
Managerial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN: 9781337912020
Author: Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher: South-Western College Pub
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Solve this accounting problem
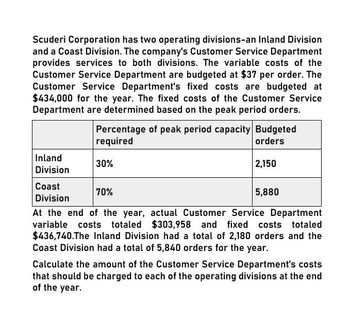
Transcribed Image Text:Scuderi Corporation has two operating divisions-an Inland Division
and a Coast Division. The company's Customer Service Department
provides services to both divisions. The variable costs of the
Customer Service Department are budgeted at $37 per order. The
Customer Service Department's fixed costs are budgeted at
$434,000 for the year. The fixed costs of the Customer Service
Department are determined based on the peak period orders.
Percentage of peak period capacity Budgeted
required
Inland
Division
30%
Coast
70%
Division
orders
2,150
5,880
At the end of the year, actual Customer Service Department
variable costs totaled $303,958 and fixed costs totaled
$436,740.The Inland Division had a total of 2,180 orders and the
Coast Division had a total of 5,840 orders for the year.
Calculate the amount of the Customer Service Department's costs
that should be charged to each of the operating divisions at the end
of the year.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Varney Corporation, a manufacturer of electronics and communications systems, allocates Computing and Communications Services Department (CCS) costs to profit centers. The following table lists the types of services and cost drivers for each service. The table also includes the budgeted cost and quantity for each service for August. One of the profit centers for Varney Corporation is the Communication Systems (COMM) division. Assume the following information for COMM: COMM has 2,500 employees, of whom 20% are office employees. All of the office employees have been issued a smartphone, and 95% of them have a computer on the network. One hundred percent of the employees with a computer also have an email account. The average number of help desk calls for August was 0.6 call per individual with a computer. There are 400 additional printers, servers, and peripherals on the network beyond the personal computers. a. Compute the service allocation rate for each of CCSs services for August. b. Compute the allocation of CCSs services to COMM for August.arrow_forwardAdam Corporation manufactures computer tables and has the following budgeted indirect manufacturing cost information for the next year: If Adam uses the step-down (sequential) method, beginning with the Maintenance Department, to allocate support department costs to production departments, the total overhead (rounded to the nearest dollar) for the Machining Department to allocate to its products would be: a. 407,500. b. 422,750. c. 442,053. d. 445,000.arrow_forwardCorazon Manufacturing Company has a purchasing department staffed by five purchasing agents. Each agent is paid 28,000 per year and is able to process 4,000 purchase orders. Last year, 17,800 purchase orders were processed by the five agents. Required: 1. Calculate the activity rate per purchase order. 2. Calculate, in terms of purchase orders, the: a. total activity availability b. unused capacity 3. Calculate the dollar cost of: a. total activity availability b. unused capacity 4. Express total activity availability in terms of activity capacity used and unused capacity. 5. What if one of the purchasing agents agreed to work half time for 14,000? How many purchase orders could be processed by four and a half purchasing agents? What would unused capacity be in purchase orders?arrow_forward
- Minor Co. has a job order cost system and applies overhead based on departmental rates. Service Department 1 has total budgeted costs of 168,000 for next year. Service Department 2 has total budgeted costs of 280,000 for next year. Minor allocates service department costs solely to the producing departments. Service Department 1 cost is allocated to producing departments on the basis of machine hours. Service Department 2 cost is allocated to producing departments on the basis of direct labor hours. Producing Department 1 has budgeted 8,000 machine hours and 12,000 direct labor hours. Producing Department 2 has budgeted 2,000 machine hours and 12,000 direct labor hours. What is the total cost allocation from the two service departments to Producing Department 1? a. 173,600 b. 140,000 c. 134,400 d. 274,400arrow_forwardColumbia Products Inc. has two divisions, Salem and Seaside. For the month ended March 31, Salem had sales and variable costs of 500,000 and 225,000, respectively, and Seaside had sales and variable costs of 800,000 and 475,000, respectively. Salem had direct fixed production and administrative expenses of 60,000 and 35,000, respectively, and Seaside had direct fixed production and administrative expenses of 80,000 and 45,000, respectively. Fixed costs that were common to both divisions and couldnt be allocated to the divisions in any meaningful way were selling, 33,000, and administration, 27,000. Prepare a segmented income statement by division for March.arrow_forwardNashler Company has the following budgeted variable costs per unit produced: Budgeted fixed overhead costs per month include supervision of 98,000, depreciation of 76,000, and other overhead of 245,000. Required: 1. Prepare a flexible budget for all costs of production for the following levels of production: 160,000 units, 170,000 units, and 175,000 units. 2. What is the per-unit total product cost for each of the production levels from Requirement 1? (Round each unit cost to the nearest cent.) 3. What if Nashler Companys cost of maintenance rose to 0.22 per unit? How would that affect the unit product costs calculated in Requirement 2?arrow_forward
