
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
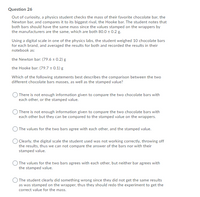
Transcribed Image Text:Question 26
Out of curiosity, a physics student checks the mass of their favorite chocolate bar, the
Newton bar, and compares it to its biggest rival, the Hooke bar. The student notes that
both bars should have the same mass since the values stamped on the wrappers by
the manufacturers are the same, which are both 80.0 0.2 g.
Using a digital scale in one of the physics labs, the student weighed 10 chocolate bars
for each brand, and averaged the results for both and recorded the results in their
notebook as:
the Newton bar: (79.6 ± 0.2) g
the Hooke bar: (79.7 ± 0.1) g
Which of the following statements best describes the comparison between the two
different chocolate bars masses, as well as the stamped value?
O There is not enough information given to compare the two chocolate bars with
each other, or the stamped value.
There is not enough information given to compare the two chocolate bars with
each other but they can be compared to the stamped value on the wrappers.
) The values for the two bars agree with each other, and the stamped value.
O Clearly, the digital scale the student used was not working correctly, throwing off
the results, thus we can not compare the answer of the bars nor with their
stamped value.
O The values for the two bars agrees with each other, but neither bar agrees with
the stamped value.
) The student clearly did something wrong since they did not get the same results
as was stamped on the wrapper, thus they should redo the experiment to get the
correct value for the mass.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the diagram below there is a thick-walled cylindrical tube. Its height is H = 5.0 m, its inner radius is R1 = 1.0 m, its outer radius is R2 = 3.0 m and its mass is M = 10.0 kg. The volume density is proportional to the square of the height h measured from the top of the cylinder: p x h?. R2 a) Proof that the proportionality constant k (p = kh?) is k = , ms 100m b) Determine the position of the center of mass of this object. c) Determine I, the moment of inertia of the cylindrical tube around the axle going through the center of the top (as shown on diagram). You can use lying =mr? (the rotational inertia of a ring of radius r and mass m rotating around an axis parallel to it, through its center).arrow_forwardYou purchased 5.2kg of apples from a store. You noticed that they used the smallest division of 4.2 g to weight them. What is the relative error of this weight measurement as a percentage. You want to calculate the area of your dorm which is in a rectangular shape. You measure the length and the width of the room as L= 4.8+(-.01) m, W= 4.4+(-.01) m. What is the absolute error in the area in m^2 units?arrow_forwardAt 9:13 A.M., a sports car is traveling 30 miles per hour. Two minutes later, the car is traveling 90 miles per hour. The mean value theorem guarantees that at some time during this two-minute interval, the car's acceleration is exactly A miles per hour squared. Compute the value of A. A = mi/h² Need Help? Read Itarrow_forward
- The radius of a sphere is known to be r = 6.27 ± 0.06 cm. The volume of a sphere is given by (4/3)?r3. Find the absolute uncertainty and the percent uncertainty in the volume of the sphere. absolute uncertainty cm3 percent uncertaintyarrow_forwardAn Olympic-size swimming pool is 50 m long, 25 m wide, and 2 m deep. In terms of volume, this pool, when full, holds how many kilogallons of water? Use the following equivalences: 1 gallon = 3.8 L 1 kilogallon = 103 gallon 1 L = 103 mL for water: 1 mL = 1 cm3 1 m = 100 cm [Numerical Problem: Just write the numerical answer without units. Express your answer to 2 significant figures in standard notation]arrow_forwardThis was wrong. Can you solve this again with these numbers? What is the root mean square velocity, vrms, for Hydrogen molecules (H2) at 20oC? Hint: How many amu does an H2 molecule contain. 1 amu = 1.67 x 10-27 kg Boltzman's Constant, k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K Give your answer in m/s to 4 significant figures (NO DECIMALS)arrow_forward
- Still think that unit conversion isn't important? Here is a widely publicized, true story about how failing to convert units resulted in a huge loss. In 1998, the Mars Climate Orbiter probe crashed into the surface of Mars, instead of entering orbit. The resulting inguiry revealed that NASA navigators had been making minor course corrections in SI units, whereas the software written by the probe's makers implicitly used British units. In the United States, most scientists use Sl units, whereas most engineers use the British, or Imperial, system of units. (Interestingly, British units are not used in Britain.) For these two groups to be able to communicate to one another, unit conversions are necessary. The unit of force in the SI system is the newton (N), which is defined in terms of basic Sl units as 1 N=1 kg · m/s?. The unit of force in the British system is the pound (lb), which is defined in terms of the slug (British unit of mass), foot (ft), and second (s) as 1 lb =1 slug ·…arrow_forwardThe laboratory balances have a precision of 0.01g. If you are obtaining the mass of an approximately 5 gram sample, which of the following is a proper way to record this measurement in your laboratory notebook and on your report sheets. 4.92 g 4.92 4.925 g 5.00 garrow_forwardInstructions: Answer must be in standard form scientific notation with SI units that do not have prefixes except for kg. Provide the answer with the correct amount of significant figures. Thank you I greatly appreciate itarrow_forward
- b) In an equation (P+) (V - b) = RT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, T is the temperature and a, b, R are constants. What is the dimensional formula of ?arrow_forwardThe Statue of Liberty in New York City is approximately 305 ft305 ft tall. How many U.S. dimes would be in a stack of the same height? Each dime is 1.35 mm1.35 mm thick. number of dimes: Each dime has a mass of 2.268 g.2.268 g. How much would the stack of dimes from the previous question weigh? mass: g What is the value, in dollars, of the same stack of dimes? value: dollars The 2017 U.S. gross domestic product (GDP) was valued at 19,390,604,000 dollars.19,390,604,000 dollars. How many Statue of Liberty‑height stacks of dimes are needed to match the GDP in value? number of stacks:arrow_forwardA series of four measurements of g are made in the physics lab. The results of these measurements in ms2/ are: 9.63, 9.58, 9.71, 9.68. The average of these four measurements is the experimental value of g and the accepted value is 9.80 ms2/. What is the percent error of these measurements?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON