
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Safari
File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help
✓
U2 Quiz #2
fo U2 Quiz #2 - Physics 12 - CLOC
(
sd43.onlinelearningbc.com
o Quizzes - Physics 12 - CLOC - Coquitlam School District
Page 1:
Question 6 (1 point)
Saved
1
N¦
2
3
Listen
--
--
>
4
--
5 >
6
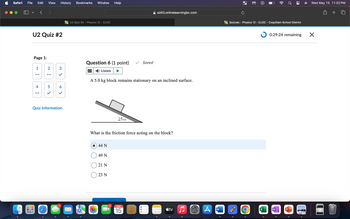
A 5.0 kg block remains stationary on an inclined surface.
Quiz Information
1
2500
What is the friction force acting on the block?
44 N
49 N
21 N
23 N
2
MAY
15
<tv
A
W
0:29:24 remaining
O
Wed May 15 11:02 PM
X
N
P
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Answer all questions please ❤️❤️arrow_forwardNewton’s Third LawExample: an object (O) is in free fall due to the gravitationalforce by Earth on the object (78 What is theNewton’s third law pair for this interaction? A. Drag force due to airfrictionB. Buoyancy force from airC. Normal force of theEarth’s surfaceD. Gravitational force of theobject (O) on the EarthE. I have no ideaarrow_forward1% Resources Lx Give Up? Feedback The objects listed are placed at the top of a ramp and roll down to the bottom without slipping. Assuming that there is no air resistance, rank them in order from fastest average rolling speed to slowest. Fastest bowling ball basketball hula hoop manhole cover Slowest Answer Bank privacy policy | help terms of use contact us about us careersarrow_forward
- Question 4 Q Zoom Q Review/v Finish ABG A train travels on a track at a constant velocity of 100 Inside one of the train cars is a table and book. The table and the book are moving with the train at constant velocity, however, the table and the book are at rest (stationary) relative to each other. Direction of movement Fie Remaining: 17 C2021 uminate Education inc 124arrow_forwardEdit View History Bookmarks Window Help le I onedrive.live.com Jobs - IDEA Public Schools Finalize Resume - Resume Now I Download Hewitt - Conceptual P..pdf PLUG AND CHUG (FORMULA FAMILIARIZATION) m¡m2 F = G- d2 36. Using the formula for gravity, show that the force of gravity on a 1-kg mass at Earth's surface is 9.8 N. You need to know that the mass of Earth is 6 X 10 its radius is 6.4 × 10° m. 39. Show that the 1024 kg) and t (The average 40. Show that the kg, and (mass = 3.0 Cance 5.6 berween arth the Maon (mass X10 N. The average Erth Mopn distance s 3ih THINK AND SOLVEarrow_forwardPhysics: Unit-Dynamics/Newton laws of motion Describe how you could use the textbook, a piece of paper, and a desk to demonstrate Newton's first law of motion?arrow_forward
- Gravitational Forces (A) Gravitational, Electrical, Magnetic, and Nuclear Forces Math Connections Law of Universal Gravitation (continued) This law states that any two objects with mass exert a gravitational force on each other. The force has the same magnitude on each object. The magnitude is directly proportional to the product of the objects' masses. It is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the objects. Where, F = gravitational force between two objects = gravitational constant = 6.673 × 1011 N x m²/kg? m, and m, = masses of the two objects in kg d = distance between the two objects in m m,m, F, = G( d 5. Calculate the gravitational force between two 150 kg objects located 25 m apart. (150)(150) 25? F = 6.673×10¯" N 6. Calculate the change in the gravitational force between the two objects if the distance between the two objects doubles. F = 6.673x10-" (150)(150) 50? 7. Use the inverse square law to describe the relationship between the gravitational force…arrow_forwardplease help with these questionsarrow_forwardCourse Home n.ecollege.com/course.html?courseld%3D156977488HeplD=D2c86a3a06e5506368bf515e8cb4923c1#10001 Physics 2620 CRN20018 Hi, h e Home And Chug 3.34 Part A Select the correct equations that show that a freely falling rock drops a distance of 45 m when it falls from rest for 3 s. O s=g² t/2= (10 m/s²)² - (3 s)/2 = 45 m %3D O s=t/(2-g) = (3 s)²/(2 - (10 m/s²)) = 45 m II O s=g t/2=D (10 m/s²) - (3 s)/2 = 45 m %3D %3D O s=g.e/2=D (10 m/s²) - (3 s)²/2 = 45 m %3D II Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining ew?assignmentProblemID=D128808933arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON