
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please help with all parts. This makes no sense.
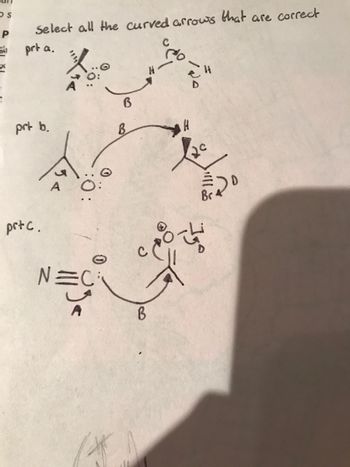
Transcribed Image Text:### Analyzing Curved Arrows in Chemical Reactions
The following diagrams exhibit various chemical structures with curved arrows, essential in illustrating electron movement during reactions. Let us analyze each part to determine the correctness of these arrows.
#### Part a.
- **Structure Description:**
- The left structure includes an atom labeled "A" with a pair of electrons, denoted as two dots, adjacent to it.
- An atom labeled "B" is shown with a curved arrow originating from the electrons next to "A" and pointing towards "B."
- To the right, another structure includes atoms labeled "C," "D," and an "H," with a curved arrow originating from the bond between "H" and "D," pointing towards "C."
- **Analysis:**
- This part focuses on nucleophilic attack, where electrons from "A" may be moving towards "B."
- The second arrow indicates a bond-breaking process, where electrons are reallocated towards the atom "C."
#### Part b.
- **Structure Description:**
- In this part, atom "A" has a similar electron representation as Part a.
- A second structure involves atoms labeled "B," "C," and "H," with two electrons set between "B" and "H" and a curved arrow pointing from "B" to "H."
- A single arrow leads from "H" to "C."
- **Analysis:**
- This suggests a potential movement of electrons from "B" to "H," followed by a possible departure of "H" and reallocation of electrons to "C."
#### Part c.
- **Structure Description:**
- Here, a molecule with a triple bond, possibly a nitrile group (represented by "N≡C"), is shown.
- Electrons are shown moving from a carbon atom (next to "N") labeled "A" towards a shared space labeled "B."
- Another structure has atoms "C" and "D," with electrons pointed from the bond between "C" and an atom towards "C."
- **Analysis:**
- This sequence suggests a nucleophilic attack by "A" on "B," complemented by the electron movement from "C" to "D."
### Conclusion
Each part exhibits important aspects of electron movement vital for understanding reaction mechanisms. The diagrams use curved arrows to demonstrate electron flow and bond formation or breaking, crucial for depicting
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given : structures
Tip : movement of Sigma bond to form double bond not possible. When there is pi bond and lone pair,lone pair move.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part C: Determination of the alcohol content of unknown liquor St tiend Volume (mL) Sample ТИШТИНА 0.00% alcohol 10.0% alcohol 20.0% alcohol 40.0% alcohol 50.0% alcohol Unknown Mass (g) 1o podina ko 9.8919 9.7899 9.600 9 9.420 д % Alcohol content of the liquor_ 9.2155 9.5089 2VLELA CVOLION EAEK EVI OK DRA IVBOKY LOBAN ocen 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 Density (g/mL) 0.00% alcohol calculation: ися → о 0.99 во 0.99 Ino7 sm dolaW 120.00 supinubst sdi na LANG 411 be: [scordas: 0.97 0.94 in oil to notisalarisi 0.92 0.95arrow_forwardWhat is the name of Hmc040 -1. jpgSOmc040-2.jpg?arrow_forwardUnknown Mixture #1 Unknown Mixture #2 Sample caffeine ibuprofen aspirin acetaminoph en Distance to solvent front 14,70 cm 14,70cm 14.70cm1u.70 cm 1나,구 cm |14.구0cm 5. 70 cm 11.90 cm I.85cm Distance Spot(s) traveled 175 cm 13.75cm 11.9 5 cm 6.4 0 cm 13,75 cm 13.75 cm 38 78 1908 .8095 Calculated R:(s) 119 ,9354 812 9 43 S .9354 9354 #1:Aspirin an d lbuprofen Components of Unknowns #2: Ace taminophen, aspirin an d ibu profen D. Additional Exercises 1. Which of the substances tested is most polar? What parts of the structure of this substance is polar? The Sul 2. Which of the substance tested is most non-polar? What parts of the structure of this substance in non-polar?arrow_forward
- Above is a fractional distillation set up. Name five things wrong with the set up.arrow_forwardCan someone help with this multistep sytheisis and explain why they got their answers.arrow_forwardAssume the data below was collected for two different sample solutions using the same experimental procedure you carried out. Based on the two lines shown below, which solution (orange data points or blue data points) corresponds to the sample that would look DARKER in terms of how much light goes through the glass. 0.9 y= 4.7713x - 0.0728 R0.99953 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 y1.414x - 0.0546 R0.99642 0.1 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1 0.12 0.14 0.16 0.18 0.2 0.1 [Concentration, M] orange data points (lower line) blue data points (upper line) Absorbancearrow_forward
- Phase change properties of pure substances Cu C6H12 C (C6H5CH₂)₂0 (CH3CH₂)20 CH3CH₂OH (CH₂OH)2 NH₂COH Au C C6H14 H₂ copper cyclohexane diamond dibenzyl ether diethyl ether ethanol ethylene glycol formamide gold graphite hexane hydrogen 1084.62 6.7 4440 1.8 -116.22 -114.14 -13.0 2.57 1064.18 4489 -95.27 -259.16 2560 80.7 298 34.4 78.24 197.5 217 2836 3825 68.72 -252.879 0.385 1.841 0.51 2.369 2.438 2.394 2.389 0.129 0.709 2.27 14.304 13.26 2.68 -- 7.19 4.931 9.96 8.44 12.55 117.4 13.08 0.12 29.97 45.6 26.52 38.56 50.5 60.2 324 28.85 0.9 280.3 193.7 242 446 -- 234.4 -240.212 40.2 35.9 61.7 80 29.9 12.69arrow_forwardProblem: If the diameter of a bicycle wheel is 622 mm, what is the diameter of the wheel in inches? (1 inch = 25.4 mm) Solution: 622 mm x 1 inch/25.4 mm = 24.5 inches. Make sure to show all the units in your solutions, as seen in the example above.arrow_forwardWhat are the limitations of distillation as a purification/isolation technique? Briefly describe two distinct situations in which distillation would not be a useful way to separate a mixture of compounds into its component parts.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY