
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
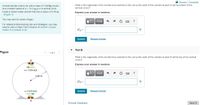
Transcribed Image Text:I Review | Constants
A small remote-control car with a mass of 1.69 kg moves
at a constant speed of v = 12.0 m/s in a vertical circle
What is the magnitude of the normal torce exerted on the car by the walls of the cylinder at point A (at the bottom of the
vertical circle)?
inside a hollow metal cylinder that has a radius of 5.00 m
(Figure 1)
Express your answer in newtons.
You may want to review (Page)
?
For related problemsolving tips and strategies, you may
want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Uniform circular
motion in a vertical circle.
|FA =
N
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Figure
1 of 1
What is the magnitude of the normal force exerted on the car by the walls of the cylinder at point B (at the top of the vertical
circle)?
Express your answer in newtons.
v = 12.0 m/s
?
5.00 m
|FB| =
v =12.0 m/s
Submit
Request Answer
A
Provide Feedback
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 2 Springy Pulley m 3m www H Consider the arrangment shown that is at rest. Each pulley has mass m and radius R. (a) If we release the system, with what speed does the 3m mass hit the spring (which was a distance h below its intial position)? (b) If the spring undergoes a maximum compression of h, what is the spring constant k? (c) Does the maximum compression of the spring depend on whether or not the pulleys had mass?arrow_forwardng An airplane flies in a horizontal circle at a speed of 485 km/h. The wings of the aircraft are at an angle of 41 degrees to the horizontal (as shown in the figure). Assume the aircraft wings generate an aerodynamic lift force perpendicular to the wings. What is the radius of the circle in which the plane is flying? Your answer should be in meters:arrow_forwardA toy car is made to run the bowl-shaped track shown in the figure below. As the car's speed increases, the car moves farther and farther up the track walls In the end, the car is able to round the vertical walls of the track, such that jts height from the bottom of the track does not change. The radius of the bowl is 1.3 m. Find the minimum speed that the car needs to go to not slip when rounding the vertical walls The coeficient of static triction between the car and the wall is 0.36 Number Unitsarrow_forward
- A 50-kg ice skater goes around a circle of radius 4 m at a constant speed of 2 m/s on a level ice rink. What are the magnitude and direction of the force that the ice exerts on the skater (the total force, not just the horizontal or vertical component of the force)arrow_forward2. A 6-lb slider is propelled upward from A along the curved bar that lies in a vertical plane. If the slider has a speed of 10 ft/sec as it passes B, find the magnitude of the normal force of the exerted on the slider by the rod and the rate at which the speed is changing. Neglect friction. Optional: Have half your AG do this in path, the other half do it in cylindrical and compare answers!arrow_forward9arrow_forward
- problem 4arrow_forwardQ Search the web.. f a New Tab Bb Announcements - PH O Microsoft Word - 10-4 x O W12C2PRACTICEEXAN X b bartleby - Bing b bartleby - Bing b My Questions | bartlet x A Not secure | faculty.ccbcmd.edu/~dbaum/PHYS151S21/10-4.pdf Sign in ... 10-4) A solid cylinder (mass M and radius R) on a table has a mechanism that attaches a spring (of constant k) to its central axis. The other end of the spring is fixed, so that the spring is horizontal. cylinder is able to roll on the table without slipping. Let's pull the mass to one side and release it so that it rolls back and forth. The Show that the motion of the center of mass is simple harmonic, and find the frequency of ocillation, w. HINT: There are two ways (at least) to do this. Each involves comparing information about this system to the simple harmonic ocillator we know, the mass on a spring. If you can get the force/torque equation to look like -kx = max or you can get the energy budget to look like /2mv? + /2kx? = ETOTAL, then the motion…arrow_forward< 8 of 18 Exercise 13.35 an Review I Constants A thin spherical shell has radius rA = 3.00 m and mass mA = 35.0 kg. It is concentric with a second thin spherical shell that has radius TB =7.00 m and mass mg = 60.0 kg Part A What is the net gravitational force that the two shells exert on a point mass of 0.0200 kg that is 2.00 m from the common center of the two shells (inside both shells)? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HÀ ? F= Value Units Submit Request Answer • Part B What is the net gravitational force that the two shells exert on a point mass of 0.0200 kg that is 5.00 m from the common center of the two shells (in the space between the two shells)? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HÀ F = Value Units Submit Request Answer • Part C What is the net gravitational force that the two shells exert on a point mass of 0.0200 kg that is 8.00 m from the common center of the two shells (outside both ahelle2 MacBook Air DII 80 888 F10 F11 F12 F7 esc F3 F4 F5 F6…arrow_forward
- Braving the Rotor at the Amusement Park (Circular Motion Due to Normal Force) The Rotor is an amusement park ride where people stand against the inside of a spinning cylinder, as shown below. Once the cylinder is spinning at a certain speed, the floor drops out of the bottom of the cylinder but the people do not fall out of the bottom. A conservative low estimate of the coefficient of static friction between people's clothes and the cylinder wall is 0.45. The radius of the cylinder is 2.4 m. What is the minimum number of rpm that the cylinder can have so that the people do not fall out the bottom? (answer: 29 rpm)arrow_forwardOn a roller coaster loop-the-loop the riders are upside-down at the top of the loop, while on a Ferris wheel the riders are upright at the top. Suppose a Ferris wheel and the loop of a roller coaster have the same diameter. If riders on each have the same magnitude of apparent weight at the top, which rider is moving faster? Explain.arrow_forwardYou have a summer internship at NASA and are working on plans for a new space station to be launched into orbit around the Earth. The design of the space station is shown. i It is to be constructed in the shape of a hollow ring of mass 52,000 kg. The structures other than the ring shown in the figure have negligible mass compared to the ring. Members of the crew will walk on a deck formed by the inner surface of the outer cylindrical wall of the ring, with radius r = 140 m. The thickness of the ring is very small compared to the radius, so we can model the ring as a hoop. At rest when constructed, the ring is to be set rotating about its axis so that the people standing inside on this deck experience an effective free-fall acceleration equal to g. The rotation is achieved by firing two small rockets attached tangentially to opposite points on the rim of the ring. Your supervisor asks you to determine the following: (a) the time interval during which the rockets must be fired if each…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON