
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
2
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
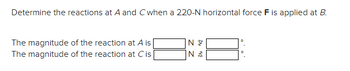
Determine the reactions at points A and C when a 220-N horizontal force \( F \) is applied at point B.
**Reaction Calculations:**
- The magnitude of the reaction at A is \( \_\_\_ \) N at \( \_\_\_ \)°.
- The magnitude of the reaction at C is \( \_\_\_ \) N at \( \_\_\_ \)°.
**Explanation:**
This problem involves calculating the reaction forces at two points (A and C) on a structure, which bears a horizontal force at point B. The specific magnitudes and directions (angles) of the reaction forces at A and C need to be determined.
**Instructions:**
1. Use equilibrium equations to solve for the unknown reaction forces.
2. Account for both horizontal and vertical force components when considering the forces acting on the structure.
3. Apply principles of statics, such as summation of forces and moments, to find the solutions.
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription and Explanation**
**Description of the System:**
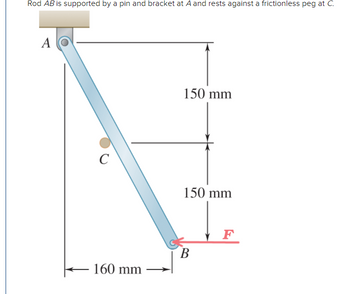
The diagram illustrates a rod \( AB \) which is supported by a pin and bracket at point \( A \) and rests against a frictionless peg at point \( C \). The rod experiences a horizontal force \( F \) applied at point \( B \).
**Key Measurements:**
- The vertical distance from point \( A \) to point \( B \) is 300 mm, indicated by two separate segments of 150 mm each.
- The horizontal distance from point \( B \) to the vertical line through point \( A \) is 160 mm.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- The rod is shown in a diagonal position with point \( A \) at the top and point \( B \) at the bottom.
- A pin and bracket at \( A \) provide support and allow rotation.
- The frictionless peg at \( C \), located approximately halfway down the rod, prevents sliding by providing lateral support.
- The force \( F \) is depicted as an arrow pointing horizontally to the right at point \( B \).
This setup is typically used to analyze equilibrium conditions, mechanics problems, and the effects of forces on rigid bodies in engineering and physics contexts.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 9 What is the location of FR, i.e., the distance d? A MB 3 m 3 m & Moving to another question will save this response. R Barrow_forwardPart I. Shorter problems focused on the fundamentals a. For the image at the right, the coordinate angles are a = 57°, ẞ= 121°, y=49°, and the point along a-a is (15,-6,3). What is the angle between lines a-a and b-b? Z b-b B LL F a (x,y,z) a-a Y b. If the magnitude of the force, F-3121bf, what is the magnitude projected along the a-a axis? yarrow_forwardanswer this; The numerical value of ? can be calculated as mmarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY