
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Explain how (a) the absence of class B gene expression produces the flower structures seen in class B mutants (see Figure 22.15c) and (b) the absence of class C gene expression produces the structures seen in class C mutants (see Figure 22.15d).
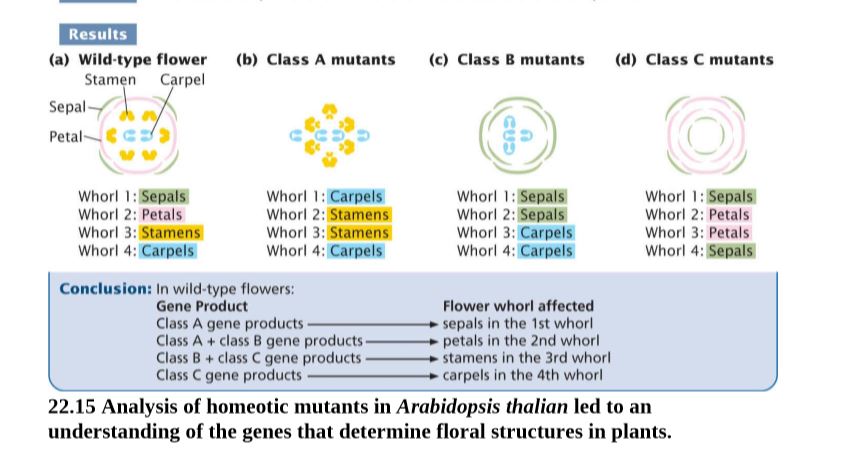
Transcribed Image Text:Results
(a) Wild-type flower
(b) Class A mutants
(c) Class B mutants
(d) Class C mutants
Stamen Carpel
Sepal-
Petal-
Whorl 1: Sepals
Whorl 2: Petals
Whorl 3: Stamens
Whorl 4: Carpels
Whorl 1: Carpels
Whorl 2: Stamens
Whorl 3: Stamens
Whorl 4: Carpels
Whorl 1: Sepals
Whorl 2: Sepals
Whorl 3: Carpels
Whorl 4: Carpels
Whorl 1: Sepals
Whorl 2: Petals
Whorl 3: Petals
Whorl 4: Sepals
Conclusion: In wild-type flowers:
Gene Product
Class A gene products -
Class A + class B gene products-
Class B+ class C gene products
Class C gene products
Flower whorl affected
sepals in the 1st whorl
petals in the 2nd whorl
stamens in the 3rd whorl
carpels in the 4th whorl
22.15 Analysis of homeotic mutants in Arabidopsis thalian led to an
understanding of the genes that determine floral structures in plants.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What will be the flower structure of a plant in which expression of the following genes is inhibited in the specified whorls? Q. Expression of class B genes is inhibited in the second whorl, but not inthe third whorl.arrow_forward#17 You have isolated a gene that is important for the production of milk and wish to study its regulation. You examine the genomes of humans, mouse, dog, chicken, pufferfish, and yeast and note that all genomes except yeast have an orthologous gene. a)How would identify the regulatory elements important for the expression of your isolated gene in mammary glands? b)What does the existence of orthologous genes in chicken and pufferfish tell you about the function of this gene?arrow_forwardWhat is the S-gene and what role does it play in plants? Be specificarrow_forward
- Looking at Figure 11-9, why were partial diploids essential for establishing the trans-acting nature of the Lacrepressor? Could one distinguish cis-acting from transacting genes in haploids?arrow_forwardIf a winter-annual strain of Arabidopsis is grown in a greenhouseand not exposed to cold temperatures, its ability to flower is inhibited.Which gene is responsible for this inhibition?arrow_forwardCan you answer part a-c if its true or false a) the AP3 and PI show auto- and cross-regulatory interactions, as well as they form obligate heterodimers to carry out the B class gene function. Therefore, if there is no PI expression, AP3 expression alone is not sufficient for establishing the petal and stamen identities. b) Angiosperm is a group of plants whose seeds are borne within a mature ovary (fruit). c) The organ in different organisms under every variety of forms and functions due to evolutionary development from the same or a corresponding part in a common ancestor is homologous.arrow_forward
- Discuss the morphological differences between the parasegments and segments of Drosophila. Discuss the evidence, providing specific examples, that suggests the parasegments of the embryo are the subdivisions for the organization of gene expression.arrow_forwardYou conduct an experiment to study the expression of the S protein through the tissues of your favorite plant (Arabidopsis thaliana). The morning of the experiment you inject in the leaves a messenger RNA that codes for the synthesis of a single protein made of two parts that are attached to each other: the functional S protein and a red fluorescent protein tag (RFP). You perform two cross sections of the same root, one section at the start of the experiment (time = Oh; corresponding to the time of injection) and one section in the afternoon (time = 8h). Through fluorescent microscopy you observe a change in the coloration inside the cells of the root's central tissues (as indicated by the arrows): from no coloration (time = Oh) to red (time = 8h). • The cells of the central tissues in the roots do not have nuclei or ribosomes. How can you explain this change of coloration? Please provide a cellular feature that can lead to this. • What is one advantage of using an RFP-tag in an mRNA?…arrow_forwardIn addition to C. elegans and Drosophila, Zebrafish are also another model organism - and have a spine. We're interested in two phenotypes, a curved spine and a gene that causes skin tumors to form on the fish's skin. We'd like to know if we could use the curved spine as an indicator if a fish may develop tumors (if the genes are linked). We'll assume that each of these traits is controlled by a single gene where: a curved spine is the result of a dominant allele S (and a normal spine is the result of recessive alleless), ⚫ and tumor growth is the result of a recessive allele t (and no tumor growths are a dominant T allele). A testcross is performed with a fish that is heterozygous for both genes and the resulting progeny are given below. TtSs x ttss curved spine & no tumors curved spine & tumors normal spine & no tumors 27 45 normal spine & tumors 30 SUN 50 Are these two genes following Mendelian inheritance patterns? Use Chi-Squared analysis to test them. x2 = (0-6)² 1. X2 value:…arrow_forward
- What will be the flower structure of a plant in which expression of the following genes is inhibited in the specified whorls? Q. Expression of class A genes is inhibited in the second whorl, but not in the first whorl.arrow_forwardBriefly explain the regulatory interactions between these three classes of patterning genes (gap, pair rule, segment polarity). What is the temporal order of action and how do the different classes of genes regulate each other?arrow_forwardIn the nematode C. elegans, some worms have blisteredcuticles due to a recessive mutation in one of the bligenes. Someone studying a suppressor mutation thatsuppressed bli-3 mutations wanted to know if it wouldalso suppress mutations in bli-4. They had a strain thatwas homozygous for this recessive suppressor mutation,and its phenotype was wild type.a. How would they determine whether this recessivesuppressor mutation would suppress mutations in bli-4?In other words, what is the genotype of the wormsrequired to answer the question?b. What cross(es) would they do to make these worms?c. What results would they expect in the F2 if(1) it did act as a suppressor of bli-4?(2) it did not act as a suppressor of bli-4?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education