- Douglas Davis, controller for Marston, Inc., prepared the following budget for manufacturing costs at two different levels of activity for 20X1: During 20X1, Marston worked a total of 80,000 direct labor hours, used 250,000 machine hours, made 32,000 moves, and performed 120 batch inspections. The following actual costs were incurred: Marston applies overhead using rates based on direct labor hours, machine hours, number of moves, and number of batches. The second level of activity (the right column in the preceding table) is the practical level of activity (the available activity for resources acquired in advance of usage) and is used to compute predetermined overhead pool rates. Required: 1. Prepare a performance report for Marstons manufacturing costs in the current year. 2. Assume that one of the products produced by Marston is budgeted to use 10,000 direct labor hours, 15,000 machine hours, and 500 moves and will be produced in five batches. A total of 10,000 units will be produced during the year. Calculate the budgeted unit manufacturing cost. 3. One of Marstons managers said the following: Budgeting at the activity level makes a lot of sense. It really helps us manage costs better. But the previous budget really needs to provide more detailed information. For example, I know that the moving materials activity involves the use of forklifts and operators, and this information is lost when only the total cost of the activity for various levels of output is reported. We have four forklifts, each capable of providing 10,000 moves per year. We lease these forklifts for five years, at 10,000 per year. Furthermore, for our two shifts, we need up to eight operators if we run all four forklifts. Each operator is paid a salary of 30,000 per year. Also, I know that fuel costs about 0.25 per move. Assuming that these are the only three items, expand the detail of the flexible budget for moving materials to reveal the cost of these three resource items for 20,000 moves and 40,000 moves, respectively. Based on these comments, explain how this additional information can help Marston better manage its costs. (Especially consider how activity-based budgeting may provide useful information for non-value-added activities.)arrow_forwardHanung Corp has two service departments, Maintenance and Personnel. Maintenance Department costs of $370,000 are allocated on the basis of budgeted maintenance-hours. Personnel Department costs of $120,000 are allocated based on the number of employees. The costs of operating departments A and B are $196,000 and $294,000, respectively. Data on budgeted maintenance-hours and number of employees are as follows: Production Departments Budgeted costs $370,000 Budgeted maintenance- hours Number of employees Maintenance Personnel Department Department 200 Support Departments 90 870 A $120,000 $196,000 $294,000 15 B 1,260 670 280 680 Using the direct method, what amount of Personnel Department costs will be allocated to Department B? (Do not round any intermediary calculations.)arrow_forwardKorvanis Corporation operates a Medical Services Department for its employees. Charges to the company’s operating departments for the variable costs of the Medical Services Department are based on the actual number of employees in each department. Charges for the fixed costs of the Medical Services Department are based on the long-run average number of employees in each operating department. Variable Medical Services Department costs are budgeted at $58 per employee. Fixed Medical Services Department costs are budgeted at $683,200 per year. Actual Medical Services Department costs for the most recent year were $105,800 for variable costs and $689,000 for fixed costs. Data concerning employees in the three operating departments follow: Cutting Milling Assembly Budgeted number of employees 604 287 918 Actual number of employees for the most recent year 504 387 818 Long-run average number of employees 720 480 1,200 Required: 1. Determine the Medical Services…arrow_forward
- Korvanis Corporation operates a Medical Services Department for its employees. Charges to the company's operating departments for the variable costs of the Medical Services Department are based on the actual number of employees in each department. Charges for the fixed costs of the Medical Services Department are based on the long-run average number of employees in each operating department. Variable Medical Services Department costs are budgeted at $57 per employee. Fixed Medical Services Department costs are budgeted at $639,300 per year. Actual Medical Services Department costs for the most recent year were $105,800 for variable costs and $645,000 for fixed costs. Data concerning employees in the three operating departments follow: Budgeted number of employees Cutting 604 Milling 293 Assembly 918 Actual number of employees for the most recent year 504 393 Long-run average number of employees 1,050 700 818 1,750 Required: 1. Determine the Medical Services Department charges for the…arrow_forwardHanung Corp has two service departments, Maintenance and Personnel. Maintenance Department costs of $310,000 are allocated on the basis of budgeted maintenance-hours. Personnel Department costs of $170,000 are allocated based on the number of employees. The costs of operating departments A and B are $192,000 and $288,000, respectively. Data on budgeted maintenance-hours and number of employees are as follows: Budgeted costs Budgeted maintenance-hours Number of employees Support Departments OA $200,588 OB. $124,235 OC. $135415 OD. $74,260 Maintenance Personnel Department Department $310,000 $170,000 NA 900 Production Departments A B $192,000 $288,000 1,210 660 75 NA 660 Using the step-down method, what amount of Maintenance Department cost will be allocated to Department A if the service department with the highest percentage of interdepartmental support service is allocated first? (Do not round any intermediary calculations.) 290arrow_forwardKorvanis Corporation operates a Medical Services Department for its employees. Charges to the company's operating departments for the variable costs of the Medical Services Department are based on the actual number of employees in each department. Charges for the fixed costs of the Medical Services Department are based on the long-run average number of employees in each operating department. Variable Medical Services Department costs are budgeted at $55 per employee. Fixed Medical Services Department costs are budgeted at $659,700 per year. Actual Medical Services Department costs for the most recent year were $105,100 for variable costs and $665,000 for fixed costs. Data concerning employees in the three operating departments follow: Rudgeted number of employees Actual number of employees for the most recent year Long-run average number of employees Cutting 610 510 990 Milling 287 387 660 Assembly 909 809 1,650 Required: 1. Determine the Medical Services Department charges for the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337902663
Author:WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning