
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:In model 1 of the activity 'Vapor Pressure vs. Temperature and Heating Curves and Vapor
Pressure', Why is the slope different between phase 1 and phase 3?
the change in temperature was different between liquid water and solid water
the liquid water was heated at a different rate than solid water
liquid water has a different heat capacity than solid water
liquid water has a greater density than solid water
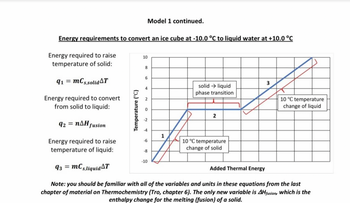
Transcribed Image Text:Energy requirements to convert an ice cube at -10.0 °C to liquid water at +10.0 °C
Energy required to raise
temperature of solid:
91 = mCs,solid T
Temperature (°C)
10
8
6
4
N
2
Model 1 continued.
Energy required to convert
from solid to liquid:
92 = n^H fusion
Energy required to raise.
temperature of liquid:
93 = mCs,liquid T
Note: you should be familiar with all of the variables and units in these equations from the last
chapter of material on Thermochemistry (Tro, chapter 6). The only new variable is AHfusion, which is the
enthalpy change for the melting (fusion) of a solid.
4
-6
-10
solid → liquid
phase transition
1
2
10 °C temperature
change of solid
3
Added Thermal Energy
10 °C temperature
change of liquid
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What quantity of heat (in J) would be required to convert 6.91 mol of a pure substance from a liquid at 40.0 °C to a gas at 113.0 °C? + Cliquid = 1.45 J/mol °C Tboiling = 88.5 °C Cgas = 0.65 J/mol•°C AHvaporization = 1.23 kJ/molarrow_forwardCalculate the energy released as heat when 18.7 g of liquid mercury at 25.00 °C is converted to solid mercury at its melting point. heat capacity of Hg(1) Constants for mercury at 1 atm melting point enthalpy of fusion 28.0 J/(mol-K) # 234.32 K 2.29 kJ/mol 9 = MacBook Proarrow_forwardHow much heat is required to raise the temperature of 4.5g of ice from -15.0ºC to 106ºC?arrow_forward
- You may want to reference Section 3.7 (Pages 80-87) while completing this problem. Using the values for the heat of fusion, specific heat of water, and/or heat of vaporization, calculate the amount of heat energy in each of the following. Keep in mind that the sign of the heat involved in the state change is ignored. 3 E D C R F 5 T ▬▬▬ B FO 6 Q Search H ▼ Part A FZ ▼ N Copyright © 2023 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Permissions | Contact Us | n 7 Calculate the joules released when 145 g of steam condenses at 100 °C and the liquid cools to 35.0 °C. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Value Submit Part B ASUS U HA J * 8 Calculate the kilocalories needed to melt a 725 g ice sculpture at 0 °C and to warm the liquid to 35.0 °C. P Pearson M Request Answer F9 1 ( → C a Units K 9 F10 Alt NYE 1 L ? F11 O IA E P : F12 Ctrl - Review | Constants Periodic Table Prt Sc I + 19 = "1 Insert 4x D Delete…arrow_forwardThe heat of fusion is equal to the heat of solidification. 73°F Partly sunny O True O Search L CHO False & 09arrow_forwardHow much heat is required to warm 25.0 g of H2O from a solid at -12ºC to a liquid at 60ºC? ∆Hfus = 6.02 kJ/mol Csolid = 2.09 J/gºC Cliq = 4.18 J/gºC Tfreezing = 0ºCarrow_forward
- Calculate the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 55.0 g of liquid water from 25°C to 99°C. The specific heat of liquid water is 1.00 cal/g °Carrow_forwardA pure sample of Substance S is put into an evacuated flask. The flask is then heated steadily and the temperature measured as time passes. The results are graphed below, in the middle (in green). Identical experiments are now run on Substance Y and Substance Z. Substance Y is just like S except that it has a higher heat capacity in the solid phase C₂ (s). Substance Z is just like S except that it has a lower enthalpy of vaporization H. Select the graphs below, on the left and right, that show the results you expect for these new experiments. Substance Y •C₁ (s)) (higher Cp (Drag the slider to choose an image) temperature (°C) Substance S added heat (kJ/mol) Substance Z (lower H₂) (Drag the slider to choose an image) ³ 5arrow_forwardHeat does not have to be present in all phase changes. True O Falsearrow_forward
- Calculate the heat change in calories for condensation of 13.0g of steam at 100 degreesarrow_forwardDetermine the amount of heat (in kJ) required to convert 8.24 moles of liquid methanol at-22°C into gaseous methanol at 98°C. Use the following information on methanol to calculate the amount of heat for each of the steps. Melting Point =-98°C Boiling Point = 65°C Molar Heat Capacities: Ciquid = 81.1 J/mol °C Cgas = 43.9 J/mol °C AHucion 3.22 kJ/mol AHvaporization 37.3 kJ/mol Type your numeric answer and submitarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY