
Principles of Accounting Volume 2
19th Edition
ISBN: 9781947172609
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
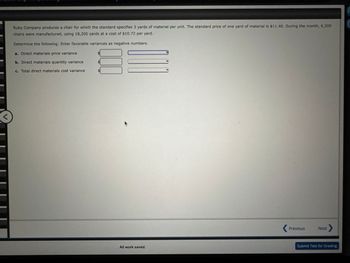
Transcribed Image Text:Ruby Company produces a chair for which the standard specifies 3 yards of material per unit. The standard price of one yard of material is $11.40. During the month, 6,200
chairs were manufactured, using 18,200 yards at a cost of $10.72 per yard.
Determine the following: Enter favorable variances as negative numbers.
a. Direct materials price variance
b. Direct materials quantity variance
c. Total direct materials cost variance
k
All work saved.
< Previous
Next >
Submit Test for Grading
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Kavallia Company set a standard cost for one item at 328,000; allowable deviation is 14,500. Actual costs for the past six months are as follows: Required: 1. Calculate the variance from standard for each month. Which months should be investigated? 2. What if the company uses a two-part rule for investigating variances? The allowable deviation is the lesser of 4 percent of the standard amount or 14,500. Now which months should be investigated?arrow_forwardEd Co. manufactures two types of O rings, large and small. Both rings use the same material but require different amounts. Standard materials for both are shown. At the beginning of the month, Edve Co. bought 25,000 feet of rubber for $6.875. The company made 3,000 large O rings and 4,000 small O rings. The company used 14,500 feet of rubber. A. What are the direct materials price variance, the direct materials quantity variance, and the total direct materials cost variance? B. If they bought 10,000 connectors costing $310, what would the direct materials price variance be for the connectors? C. If there was an unfavorable direct materials price variance of $125, how much did they pay per toot for the rubber?arrow_forwardIn all of the exercises involving variances, use F and U to designate favorable and unfavorable variances, respectively. E8-1 through E8-5 use the following data: The standard operating capacity of Tecate Manufacturing Co. is 1,000 units. A detailed study of the manufacturing data relating to the standard production cost of one product revealed the following: 1. Two pounds of materials are needed to produce one unit. 2. Standard unit cost of materials is 8 per pound. 3. It takes one hour of labor to produce one unit. 4. Standard labor rate is 10 per hour. 5. Standard overhead (all variable) for this volume is 4,000. Each case in E8-1 through E8-5 requires the following: a. Set up a standard cost summary showing the standard unit cost. b. Analyze the variances for materials and labor. c. Make journal entries to record the transfer to Work in Process of: 1. Materials costs 2. Labor costs 3. Overhead costs (When making these entries, include the variances.) d. Prepare the journal entry to record the transfer of costs to the finished goods account. Standard unit cost; variance analysis; journal entries 1,000 units were started and finished. Case 1: All prices and quantities for the cost elements are standard, except for materials cost, which is 8.50 per pound. Case 2: All prices and quantities for the cost elements are standard, except that 1,900 lb of materials were used.arrow_forward
- Sunny Corporation has collected the following data for one of its products: Direct materials standard (3 pounds per unit @ $0.40/lb.) Actual direct materials purchased Actual Direct Materials Used (AQU) Actual Price (AP) paid per pound How much is the direct materials price variance? O A. $1,610 unfavorable B. $2,240 favorable C. $1,610 favorable O D. $2,240 unfavorable $1.20 per finished good 32,000 pounds 23,000 pounds $0.47arrow_forwardRuby Company produces a chair for which the standard specifies 5 yards of material per unit. The standard price of one yard of material is $7.60. During the month, 8,500 cha manufactured, using 40,000 yards at a cost of $7.50. Determine the following: Enter favorable variances as negative numbers. a. Direct materials price variance b. Direct materials quantity variance c. Total direct materials cost variance Favorable Unfavorable Previous Nextarrow_forwardPrimary Co. has a standard materials price of $4.00 per pound and a standard direct labor rate of $18.00 per hour. Primary's actual direct materials price was $4.10 per pound and paid direct labor of $17.50 per hour. Assume an actual materials usage of 26,000 pounds and actual labor totaling 8,000 hours. A. Calculate the direct materials price variance. Indicate whether the variance is favorable or unfavorable. B. Calculate the direct labor rate variance. Indicate whether the variance is favorable or unfavorable.arrow_forward
- Franklin Manufacturing Company established the following standard price and cost data: Sales price $ 8.60 per unit Variable manufacturing cost $ 3.90 per unit Fixed manufacturing cost Fixed selling and administrative cost Franklin planned to produce and sell 2,300 units. Actual production and sales amounted to 2,400 units. Required a. Determine the sales and variable cost volume variances. b. Classify the variances as favorable or unfavorable, d. Determine the amount of fixed cost that will appear in the flexible budget. e. Determine the fixed cost per unit based on planned activity and the fixed cost per unit based on actual activity. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. $ 2,700 total $ 700 total Req A and B Reg D a. Determine the sales and variable cost volume variances. b. Classify the variances as favorable or unfavorable. Note: Select "None" if there is no effect (i.e., zero variance). Sales Variable manufacturing Reg E Volume Variancesarrow_forwardRuby Company produces a chair for which the standard specifies 3 yards of material per unit. The standard price of one yard of material is $9.90. During the month, 7,500 chairs were manufactured, using 22,300 yards at a cost of $10.49 per yard. Determine the following: Enter favorable variances as negative numbers. a. Direct materials price variance b. Direct materials quantity variance c. Total direct materials cost variancearrow_forwardplease solve and show full work with steps for better understanding Compute the direct materials variance, including its price and quantity variances. Note: Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.arrow_forward
- Need help ASAP! Thanks for the help!arrow_forwardRuby Company produces a chair that requires 4 yards of material per unit. The standard price of one yard of material is $10.20. During the month, 4,700 chairs were manufactured, using 19,200 yards at a cost of $10.81 per yard. Enter favorable variances as negative numbers. (a) Determine the price variance. Favorable (b) Determine the quantity variance. Unfavorable (c) Determine the cost variance. Favorable %24 %24arrow_forwardOriole Company's actual results reveal that it was profitable in the sale of its star product: a high-end spot-cleaning vacuum for upholstery. But it was not nearly as profitable as management had hoped. Oriole's actual income statement and master budget income statement are as follows. In order to keep the focus on product costs, SG&A costs were omitted. Units sold Revenues Variable costs DM DL Variable-MOH Contribution margin Fixed-MOH Operating income DM DL Input Variable-MOH Actual Results Fixed-MOH 10,000 $1,670,000 560,500 216,000 Here are the company's standard cost cards for each product cost. 130,500 763,000 306,000 $457,000 Quantity Standards 3.0 yards 1.6 hours 1.6 hours. Flexible Budget 1.6 hours Price Standards $18.00 per yard $11.00 per hour $7.50 per hour $15.50 per hour Master Budget 12,000 $2,076,000 648,000 211,200 144,000 1,072,800 297,600 $775,200 Standard Cost per Unit $54.00 $17.60 $12.00 $24.80arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning