic effect drives bilayer formation from individual lipids in an aqueous environment. Describe how the physical properties of the lipid bilayer are determined by the chemical properties of the membrane lipid components. Diagrams are encouraged for both parts of the question.arrow_forward
- A protein has an asp glu/arg lys ratio of 3. What would the overall charge on this molecule likely be at pH 7? positive negative none of the abovearrow_forwardOils/Fatty acids have both a polar-head and a long tail that is non-polar. The term for a molecule with both polar (hydrophilic) and non-polar (hydrophobic) ends is Group of answer choices amphiphilic amphoteric zwitter ion lipidarrow_forwardWhich of the following are not driving forces for protein folding? Salt Bridges Conformational Entropy Entropy of the Solvent Internal Hydrogen Bonding Disulfide Bonds i. ii. iii. iv. V. O i, iii, iv O ii, iii, iv, v O ii, v Oi, v Oi, ivarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON