
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I am having trouble with this I do not know how to get the rest of the units. I have tried to multiply and divide and I cannot figure it out.
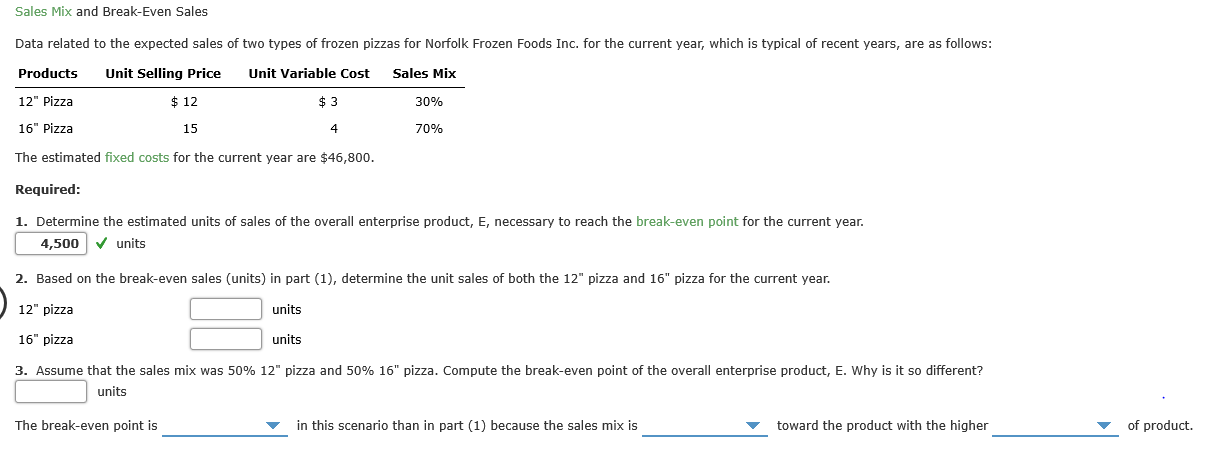
Transcribed Image Text:Sales Mix and Break-Even Sales
Data related to the expected sales of two types of frozen pizzas for Norfolk Frozen Foods Inc. for the current year, which is typical of recent years, are as follows:
Unit Selling Price
$ 12
Products
Unit Variable Cost
Sales Mix
12" Pizza
$ 3
30%
16" Pizza
15
70%
The estimated fixed costs for the current year are $46,800.
Required:
1. Determine the estimated units of sales of the overall enterprise product, E, necessary to reach the break-even point for the current year.
4,500 v units
2. Based on the break-even sales (units) in part (1), determine the unit sales of both the 12" pizza and 16" pizza for the current year.
12" pizza
units
16" pizza
units
3. Assume that the sales mix was 50% 12" pizza and 50% 16" pizza. Compute the break-even point of the overall enterprise product, E. Why is it so different?
units
The break-even point is
in this scenario than in part (1) because the sales mix is
toward the product with the higher
of product.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Would you please remind me how the debits and credits system works? Why do the assets get debit increased and the liabilities and owner’s equity get debit decreased? I know the parts must balance and clear each other out, but reviewing my notes from a previous class, I’m having a hard time getting a perspective on the principle of the T-balance.arrow_forwardJames is considering replacing his worn-out machines. Which of the following is not a relevant cost for James when considering various available options? Select one: a. Changes in costs of labour needed to operate the new machines. b. Costs of acquiring the current worn-out machines. c. Costs of delivering the new machine. d. Costs of replacing old machines. e. None of the above answers is correct.arrow_forwardI am confused on #36 of 3.3 in Finite Math for Business. My teacher wants me to find the interest using the TVM solver on my TI-84 and using the formula I=PRT. I am not sure what values to plug into my calculator though.arrow_forward
- What did you guys get for the last two blank spots. The other question didn't give me a full answer for it.arrow_forwardZara wants to export her estimates report into an Excel spreadsheet. Once Zara exports the report, what limitation will she have? Select an answer: She will not be able to export the Excel spreadsheet back into QuickBooks. She will not be able to save the Excel spreadsheet to her computer. She will not be able to make any additions to the Excel spreadsheet.arrow_forward* no trial balance was given along with case study just tables typed out below or featured in the images* Trying this again... We were asked to calculate the missing values (which I have written down on my copy of the table in the image attached). After attending the lecture with hopes to get a better understanding of how the numbers we obtained, I ended up coming home and copying the answers down as my professor did not review as to how he calculated them. I copied all the numbers down onto excel with hopes to see if I can understand where the numbers came from but to no avail. There are no requirements asked for other than to simply calculate and input the missing values which I have noted down from the answer sheet. I am hoping to get an understanding as to how the numbers were computed for the income statement for now. Table 1: given values 1997 1998 1999 net sales 26820 28966 30703 cogs 21216 23550 26140 gross profit 5604 5416 4563 admin and selling expenses…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education