
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Find the following answers to questions 1-3 from the information in the picture provided please.
1. Initial concentration of iodine in reaction (mM)
2. Initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in reaction (mM)
3. Initial rate (mM/s)

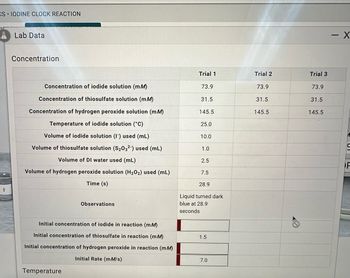
Transcribed Image Text:CS IODINE CLOCK REACTION
|
Lab Data
Concentration
Concentration of iodide solution (mm)
Concentration of thiosulfate solution (mm)
Concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution (mm)
Temperature of iodide solution (°C)
Volume of iodide solution (1) used (mL)
Volume of thiosulfate solution (S203²-) used (ml)
Volume of DI water used (mL)
Volume of hydrogen peroxide solution (H₂O₂) used (mL)
Time (s)
Observations
Initial concentration of iodide in reaction (mm)
Initial concentration of thiosulfate in reaction (mm)
Initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in reaction (mm)
Initial Rate (mm/s)
Temperature
Trial 1
73.9
31.5
145.5
25.0
10.0
1.0
2.5
7.5
28.9
Liquid turned dark
blue at 28.9
seconds
1.5
7.0
Trial 2
73.9
31.5
145.5
Trial 3
73.9
31.5
145.5
- X
U
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 34 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a hypothetical chemical reaction: A+B C+D (In this equation A, B, C and D stand for some unknown chemical formulas.) Here is an energy diagram for the reaction: energy (kJ/mol) 400 Explanation 300- 200 100 0 A + B C + D reaction coordinate Use the energy diagram to answer these questions. Check Muumalarrow_forwardUsing the Collision theory, discuss five factors that can increase the rate of a chemical reaction.arrow_forwardgrade 12 chemistry:arrow_forward
- drc=D0&gi-24758088.cfgl-1&.drt- Which of the following equations shows a correct chemical reaction for the following graph? 50 40 30 20 Time (min) Energy (kJ)arrow_forwardTopic: Measurements of Reaction Rate Answer the following questions. 1) Which of the following is NOT a viable unit for a reaction rate? ( a kilogram/second b. time/day c. Molarity/min d. Hours/second e gram/second 2) The rate of a reaction can be determined by measuring changes in the physical properties of the reaction mixture. Which of the following parameters is not typically monitored to obtain a measure of reaction rate? a. Temperature b. Volume c. Color d. Cloudiness e. Mass 3) What is the formula for calculating the rate of a reaction from the reaction time and the amount of product formed? (.) a. Rate of reaction = time/ amount of product formed b. Rate of reaction = amount of product formed X time c. Rate of reaction = time/ amount of product formed X 100% d. Rate of reaction = amount of product formed/time X 100% e. Rate of reaction = amount of product formed/time do Date Completed: .. a. B b. A, B, and D 4) Shown in the diagram is the experimental apparatus used to identify…arrow_forwardConsider a hypothetical chemical reaction: A+B → C+D (In this equation A, B, C and D stand for some unknown chemical formulas.) Here is an energy diagram for the reaction: energy (kJ/mol) 400 300 200 100 0 C + D SCA A + B reaction coordinate Use the energy diagram to answer these questions. What is the heat of reaction? Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? Can you determine the activation energy? Can you determine the activation energy of the reverse reaction? C+DA+B kJ/mol Exothermic Endothermic Neither Yes, No. it's No. kJ/mol Yes, it's kJ/molarrow_forward
- Consider the balanced chemical equation. Submit Request Answer H2O2 (aq) + 31 (aq) + 2H+(aq) → I3 (aq) + 2H2O(1) In the first 12.0 s of the reaction, the concentration of I drops from 1.000 M to 0.773 M . Part B You may want to reference (Pages 587 - 592) Section 14.3 while completing this problem. Predict the rate of change in the concentration of I3 (AI3]/At). Express the rate to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. A[l; ]/At = Value Unitsarrow_forwardOf the following, all are valid units for a reaction rate except ______ . mole/hour molarity/second gram/second mole/literarrow_forwardUse the graphic below to answer the following question. Which letter choice would have the slowest reaction rate and why? Question 8 options: A because it will have the most collisions due to its large surface area. C because it will have the fewest collisions due to its large surface area C because it will have the fewest collisions due to its small surface area A because it will have the most collisions due to its small surface area.arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction: 4 PH3 (g) à P4 (g) + 6 H2 (g). If, in a certain experiment over a specific time period, 0.036 mol of PH3 is consumed in a 1.0-L container each second of reaction, which of the following is correct about the production rate of H2? Choose one option only. Options: a. 0.0090 M/sec b. 0.024 M/sec c. 0.054 M/sec d. 0.216 M/sec e. None of the abovearrow_forwardAccording to the kinetic molecular theory for a reaction to take place the reactants must collide. However, not all collisions will result in a reaction. What two criteria must be met for a collision to be effective (result in a reaction)?arrow_forward4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY