
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Scenario depicts rigid object in static equilibrium. Pivot point is provided. Assume that the pivot point does not provide any forces and some forces may be negative.
Need help understanding how to find unknown forces Fa, Fb, and Fc.
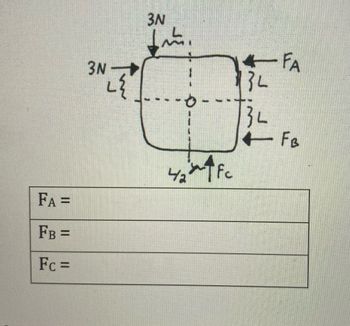
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a system of forces acting on a rectangular object. There are vectors labeled with forces and distances. The forces are acting along and perpendicular to the sides of the rectangle as follows:
1. **Vectors & Forces:**
- A force of 3N (Newtons) is acting vertically downward from the top center of the rectangle at a distance labeled \( L \) from the center.
- Another force of 3N is acting horizontally to the left from the left center of the rectangle at a distance \( L \).
- Two horizontal and vertical forces are labeled as \( F_A \) and \( F_B \) acting on the right side of the rectangle, at a distance of \( 3L \) from the center.
- A force labeled \( F_C \) is acting vertically upwards from the bottom center of the rectangle at a distance of \( \frac{4}{2} \times L \) (equal to \( 2L \)) from the center.
2. **Boxes for Calculations:**
- There are three empty fields labeled \( F_A = \), \( F_B = \), and \( F_C = \) for calculations related to the forces acting on the system.
This arrangement is likely part of a physics problem involving equilibrium or torque, where you'll calculate the unknown forces \( F_A \), \( F_B \), and \( F_C \) to satisfy the conditions of equilibrium.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Responses/submit?d... tleb USCIS | U.S. Citizens... 4 Google Drive Ebooks Z-Library * Cengage C Get Homework Hel... Google Jamboard >> Go A beam resting on two pivots has a length of L = 6.00 m and mass M = 84.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force on the beam, and the second pivot placed a distance l = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n,. A woman of mass m = 63.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in the figure below. The goal is to find the woman's position when the beam begins to tip. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman x meters to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (Do this on paper. Your instructor may ask you to turn in this work.) (b) Where is the woman when the normal force n, is the greatest? 1 typica This answer has not been graded yet. y and inte ject and X W 81°F Mostly cloudyarrow_forward2. A 3.0-m-long ladder leans against a wall at an angle of 60° with respect to the floor. What is the minimum value of us, the coefficient of static friction with the ground, that will prevent the ladder from slipping? Assume that friction between the ladder and the wall is negligible. Center of gravity 19 TULO L 60⁰ Weight acts at the center of gravity. Known L-30 m Find Me Contro <= 0 about this point. Static friction prevents slipping.arrow_forwarda meter log is a uniform bar of mass m = 77 kg. You want to support it at a rest parallel to the ground. so you place it on a triangle support at 33 cm mark and tie it with a rope on the ground at the 28 cm mark. A) draw your own configuration out. calculate the tension of the rope ____ N, downward, upward, right, left, or none and support force provided by the triangle support _______ N, downward, upward, right, left, or none b) suppose a gumdrop (point mass mb = 14.00 kg) hangs on to the meter log at the 91 cm mark How large will the tension be on the rope? ______ N conceptually explain why it should increase, decrease, or stay the same, compared to part A. C) Now with everything including the gumdrop, the triangle support has been moved away from the rope, to the end of the meter log.Explain why the system itself cannot stay balanced anymore, and the rope goes (T→0). Calculate: rotational inertia of the system below. I = _______ kg·m2Calculate the sizes (+ only) of both the…arrow_forward
- 1. A 80.0-N board 10.0 m long rests on two supports, each 1.00 m from the end of the board. A 300-N block is placed on the board 4.00 m from the right end. Find the force exerted by each support on the board.arrow_forwardA 12 000-N shark is supported by a rope attached to a 4.60-m rod that can pivot at the base. (a) Calculate the tension in the cable between the rod and the wall, assuming the cable is holding the system in the position shown in the figure. (Give you answer to three significant digits.) b) Find the horizontal force exerted on the base of the rod magnitude ------- N c) Find the vertical force exerted on the base of the rod. Ignore the weight of the rod. magnitude ------ Narrow_forwarda meter log is a uniform bar of mass m = 77 kg. You want to support it at a rest parallel to the ground. so you place it on a triangle support at 33 cm mark and tie it with a rope on the ground at the 28 cm mark. A) draw your own configuration out. calculate the tension of the rope ____ N, downward, upward, right, left, or none and support force provided by the triangle support _______ N, downward, upward, right, left, or none b) suppose a gumdrop (point mass mb = 14.00 kg) hangs on to the meter log at the 91 cm mark How large will the tension be on the rope? ______ N conceptually explain why it should increase, decrease, or stay the same, compared to part A. C) Now with everything including the gumdrop, the triangle support has been moved away from the rope, to the end of the meter log.Explain why the system itself cannot stay balanced anymore, and the rope goes (T→0). Calculate: rotational inertia of the system below. I = _______ kg·m2Calculate the sizes (+ only) of both the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON