
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Temperature (°C)
125
100
75
50
25
0
-25
BC
Ice
D
Water vapor.
Liquid water and vapor
(vaporization)
Liquid water
Ice and liquid water (melting)
F
E
A
Heat added (each division corresponds to 4 kJ)

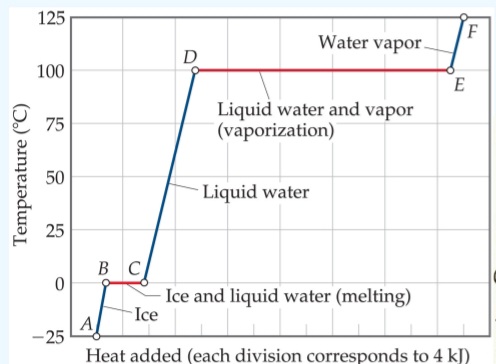
Transcribed Image Text:Sample Exercise 10.3 Calculating AH for Temperature and Phase Changes
Calculate the total enthalpy change upon converting 1.00 mol of ice at -25 °C to water
vapor (steam) at 125 °C under a constant pressure of 1 atm. The specific heats of ice,
water, and steam are 2.03 J/g-K, 4.18 J/g-K, and 1.84 J/g-K, respectively. For H₂O, AHfus
= 6.01 kJ/mol and Ahvap
40.67 kJ/mol.
Format for AB, CD, or EF:
=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 40 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9 080 LAB EXERCISE 11.D Testing A, Hᵒ from Formation Data The molar enthalpies of formation method was created earlier in this section from Hess' law. Both problem-solving methods are consistent with the law of conservation of energy. This lab exercise tests this new method against evidence gathered from calorimetry. Purpose The purpose of this problem is to test the use of molar enthalpies of formation as a method of predicting the enthalpy change of a reaction. Problem What is the standard molar enthalpy of combustion of methanol? Report Checklist O Purpose O Problem O Hypothesis ● Prediction O Design O Materials O Procedure O Evidence ● Analysis Evaluation (2, 3) Design Methanol is burned in excess oxygen in a special calorimeter. Assume that liquid water is produced. Evidence mass of methanol reacted = 4.38 g mass of water equivalent to calorimeter = 2.60 kg initial temperature of calorimeter = 20.4 °C final temperature of calorimeter = 27.9 °C (Note that the calorimeter has the…arrow_forwardchemistry helparrow_forwardQuestion 20 10 pts 20. Calculate the change in internal energy (AE) for a system that is giving off 25.0 kJ of heat and is changing from 12.00 L to 6.00 L in volume at 1.50 atm pressure. (Remember that 101.3J = 1 Latm) +25.9 kJ ○ -16.0 kJ -25.9 kJ O-24.1 kJ +937 kJarrow_forward
- Evolution Chemisty 를 Op II 17. I Ch. I An S Sol 101 b Ans Co Lab Email Searches The if d Titi + i app.101edu.co Apps School SWGOH MSF SWTOR Amazon Noodle Bills Possible Purchases Reading list Question 26 of 35 Submit Calculate AS° for C(g) + 2 H2(g) → CH«(g). Substance S° (J/mol·K) J/mol · K С (9) 5.7 H2 (g) 130.6 1 2 3 CH4 (g) 186.2 4 6 C 7 9. +/- x 100 LO 00arrow_forwardQUESTION 29 If 1.82 g of HCI is made to react with 2 grams of NaOH in water in a calorimeter (Ccal =25.0 J/°C) which registered a temperature increased by 15 °C what will be the molar heat of reaction in Kj/mol, if the reaction produced .05 mole of the product. 2 decimal place and indicate the required unit with space ex. 100.25 KJ/molarrow_forwardIf the value of ΔHvap = 26.8 kJ/mol, what is the value of ΔHcond? Question 19 options: --40.2 kJ 53.6 kJ/mol -26.8 kJ/mol 13.4 kJ/molarrow_forward
- A quart of water (950 g) at 28.0°C was placed in ice. When the water cools to 4°C, how much heat is transferred to the ice? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g·°C. Answer: 95.4 kj, I just need steps ty!arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are correct? [Select all that apply.] When energy comes out of the system, the process will be endothermic. Energy is stored in chemical bonds Energy is released when bonds are formed. We can calculate heat transferred during a phase transition using q = C, m AT, where C, is the heat capacity of the phase change.arrow_forwardInstructions are in the attached image. Thank you!arrow_forward
- 2 attempts left Check my work Enter your answer in the provided box. From the data below, calculate the total heat (in J) needed to convert 0.611 mol of gaseous ethanol at 300.0°C and atm to liquid ethanol at 25.0°C and 1 atm: b.p. at 1 atm: 78.5°C AH" : 40.5 kJ/mol vap Cgas 1.43 J/g °C Cliquid: 2.45 J/g °Carrow_forward14. Calculate how many Joules of energy would be required to change 32.9 g of water at 35°C to steam at 120°C. You will need to break this problem into four steps. a) Find the Joules needed to heat the water to the boiling point. (8938.9 J) b) Find the Joules needed to vaporize the water. (74,354 J) c) Find the Joules needed to heat the vapor (steam) from the boiling point to 120°C. (1329 J) d) Add your answers to steps a, b, and c. (84,622 J)arrow_forwardLearning Two 20.0 g ice cubes at -18.0 °C are placed into 255 g of water at 25.0 °C. Assuming no energy is transferred to or from the surroundings, calculate the final temperature, Tf, of the water after all the ice melts. heat capacity of H, O(s) 37.7 J/ (mol-K) heat capacity of H, O(1) 75.3 J/ (mol-K) Tf = °C enthalpy of fusion of H, O 6.01 kJ/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY